
| Cruise Region : Mediterranean Sea |
| Company : Oceania Cruises |
| Ship : Insignia |
| Journey Start : Mon 02 Nov 2026 |
| Journey End : Sat 19 Dec 2026 |
| Count Nights : 47 nights |
| Day | Date | Port | Arrival | Departure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.11 Mon | Barcelona / Spain | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 2 | 3.11 Tue | Palma de Mallorca / Spain | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 3 | 4.11 Wed | Alicante / Spain | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 4 | 5.11 Thu | Cartagena (Bolívar) / Colombia | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 5 | 6.11 Fri | Malaga / Spain | 08:00 | 19:00 |
| 6 | 7.11 Sat | Seville / Spain | 07:00 | 19:00 |
| 7 | 8.11 Sun | Portman / Portugal | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 8 | 9.11 Mon | Lisbon / Portugal | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 9 | 10.11 Tue | Day at sea / Sea | ||
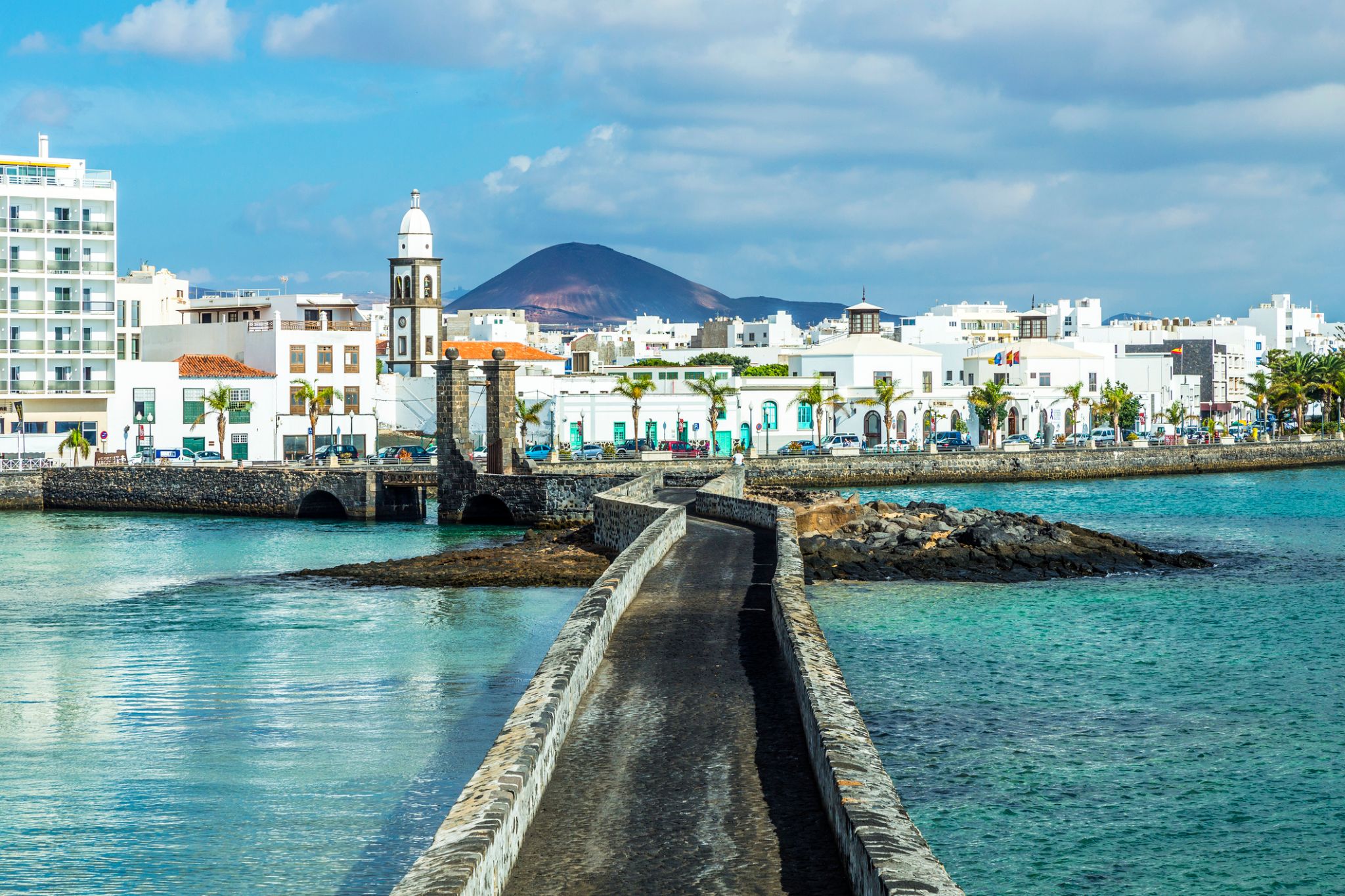
| 10 | 11.11 Wed | Arrecife / Spain | 10:00 | 18:00 |
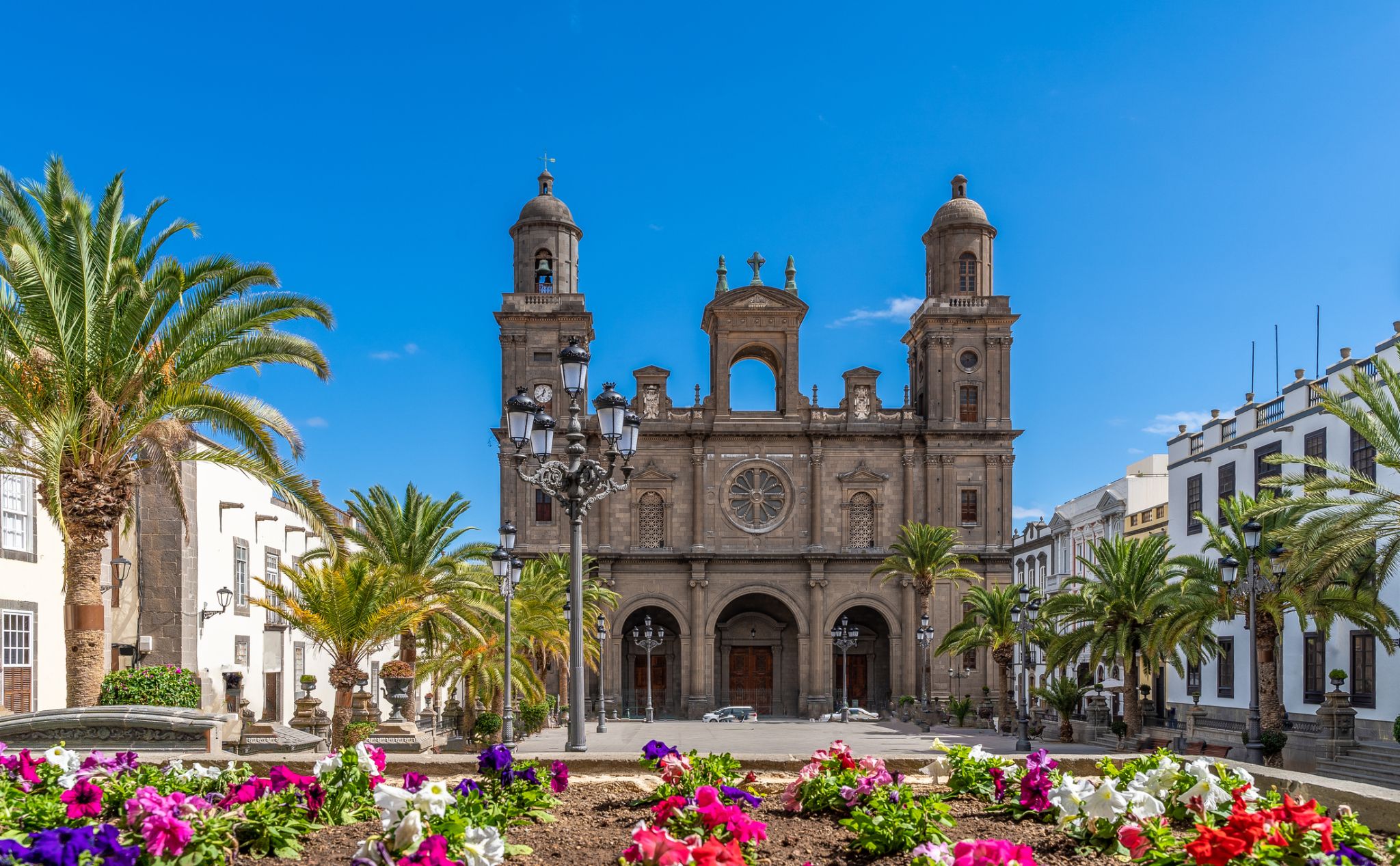
| 11 | 12.11 Thu | Las Palmas (Gran Canaria) / Spain | 07:00 | 17:00 |
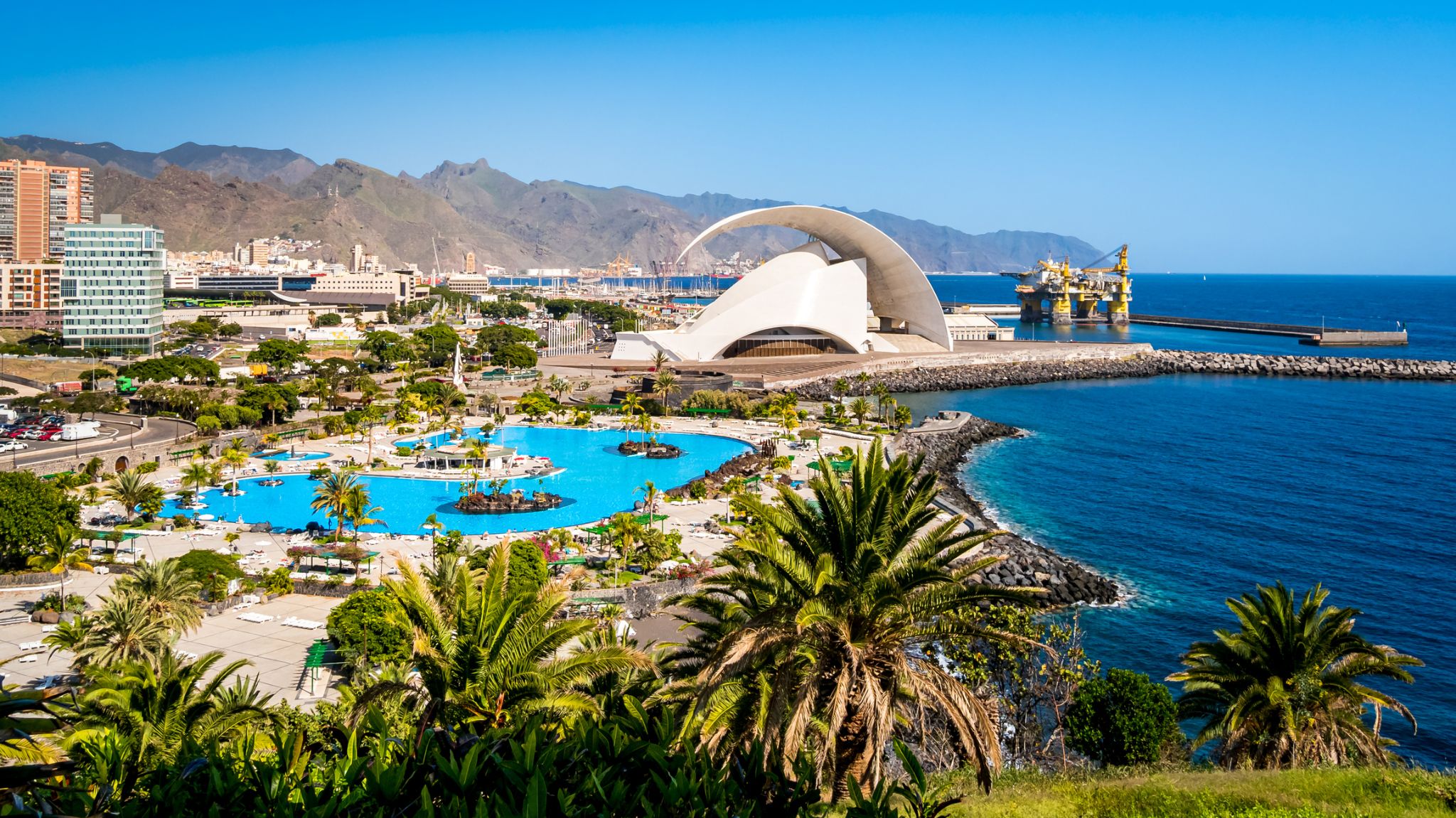
| 12 | 13.11 Fri | Santa Cruz de Tenerife(Canary Islands) / Spain | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 13 | 14.11 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 14 | 15.11 Sun | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 15 | 16.11 Mon | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 16 | 17.11 Tue | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 17 | 18.11 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 18 | 19.11 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 19 | 20.11 Fri | San Juan / Puerto Rrico | 11:00 | |
| 20 | 21.11 Sat | San Juan / Puerto Rrico | 11:00 | |
| 21 | 22.11 Sun | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 22 | 23.11 Mon | Nassau / Bahamas | 11:00 | 17:00 |
| 23 | 24.11 Tue | Miami / USA | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 24 | 25.11 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 25 | 26.11 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 26 | 27.11 Fri | Tortola / British Virgin Islands | 10:00 | 18:00 |
| 27 | 28.11 Sat | St. John's / Canada | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 28 | 29.11 Sun | Castries / Saint Lucia | 08:00 | 17:00 |
| 29 | 30.11 Mon | Scarborough / Trinidad and Tobago | 07:00 | 16:00 |
| 30 | 1.12 Tue | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 31 | 2.12 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 32 | 3.12 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | 10:00 | 11:00 |
| 33 | 4.12 Fri | Santarem / Brazil | 09:00 | 18:00 |
| 34 | 5.12 Sat | Valeria Village Mouth / Brazil | 07:00 | 15:00 |
| 35 | 6.12 Sun | Manaus / Brazil | 10:00 | |
| 36 | 7.12 Mon | Manaus / Brazil | 16:00 | |
| 37 | 8.12 Tue | Parintins / Brazil | 11:00 | 19:00 |
| 38 | 9.12 Wed | Alter do Chao / Brazil | 07:30 | 15:00 |
| 39 | 10.12 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | 13:00 | 14:00 |
| 40 | 11.12 Fri | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 41 | 12.12 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 42 | 13.12 Sun | Bridgetown / Barbados | 11:00 | 18:00 |
| 43 | 14.12 Mon | Roseau / Dominica | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 44 | 15.12 Tue | PHILIPSBURG / Anguilla | 08:00 | 17:00 |
| 45 | 16.12 Wed | San Juan / Puerto Rrico | 07:00 | 13:00 |
| 46 | 17.12 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 47 | 18.12 Fri | Nassau / Bahamas | 11:30 | 17:00 |
| 48 | 19.12 Sat | Miami / USA | 07:00 | 17:00 |
Your World Included
With Your World Included, you’ll enjoy a wide array of included amenities for the ultimate comfort and value in ultra-premium cruising.
Unforgettable dining experiences at a variety of exquisite restaurants — all at no extra charge.
Complimentary specialty coffees, sodas, freshly pressed juices, and still and sparkling Vero Water® served throughout the ship.
Unlimited free Wi-Fi available in your suite, stateroom, and all public areas.
In-room dining with a superb variety of hot and cold selections.
Smoothies, milkshakes, gelato, and signature Humphry Slocombe ice cream — always included.
Group fitness classes at Aquamar® Spa + Vitality Center are complimentary.
Gratuities are included for your convenience.
Laundry is free for all guests.
With complimentary self-service launderettes on board, plus laundry and pressing services for Concierge and Suite categories, you’ll always look your finest.
Along with our hallmark personalized service, you’ll enjoy an enriching cruise experience with no hidden costs or nickel-and-diming.
Elevate Your Experience
Concierge Level Veranda Staterooms offer an unrivaled combination of luxury, privilege, and value. A wealth of amenities and exclusive benefits elevate your experience to the sublime — from in-room dining selections from The Grand Dining Room and complimentary laundry services to unlimited access to the Aquamar Spa Terrace.
On board Oceania Marina and Oceania Riviera, you’ll also enjoy the services of a dedicated Concierge and exclusive access to the private Concierge Lounge.
Located in the most desired areas of the ship, Concierge Level Veranda Staterooms are far more than just staterooms — they are an experience in themselves.
Concierge Level Veranda — Exclusive Privileges
Expanded in-room dining menu for lunch and dinner from The Grand Dining Room
Laundry service — up to 3 bags per stateroom
Exclusive key-card access to the private Concierge Lounge aboard Oceania Marina, Oceania Riviera, Oceania Vista, and Oceania Allura, featuring complimentary beverages, coffees, snacks, and the services of a dedicated Concierge
Welcome bottle of fine Italian Prosecco
Priority online reservations for specialty restaurants
Unlimited access to the Aquamar Spa Terrace
Oceania Cruises logo tote bag
Cashmere lap blankets — perfect for relaxing or snuggling
Pressing of garments upon embarkation
Complimentary shoeshine service
Deposit and Payments – Oceania Cruises
General Deposit:
For Owner’s, Vista, and Oceania Suites, a deposit of 20% of the cruise fare per person is required.
For all other suite/stateroom categories, the deposit is $500 per person.
For Grand Voyages, the deposit is $1,500 per person.
Deposit and Final Payment Deadlines:
Bookings more than 150 days from sailing:
Deposit 20% for Owner’s, Vista, and Oceania Suites and $500 for all other categories is required within 5 days of booking.
Bookings 90–120 days from sailing:
Full payment required within 3 days of booking.
Bookings 0–90 days from sailing:
Full payment due on the day of booking.
Important:
Bookings that are not deposited or paid in full according to this schedule will be automatically cancelled.
Unless otherwise noted, final payment must be received by Oceania Cruises 150 days prior to departure for cruises less than 15 days, and 150 days for cruises 15 days or longer.
Oceania Cruises reserves the right to cancel any booking not fully paid at the time of final payment.
Additional Information:
Passport details and special onboard service requests are due at final payment.
Payment may be made by personal check, American Express, Discover, MasterCard, or Visa.
For convenience, final payment may be automatically charged to the credit card used for the initial deposit.
Oceania Cruises is not responsible for foreign currency or transaction fees independently charged by issuing banks. These fees do not benefit Oceania Cruises.
Third-party credit card payments are accepted only with valid authorization from the cardholder.
Deposit and Payment – 180-Day Voyages
For 180-day voyages, a deposit of 20% of the cruise fare per person for all suites and staterooms is required within 7 days of booking.
Final payment must be received no later than 181 days prior to departure, along with passport details and any special onboard service requests.
Otherwise, the booking may be immediately cancelled, and applicable penalties will apply.
Oceania Cruises accepts payment for reservations by credit/debit card or bank transfer.
Unfortunately, personal checks are not accepted.
Credit/Debit Cards:
American Express, Visa, and Mastercard are accepted.
Please note: Oceania Cruises assumes no responsibility for foreign currency/transaction processing fees assessed by your issuing bank.
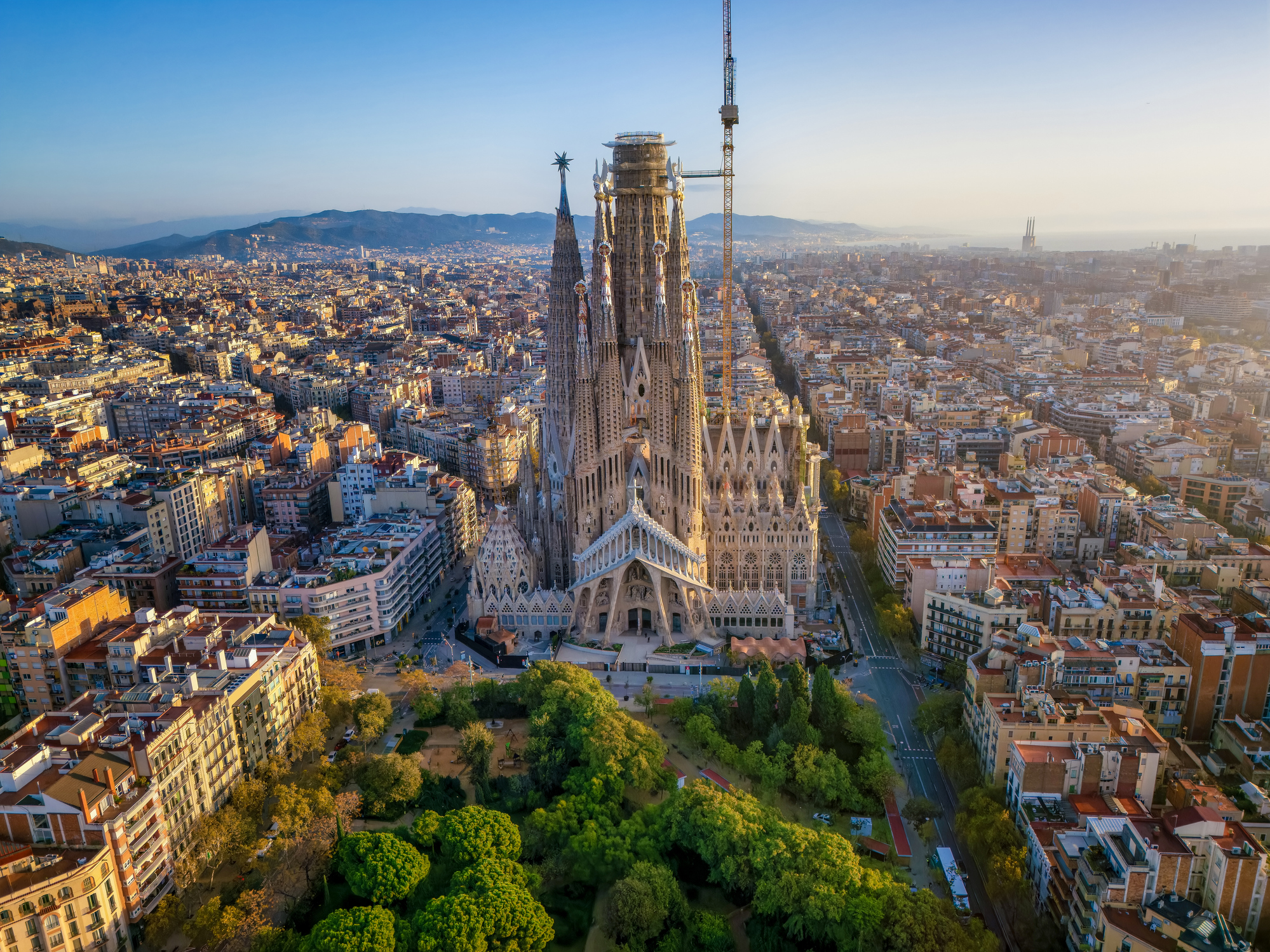

Barcelona is a city in Spain. It is the capital and largest city of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within city limits, its urban area extends to numerous neighbouring municipalities within the Province of Barcelona and is home to around 4.8 million people, making it the sixth most populous urban area in the European Union after Paris, London, Madrid, the Ruhr area and Milan. It is one of the largest metropolises on the Mediterranean Sea, located on the coast between the mouths of the rivers Llobregat and Besòs, and bounded to the west by the Serra de Collserola mountain range, the tallest peak of which is 512 metres (1,680 feet) high.
Founded as a Roman city, in the Middle Ages Barcelona became the capital of the County of Barcelona. After merging with the Kingdom of Aragon, Barcelona continued to be an important city in the Crown of Aragon as an economic and administrative centre of this Crown and the capital of the Principality of Catalonia. Barcelona has a rich cultural heritage and is today an important cultural centre and a major tourist destination. Particularly renowned are the architectural works of Antoni Gaudí and Lluís Domènech i Montaner, which have been designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The headquarters of the Union for the Mediterranean are located in Barcelona. The city is known for hosting the 1992 Summer Olympics as well as world-class conferences and expositions and also many international sport tournaments.
Barcelona is one of the world's leading tourist, economic, trade fair and cultural centres, and its influence in commerce, education, entertainment, media, fashion, science, and the arts all contribute to its status as one of the world's major global cities. It is a major cultural and economic centre in southwestern Europe, 24th in the world (before Zürich, after Frankfurt) and a financial centre. In 2008 it was the fourth most economically powerful city by GDP in the European Union and 35th in the world with GDP amounting to €177 billion. In 2012 Barcelona had a GDP of $170 billion; and it was leading Spain in employment rate in that moment.
In 2009 the city was ranked Europe's third and one of the world's most successful as a city brand. In the same year the city was ranked Europe's fourth best city for business and fastest improving European city, with growth improved by 17% per year, and the city has been experiencing strong and renewed growth for the past three years. Since 2011 Barcelona has been a leading smart city in Europe. Barcelona is a transport hub, with the Port of Barcelona being one of Europe's principal seaports and busiest European passenger port, an international airport, Barcelona–El Prat Airport, which handles over 50 million passengers per year, an extensive motorway network, and a high-speed rail line with a link to France and the rest of Europe.
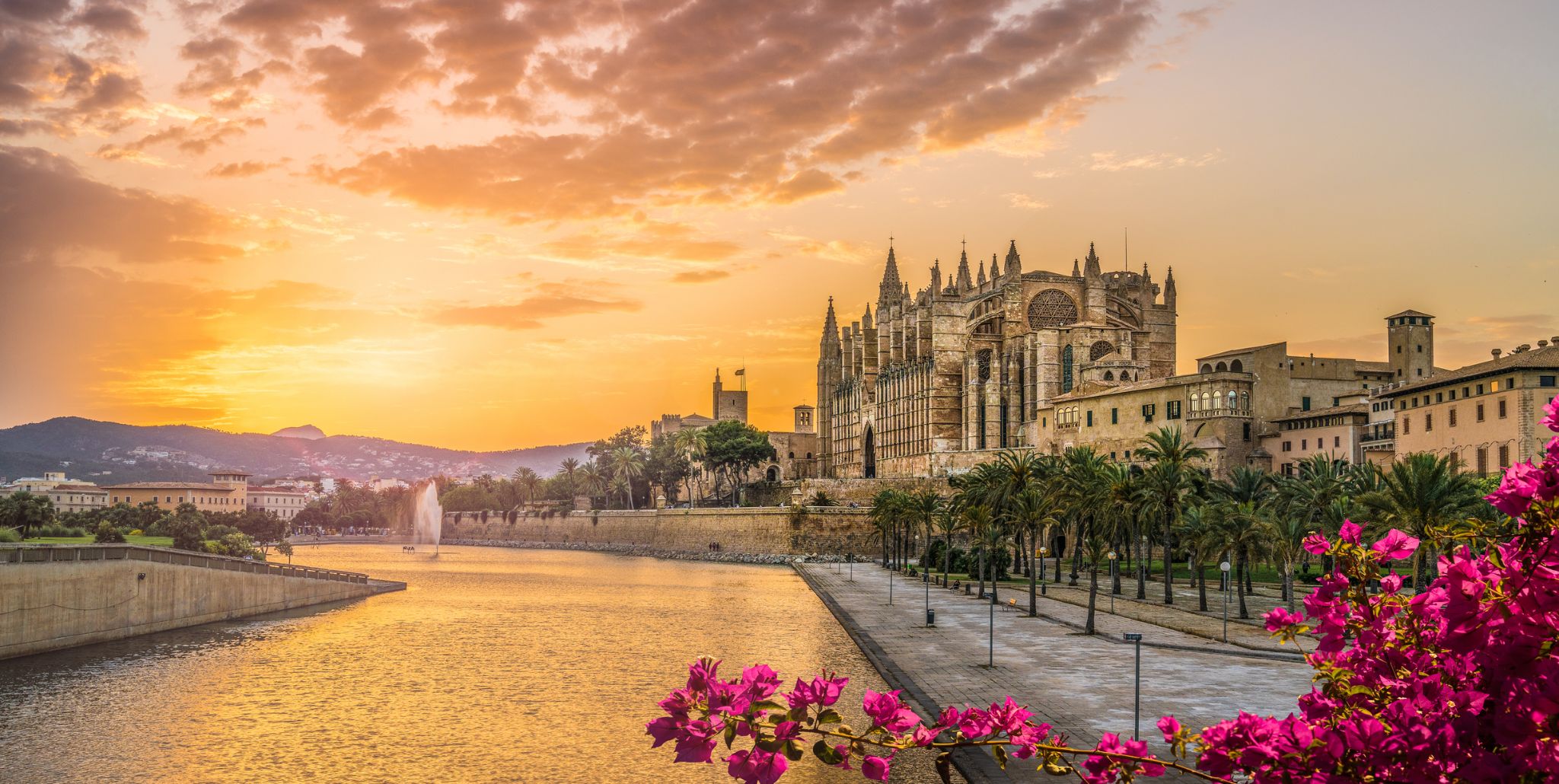

Mallorca is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean. The native language, as on the rest of the Balearic Islands, is Catalan, which is co-official with Spanish.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Balearic Islands have been an autonomous region of Spain since 1983. There are two small islands off the coast of Mallorca: Cabrera (southeast of Palma) and Dragonera (west of Palma). The anthem of Mallorca is "La Balanguera".
Like the other Balearic Islands of Menorca, Ibiza and Formentera, the island is an extremely popular holiday destination, particularly for tourists from Germany and the United Kingdom. The international airport, Palma de Mallorca Airport, is one of the busiest in Spain; it was used by 28.0 million passengers in 2017, increasing every year since 2012.
The name derives from Classical Latin insula maior, "larger island". Later, in Medieval Latin, this became Maiorica, "the larger one", in comparison to Menorca, "the smaller one".
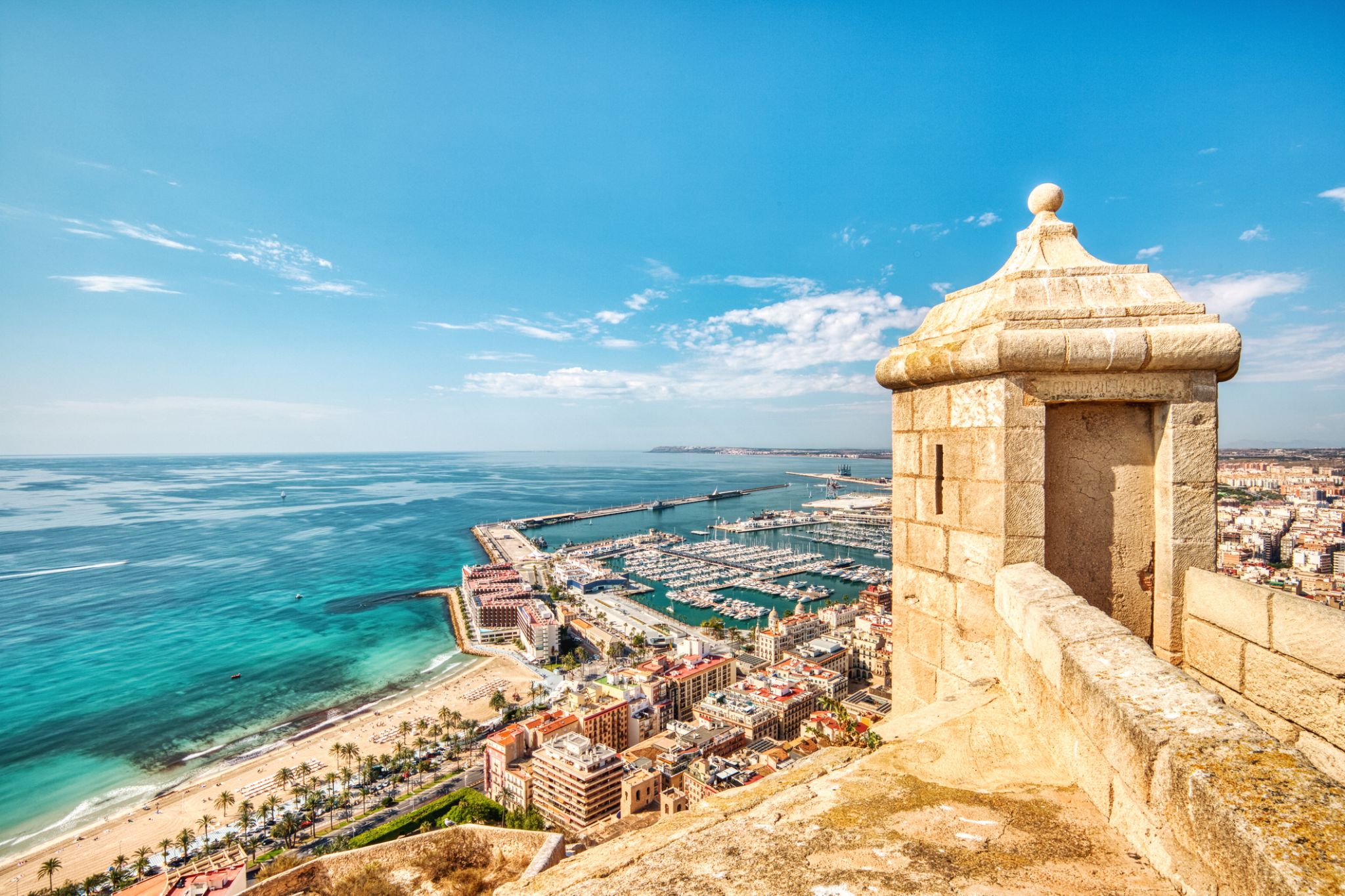

Alicante, or Alacant , both the Spanish and Valencian being official names, is a city and port in Spain on the Costa Blanca, the capital of the province of Alicante and of the comarca of Alacantí, in the south of the Valencian Community. It is also a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city of Alicante proper was 330,525, estimated as of 2016, ranking as the second-largest Valencian city. Including nearby municipalities, the Alicante conurbation had 452,462 residents. The population of the metropolitan area (including Elche and satellite towns) was 757,085 as of 2014 estimates, ranking as the eighth-largest metropolitan area of Spain.
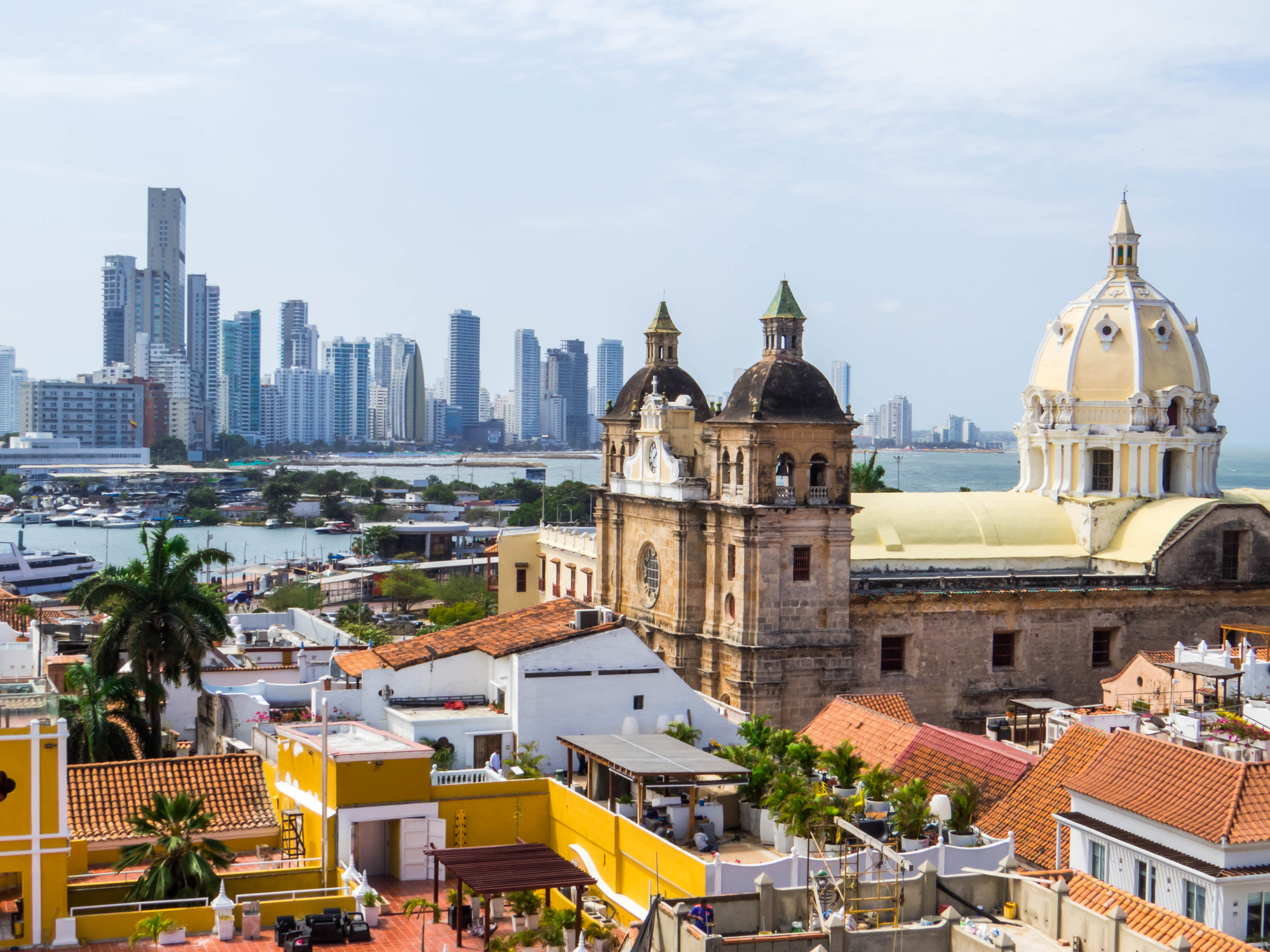

Ancient fortress walls, street musicians, and the Caribbean sun create an unforgettable atmosphere in Cartagena (Bolívar) — the gem of Colombia's coast. This city, listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, enchants visitors with its colonial architecture, charming courtyards, and the aroma of fresh coffee wafting from countless cafés.
Immerse yourself in the vibrant rhythm of Cartagena, strolling through the cobbled streets of the Old Town, where every corner holds tales of pirates and Spanish conquistadors. And the sunset near the ancient Castillo San Felipe de Barajas is the perfect ending to a day filled with culture, history, and tropical romance.
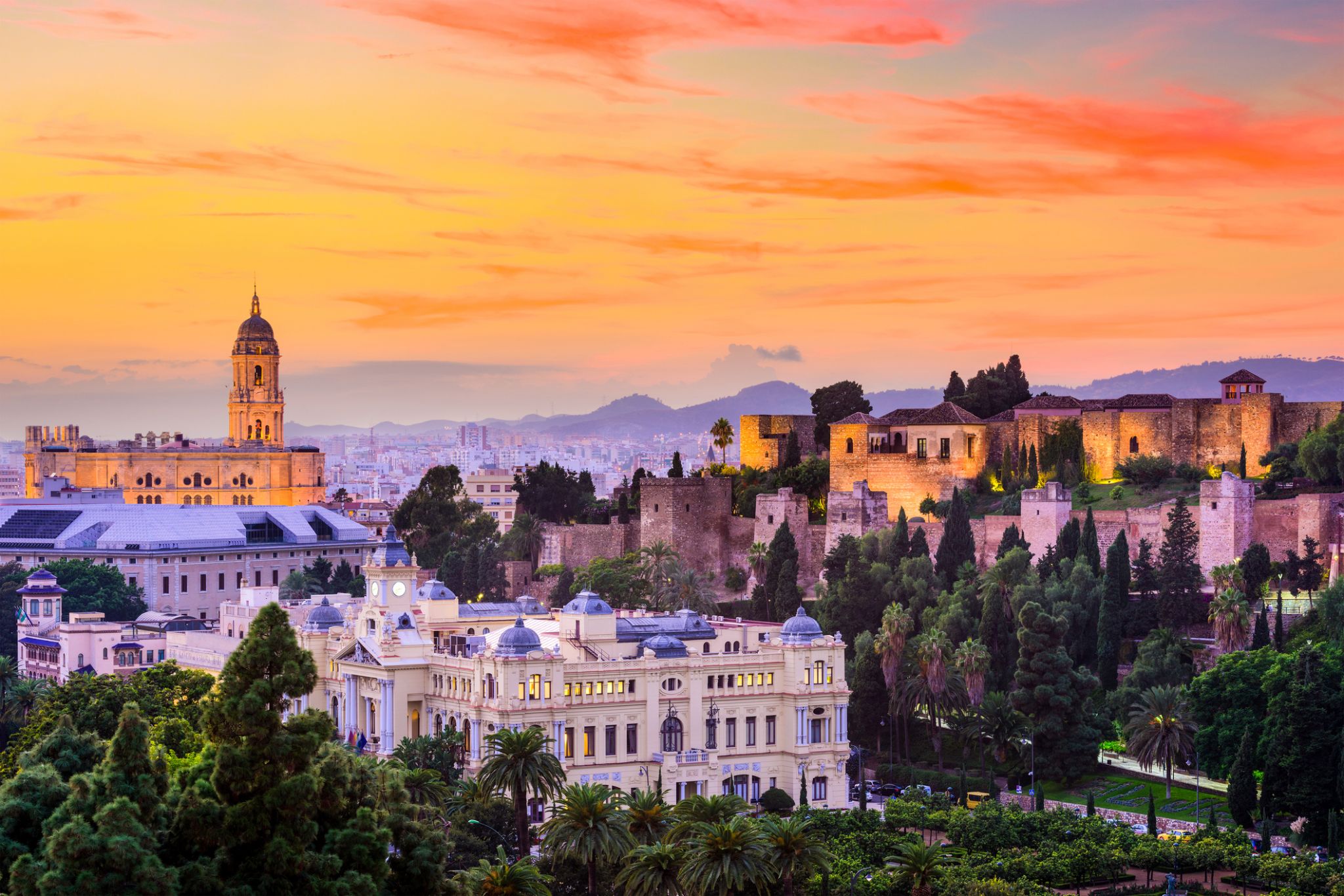

Málaga is a municipality, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the Autonomous Community of Andalusia, Spain. With a population of 569,130 in 2015, it is the second-most populous city of Andalusia and the sixth-largest in Spain. The southernmost large city in Europe, it lies on the Costa del Sol (Coast of the Sun) of the Mediterranean, about 100 kilometres (62.14 miles) east of the Strait of Gibraltar and about 130 km (80.78 mi) north of Africa.
Málaga's history spans about 2,800 years, making it one of the oldest cities in the world. According to most scholars, it was founded about 770 BC by the Phoenicians as Malaka From the 6th century BC the city was under the hegemony of Ancient Carthage, and from 218 BC, it was ruled by the Roman Republic and then empire as Malaca (Latin). After the fall of the empire and the end of Visigothic rule, it was under Islamic rule as Mālaqah for 800 years, but in 1487, the Crown of Castille gained control after the Reconquista. The archaeological remains and monuments from the Phoenician, Roman, Arabic and Christian eras make the historic center of the city an "open museum", displaying its history of nearly 3,000 years.
This important cultural infrastructure and the artistic heritage have culminated in the nomination of Málaga as a candidate for the 2016 European Capital of Culture.
The painter and sculptor Pablo Picasso, Hebrew poet and Jewish philosopher Solomon Ibn Gabirol and the actor Antonio Banderas were born in Málaga. The magnum opus of Cuban composer Ernesto Lecuona, "Malagueña", is named after the music of this region of Spain.
The most important business sectors in Málaga are tourism, construction and technology services, but other sectors such as transportation and logistics are beginning to expand. The Andalusia Technology Park (PTA), located in Málaga, has enjoyed significant growth since its inauguration in 1992. Málaga is the main economic and financial centre of southern Spain, home of the region's largest bank, Unicaja, and the fourth-ranking city in economic activity in Spain behind Madrid, Barcelona and Valencia.
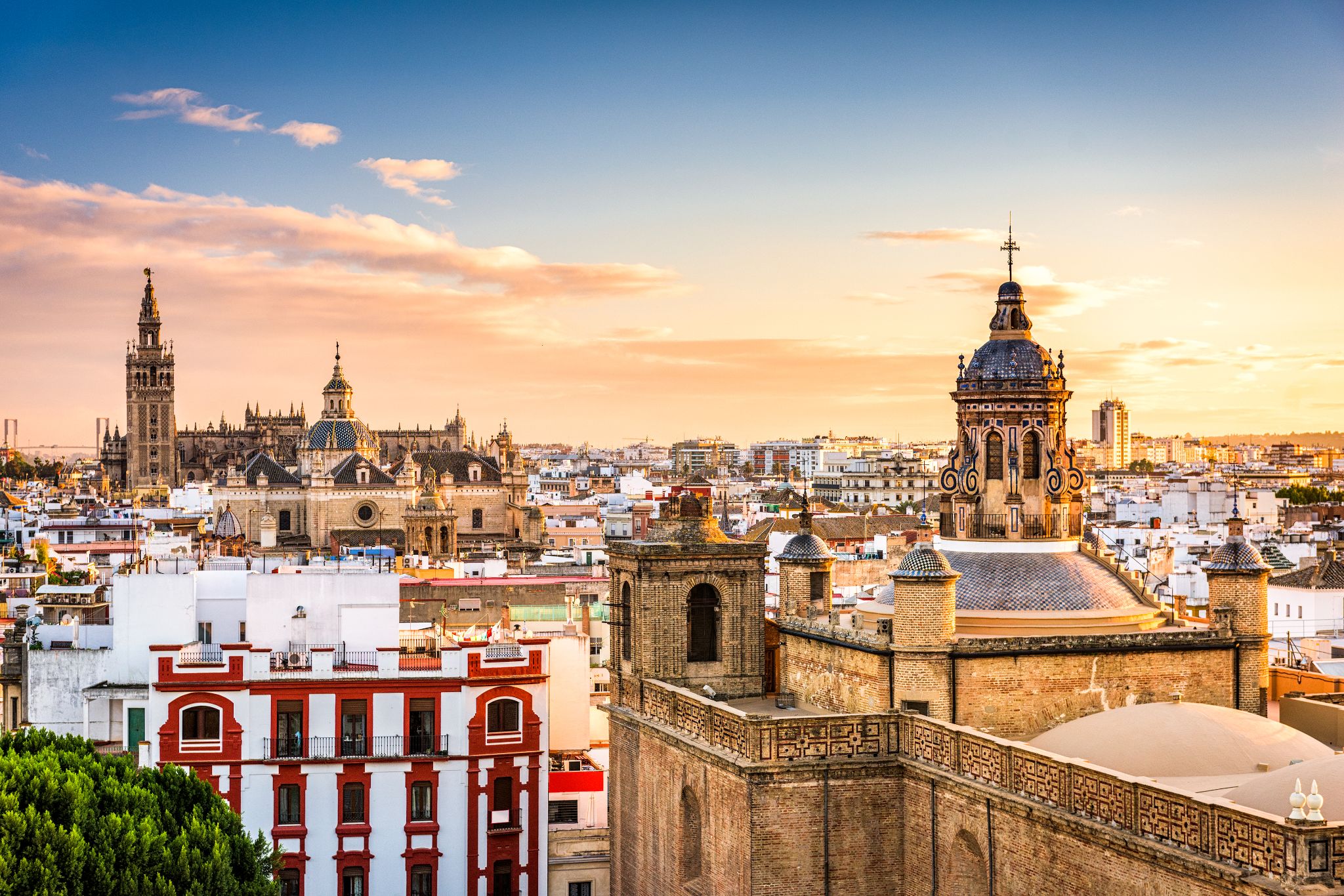

Seville is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville, Spain. It is situated on the plain of the river Guadalquivir. The inhabitants of the city are known as sevillanos (feminine form: sevillanas) or hispalenses, after the Roman name of the city, Hispalis. Seville has a municipal population of about 690,000 as of 2016, and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 30th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its Old Town, with an area of 4 square kilometres (2 sq mi), contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about 80 kilometres (50 miles) from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. Seville is also the hottest major metropolitan area in the geographical Southwestern Europe, with summer average high temperatures of above 35 °C (95 °F).
Seville was founded as the Roman city of Hispalis. It later became known as Ishbiliyya after the Muslim conquest in 712. During the Muslim rule in Spain, Seville came under the jurisdiction of the Caliphate of Córdoba before becoming the independent Taifa of Seville; later it was ruled by the Muslim Almoravids and the Almohads until finally being incorporated into the Christian Kingdom of Castile under Ferdinand III in 1248. After the discovery of the Americas, Seville became one of the economic centres of the Spanish Empire as its port monopolised the trans-oceanic trade and the Casa de Contratación (House of Trade) wielded its power, opening a Golden Age of arts and literature. In 1519, Ferdinand Magellan departed from Seville for the first circumnavigation of the Earth. Coinciding with the Baroque period of European history, the 17th century in Seville represented the most brilliant flowering of the city's culture; then began a gradual economic and demographic decline as silting in the Guadalquivirforced the trade monopoly to relocate to the nearby port of Cádiz.
The 20th century in Seville saw the tribulations of the Spanish Civil War, decisive cultural milestones such as the Ibero-American Exposition of 1929 and Expo '92, and the city's election as the capital of the Autonomous Community of Andalusia.
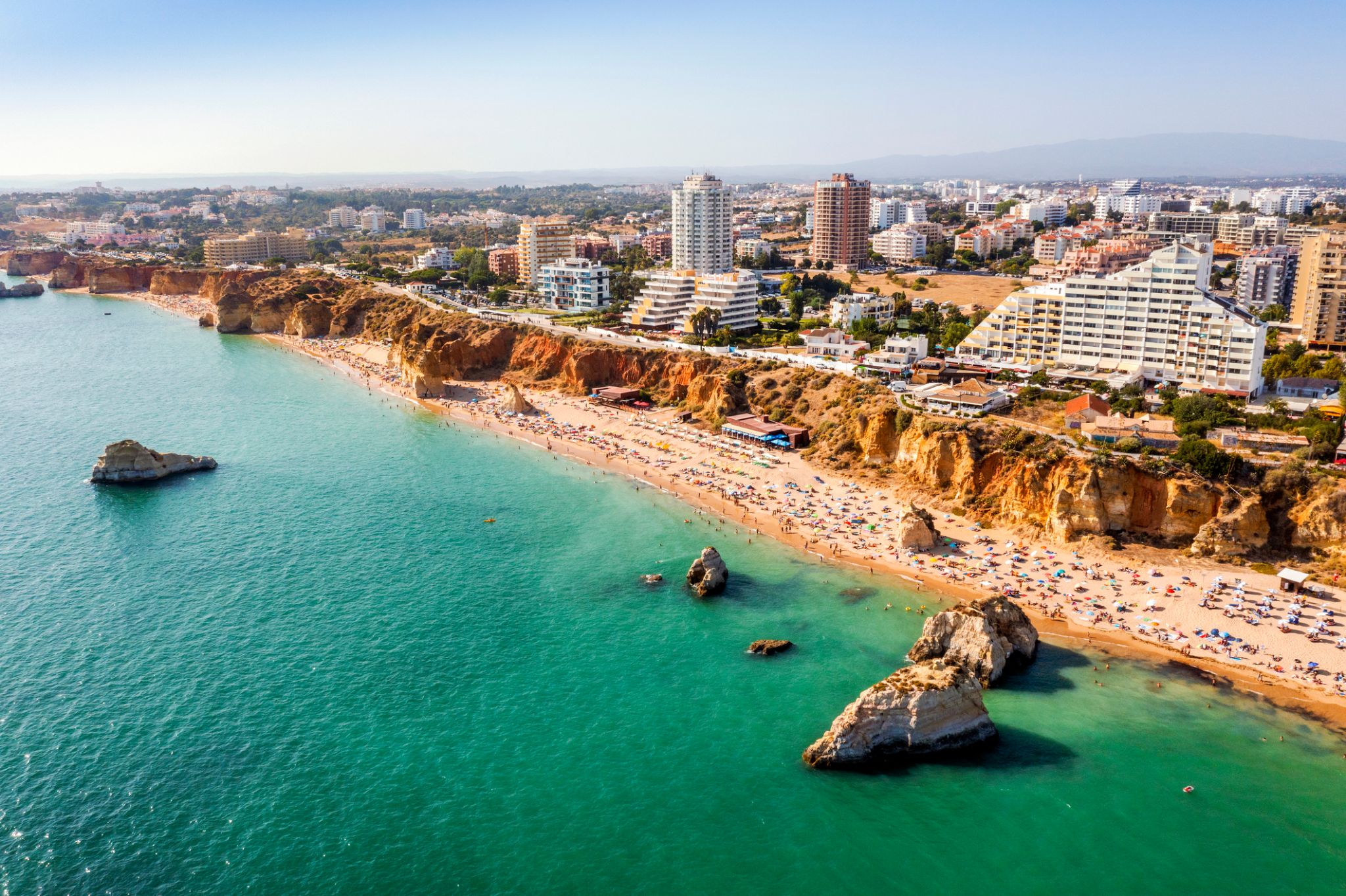

Portimão is a town and a municipality in the district of Faro, in the Algarve region of southern Portugal. The population in 2011 was 55,614, in an area of 182.06 km². It was formerly known as Vila Nova de Portimão. In 1924, it was incorporated as a cidadeand became known merely as Portimão. Historically a fishing and shipbuilding centre, it has nonetheless developed into a strong tourist centre oriented along its beaches and southern coast. The two most populous towns in the Algarve are Portimão and Faro.
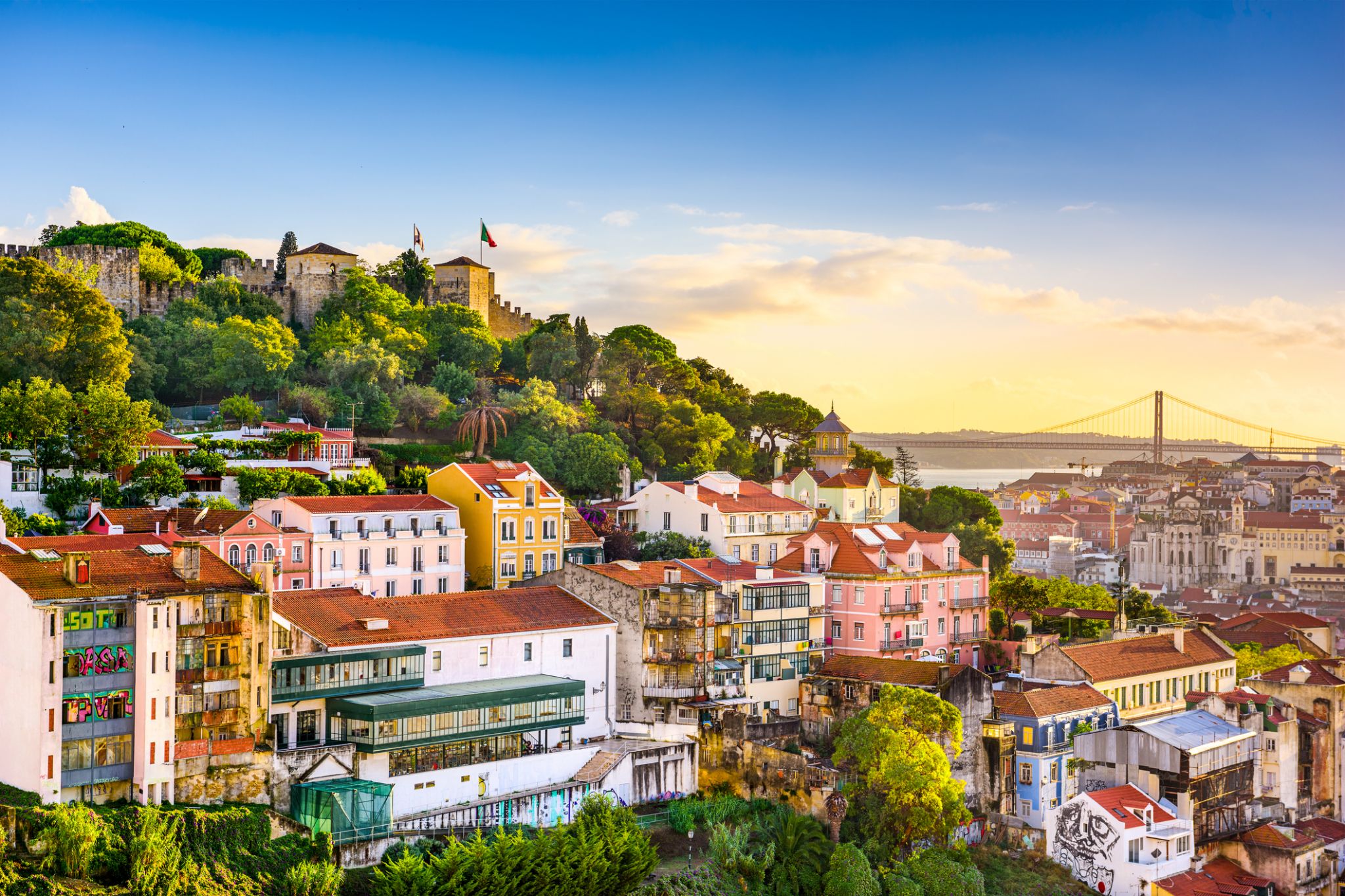

Lisbon is the capital and the largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 505,526 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Its urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits with a population of around 2.8 million people, being the 11th-most populous urban area in the European Union. About 3 million people live in the Lisbon Metropolitan Area (which represents approximately 27% of the country's population). It is mainland Europe's westernmost capital city and the only one along the Atlantic coast. Lisbon lies in the western Iberian Peninsula on the Atlantic Ocean and the River Tagus. The westernmost areas of its metro area form the westernmost point of Continental Europe, which is known as Cabo da Roca, located in the Sintra Mountains.
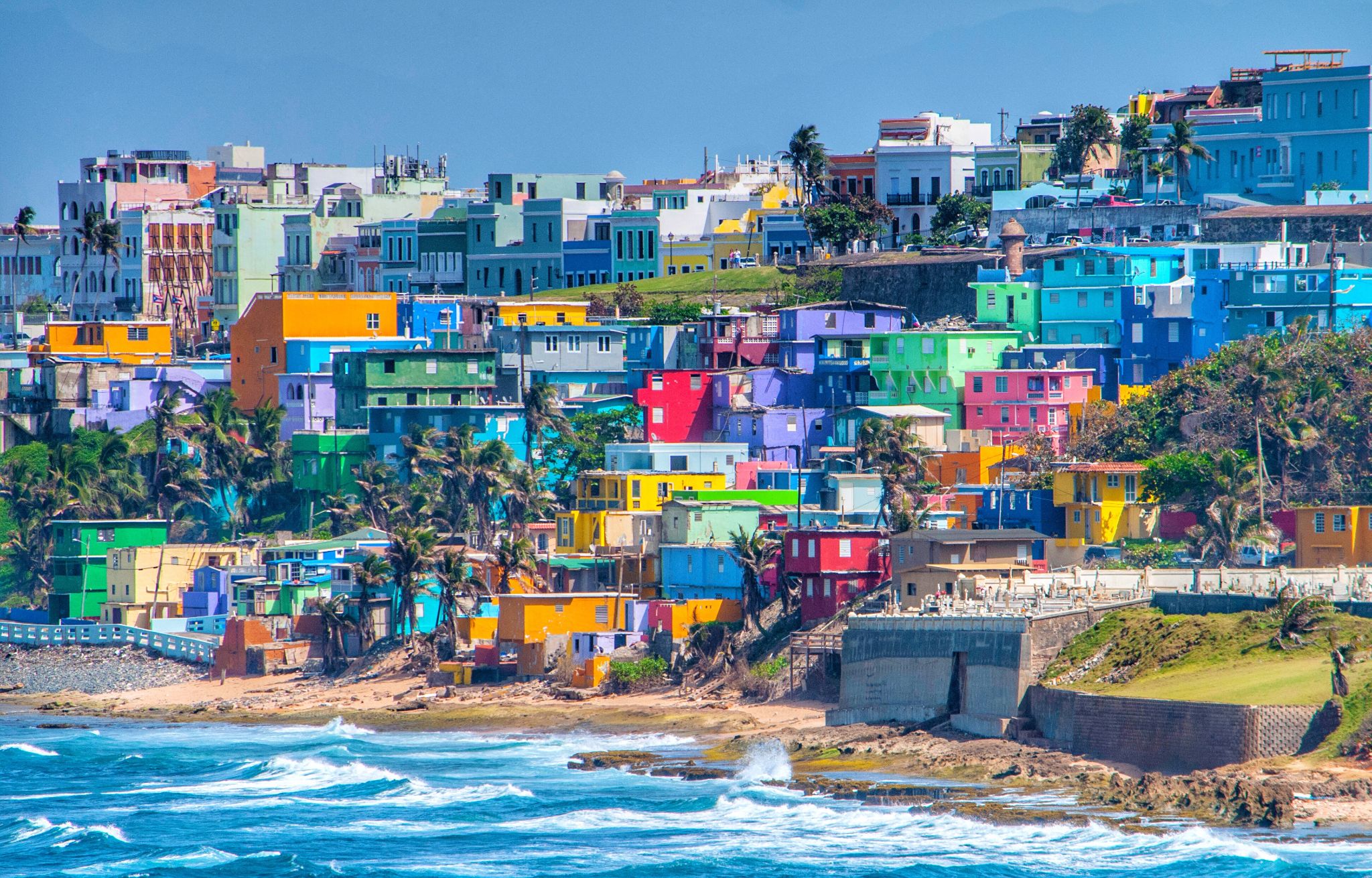











San Juan

San Juan
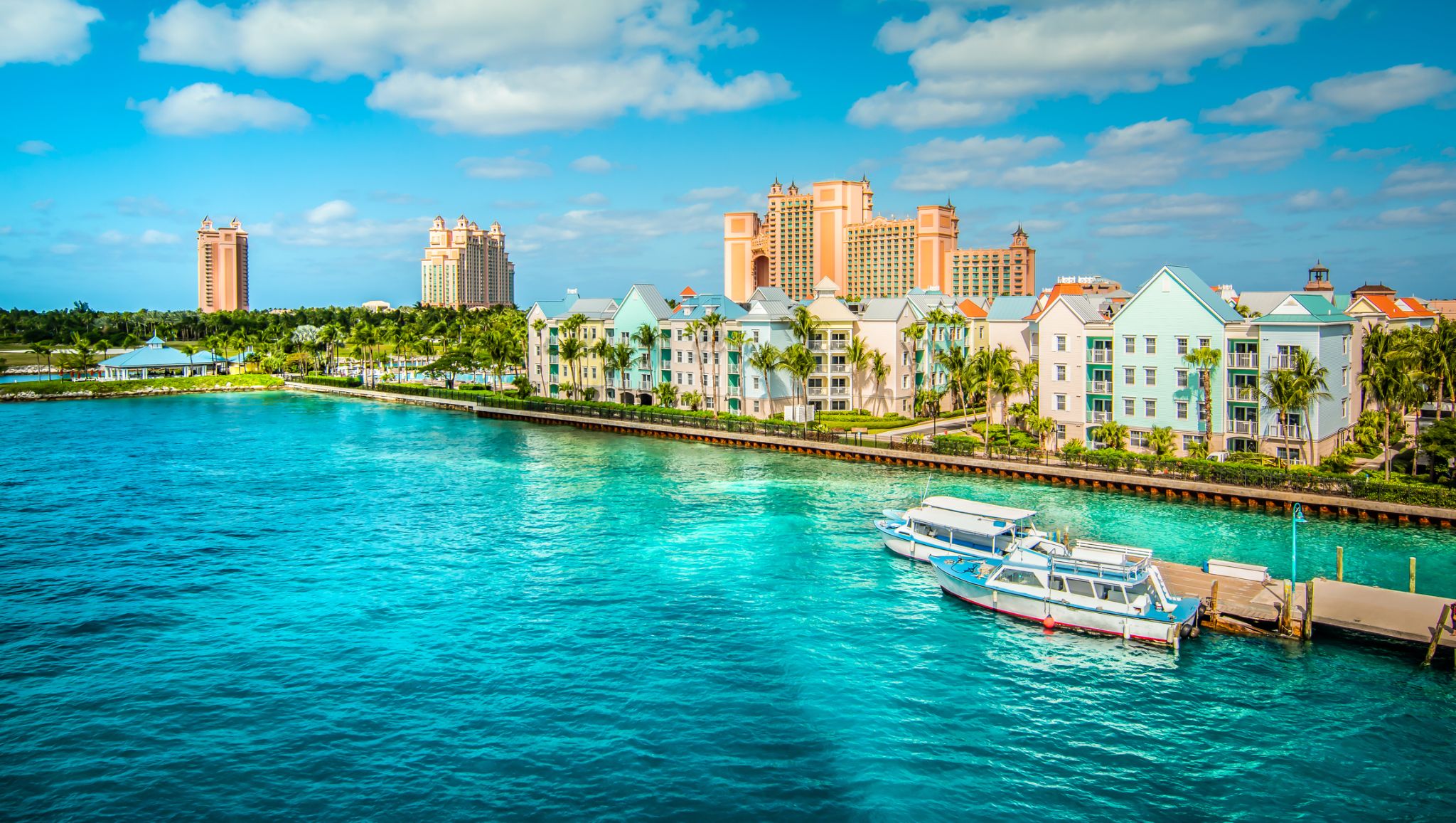


a port on the island of New Providence, capital of the Bahamas; population 240,000 (est. 2007).
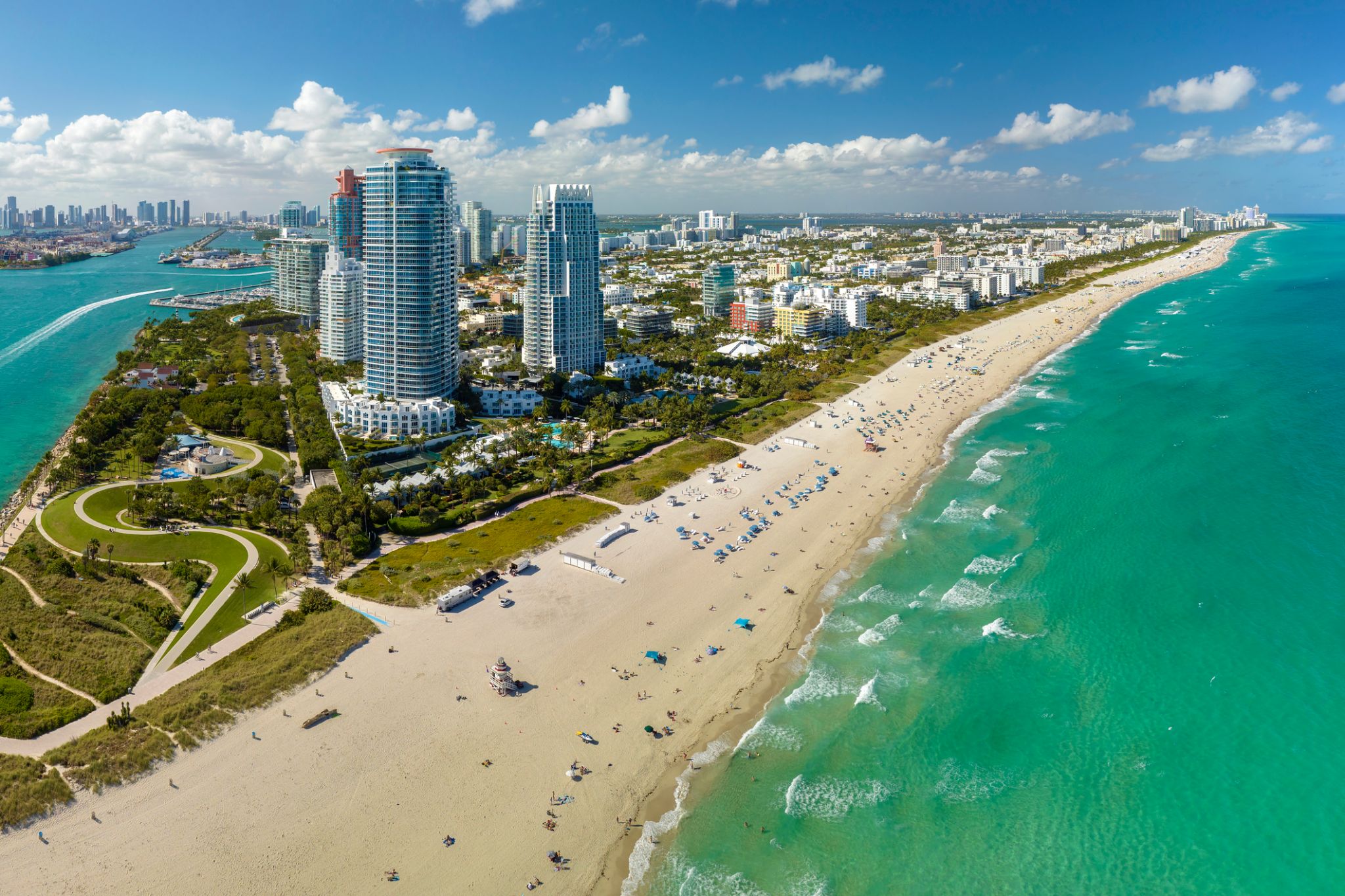

Miami, officially the City of Miami, is the cultural, economic and financial center of South Florida. Miami is the seat of Miami-Dade County, the most populous county in Florida. The city covers an area of about 56.6 square miles (147 km2), between the Everglades to the west and Biscayne Bay on the east; with a 2017 estimated population of 463,347, Miami is the sixth most densely populated major city in the United States. The Miami metropolitan area is home to 6.1 million people and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in the nation. Miami's metro area is the second-most populous metropolis in the southeastern United States and fourth-largest urban area in the U.S.
Miami is a major center, and a leader in finance, commerce, culture, media, entertainment, the arts, and international trade. The Miami Metropolitan Area is by far the largest urban economy in Florida and the 12th largest in the United States with a GDP of $344.9 billion as of 2017. In 2012, Miami was classified as an "Alpha−" level world city in the World Cities Study Group's inventory. In 2010, Miami ranked seventh in the United States and 33rd among global cities in terms of business activity, human capital, information exchange, cultural experience, and political engagement. In 2008, Forbes magazine ranked Miami "America's Cleanest City", for its year-round good air quality, vast green spaces, clean drinking water, clean streets, and citywide recycling programs. According to a 2009 UBS study of 73 world cities, Miami was ranked as the richest city in the United States, and the world's seventh-richest city in terms of purchasing power. Miami is nicknamed the "Capital of Latin America" and is the largest city with a Cuban-American plurality.
Greater Downtown Miami has one of the largest concentrations of international banks in the United States, and is home to many large national and international companies. The Civic Center is a major center for hospitals, research institutes, medical centers, and biotechnology industries. For more than two decades, the Port of Miami, known as the "Cruise Capital of the World", has been the number one cruise passenger port in the world. It accommodates some of the world's largest cruise ships and operations, and is the busiest port in both passenger traffic and cruise lines. Metropolitan Miami is also a major tourism hub in the southeastern U.S. for international visitors, ranking number two in the country after New York City.
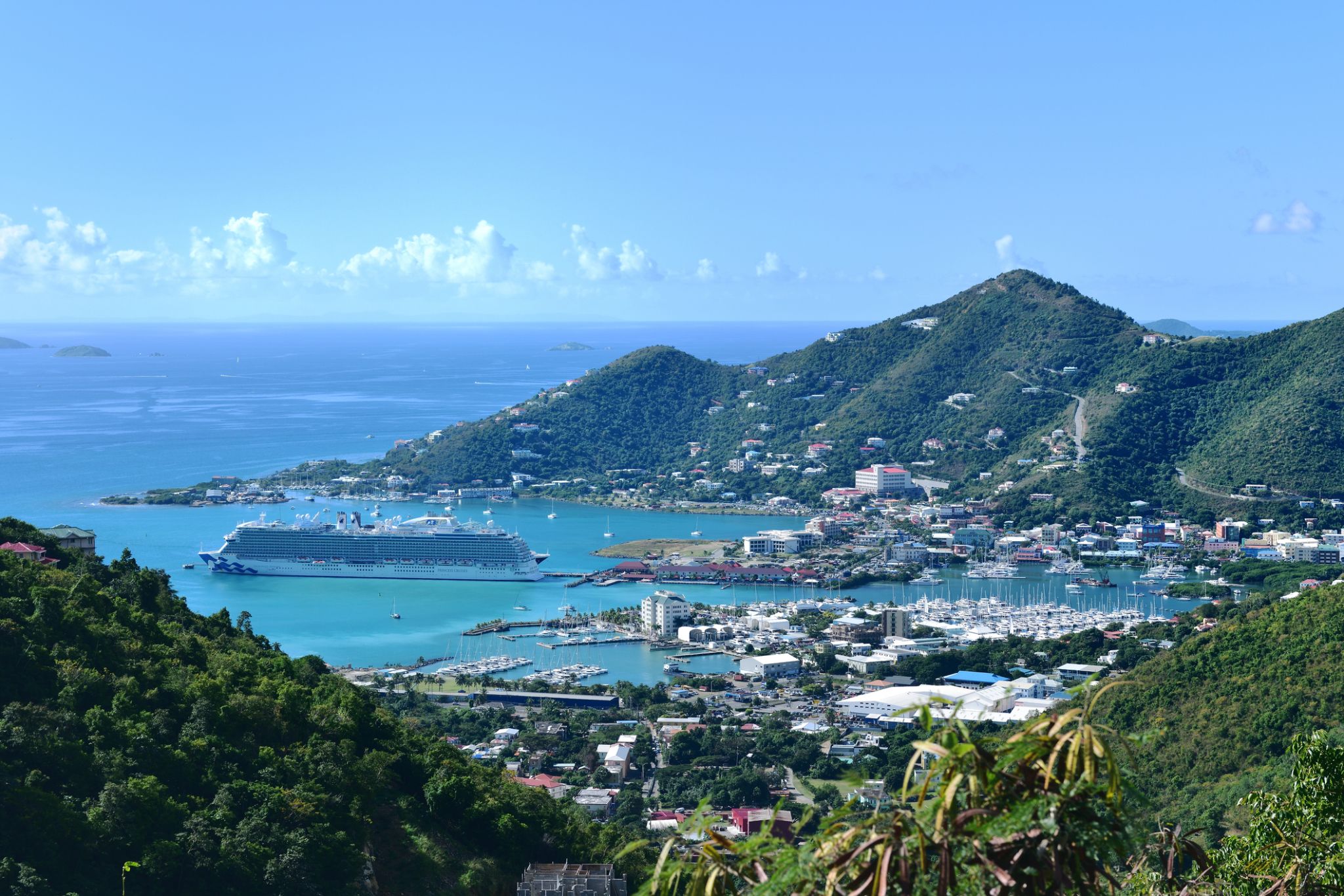
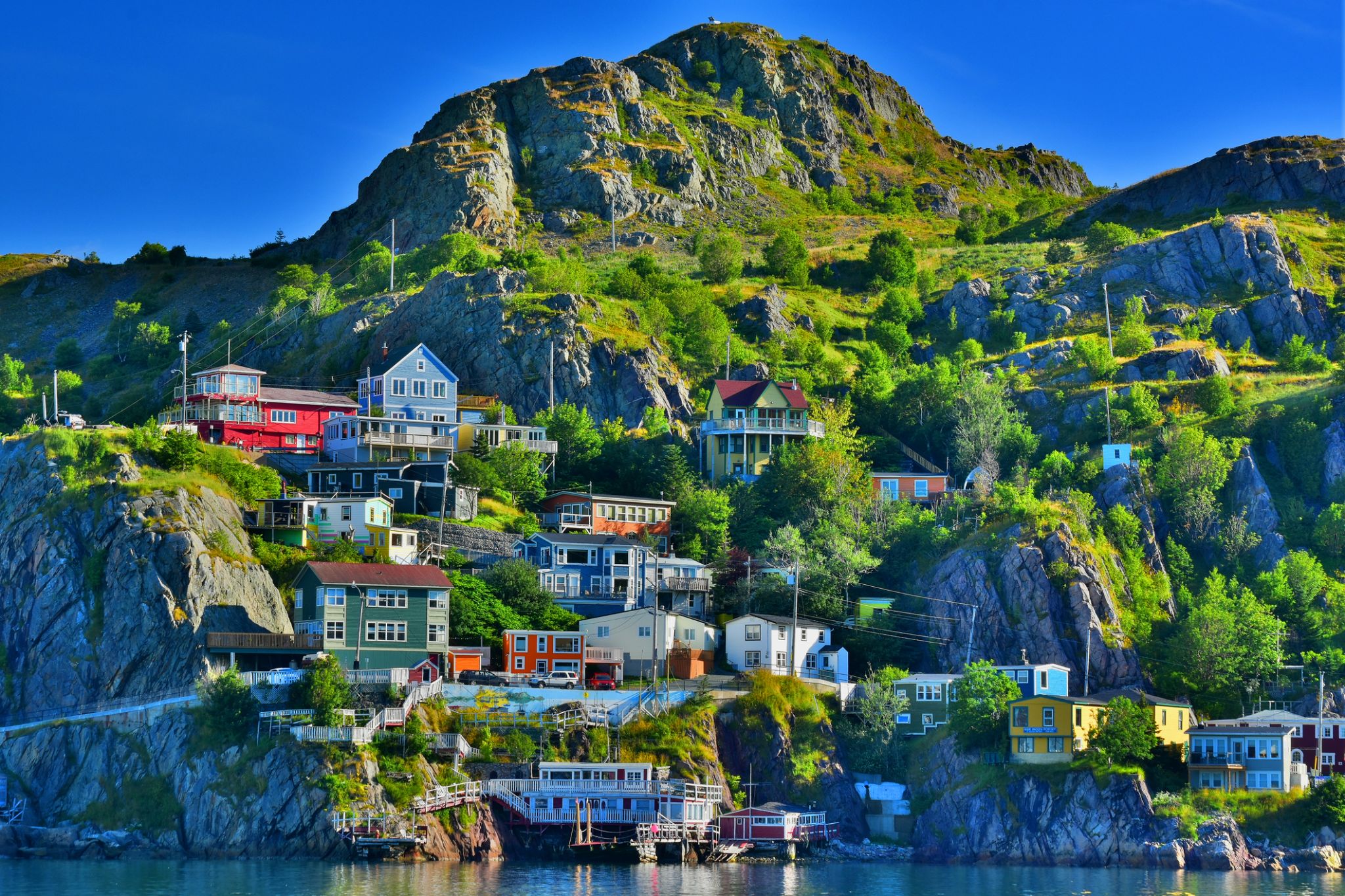




St. John's is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the large Canadian island, Newfoundland. The city spans 446.04 square kilometres (172.22 sq mi) and is North America's easternmost city.
Its name has been attributed to the Nativity of John the Baptist, when John Cabot was believed to have sailed into the harbour in 1497 and to a Basque fishing town with the same name. Existing on maps as early as 1519, it is the oldest city in North America. It was officially incorporated as a city in 1888. With a metropolitan population of approximately 219,207 (as of July 1, 2017), the St. John's Metropolitan Area is Canada's 20th largest metropolitan area and the second largest Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) in Atlantic Canada, after Halifax.
The city has a rich history, having played a role in the French and Indian War, the American Revolutionary War, and the War of 1812. Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi received the first transatlantic wireless signal in St. John's. Its history and culture have made it into an important tourist destination.


Scarborough (Tobago) is a charming town located on the eastern coast of the island of Tobago in the Caribbean Sea. As the capital of the island, it serves as the cultural and historical heart of Tobago. The town is known for its picturesque streets, vibrant markets, and old buildings that blend harmoniously with modern architecture. One of the main landmarks is the historic St. Anne’s Church, built in 1770, which remains an important part of the town’s heritage. Visitors are also drawn to the local market, where fresh fruits, spices, and handmade crafts showcase the island’s rich traditions.
Beyond its cultural and historical appeal, Scarborough offers travelers stunning natural surroundings. Nearby beaches with white sand and crystal-clear waters are perfect for swimming and diving. Pleasant Bay, popular among tourists, offers scenic views and a colorful underwater world. Scarborough is also an ideal base for exploring Tobago’s nature reserves and enjoying active outdoor adventures.
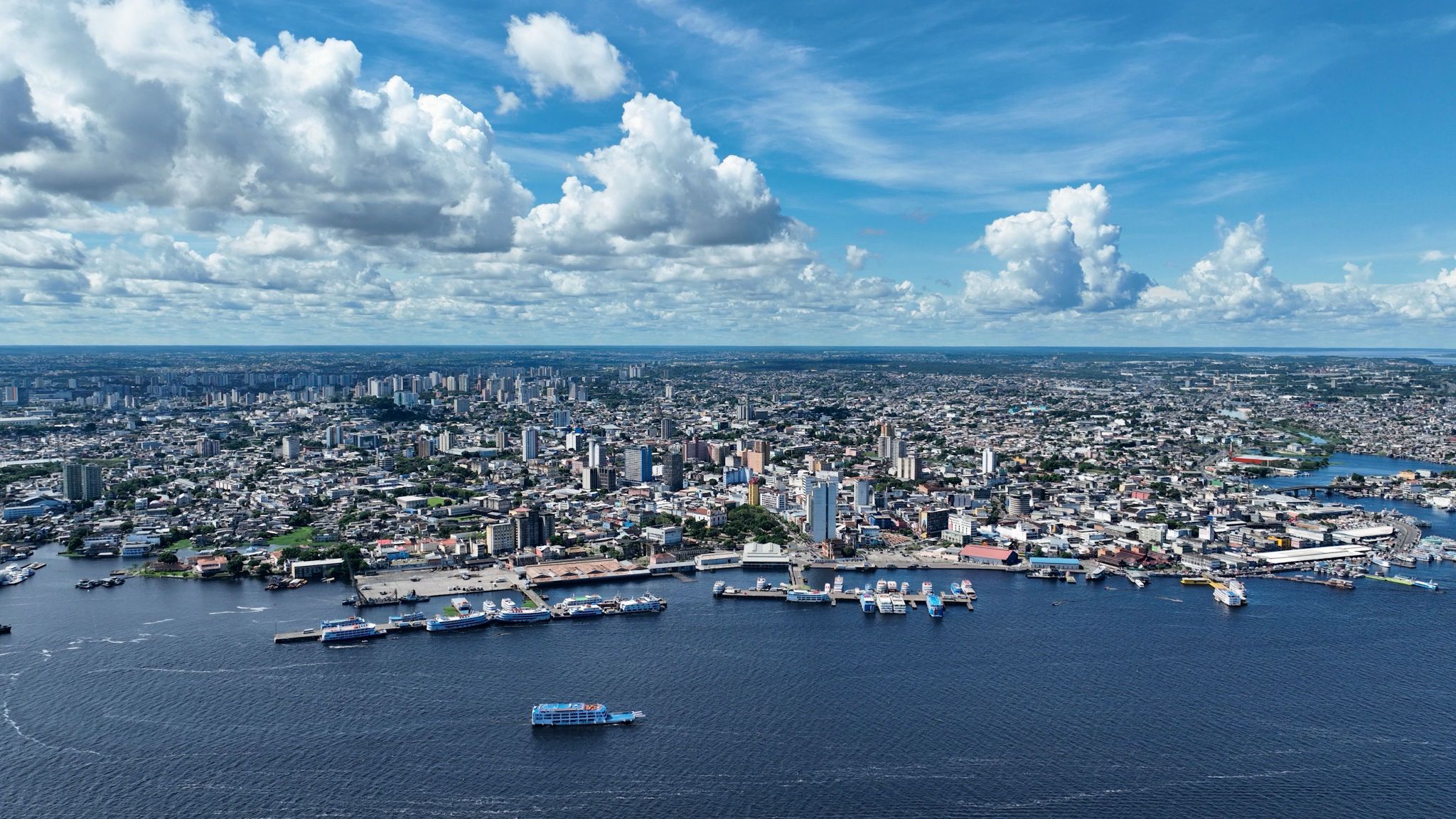






In the heart of the Amazon, where nature and history blend uniquely, lies the city of Manaus — the capital of the Amazonas state and the largest city in the region with over a million inhabitants. It gained fame during the rubber boom of the last century, when the luxurious Opera House was built in 1896 using materials imported from Europe despite the high costs. Surrounded by jungle on three sides, Manaus stands apart from European cities with its shaded streets, small parks, and traditional boot cleaners. Just a ten-minute walk from the city center, you can find palm-thatched stilt houses inhabited by indigenous families, offering a genuine Amazonian experience.
One of the city’s natural wonders is the "Meeting of the Waters." Here, the dark mineral-rich waters of the Rio Negro merge with the yellowish waters of the Solimões River to form the mighty Amazon. For about two kilometers, these waters flow side by side without mixing due to their temperature difference, creating a stunning natural spectacle. Manaus is considered one of the cleanest ecological cities in the world and is located just five hours by plane from Rio de Janeiro — a perfect starting point for exploring the amazing Amazon rainforest.

In the heart of the Amazon, where nature and history blend uniquely, lies the city of Manaus — the capital of the Amazonas state and the largest city in the region with over a million inhabitants. It gained fame during the rubber boom of the last century, when the luxurious Opera House was built in 1896 using materials imported from Europe despite the high costs. Surrounded by jungle on three sides, Manaus stands apart from European cities with its shaded streets, small parks, and traditional boot cleaners. Just a ten-minute walk from the city center, you can find palm-thatched stilt houses inhabited by indigenous families, offering a genuine Amazonian experience.
One of the city’s natural wonders is the "Meeting of the Waters." Here, the dark mineral-rich waters of the Rio Negro merge with the yellowish waters of the Solimões River to form the mighty Amazon. For about two kilometers, these waters flow side by side without mixing due to their temperature difference, creating a stunning natural spectacle. Manaus is considered one of the cleanest ecological cities in the world and is located just five hours by plane from Rio de Janeiro — a perfect starting point for exploring the amazing Amazon rainforest.
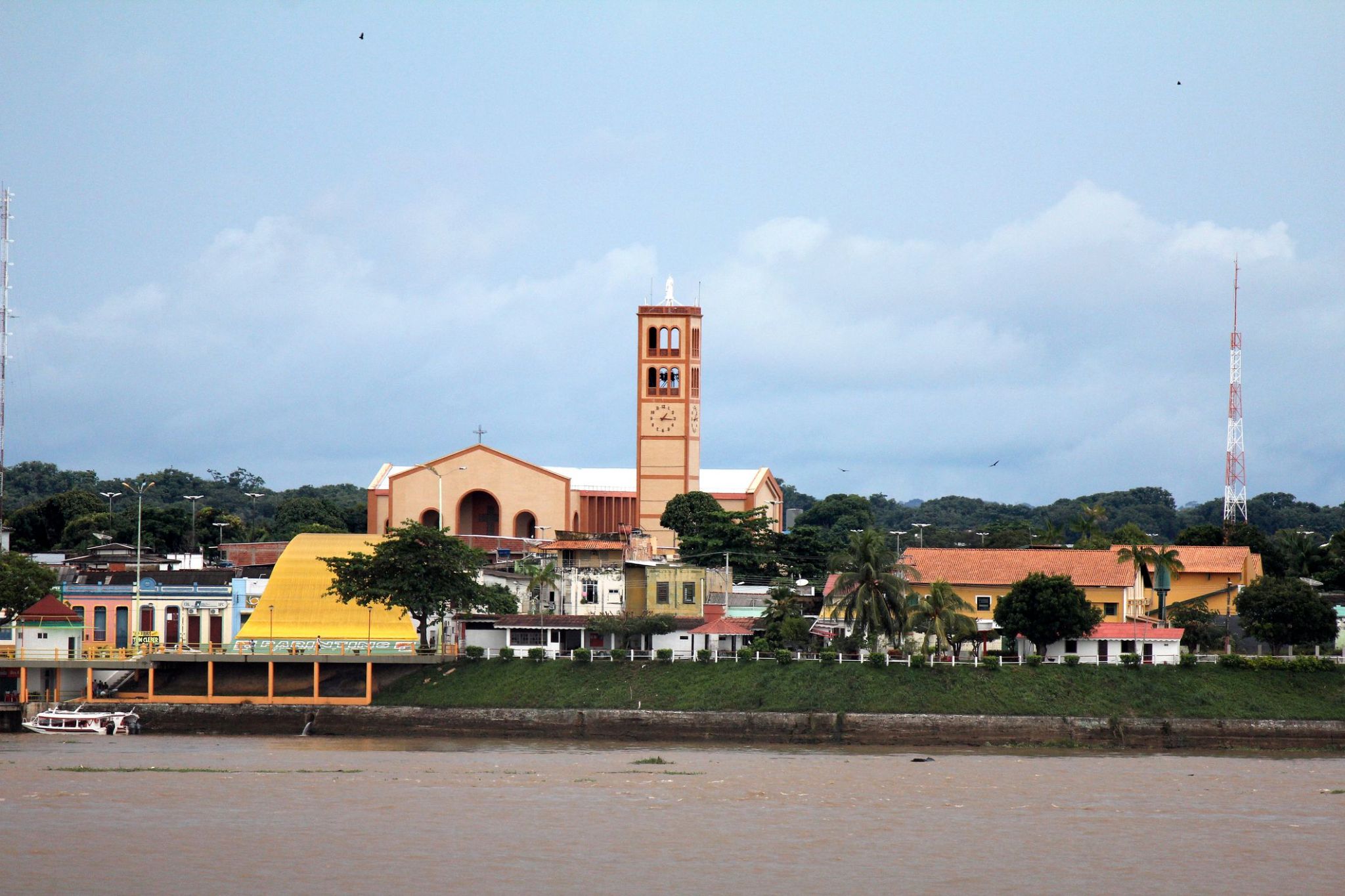

Surrounded by vibrant traditions and picturesque nature, the region on the island of Parintins offers a unique blend of cultural celebration and tropical wilderness. Every year, the famous Bumba-Meu-Boi festival takes place here, attracting thousands of tourists from around the world eager to immerse themselves in local legends, music, and dance. Additionally, the surroundings are rich with rivers and forests where visitors can enjoy walks and explore the abundant Amazon wildlife.
A trip to Parintins is an opportunity to discover not only the beauty of Amazonian landscapes but also the living culture of the Brazilian people. Small villages with friendly locals, traditional crafts, and cuisine create an atmosphere of coziness and authenticity. This is a place where every guest will find something special — from breathtaking natural adventures to unforgettable cultural experiences.
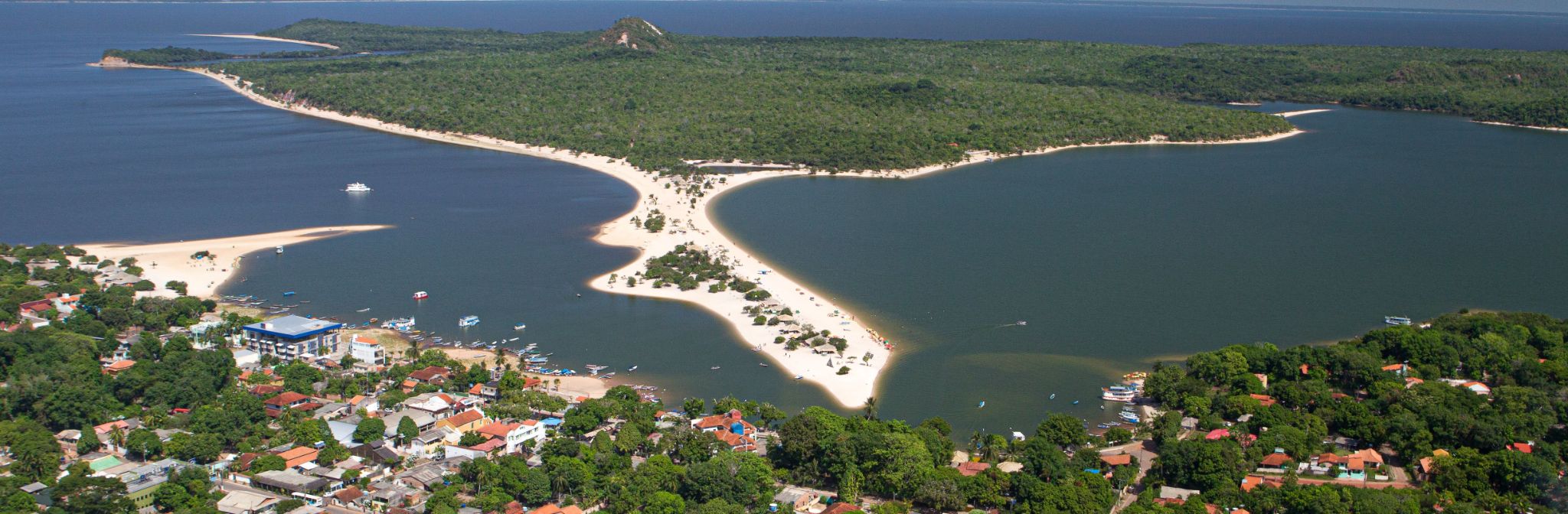

White-sand beaches that appear and disappear with the changing water levels of the Amazon River make Alter do Chão a true natural wonder of Brazil. Located in the state of Pará, it is often called the “Brazilian Caribbean” for its crystal-clear waters, palm-fringed scenery, and soft sands. Visitors come not only for the beach experience but also for the charm of a fishing village where fresh fish dishes and jungle serenity await.
Alter do Chão is especially popular in September during the annual Sairé Festival — a vibrant celebration with traditional dances, costumes, and river parades. Adventure seekers can enjoy kayaking through flooded forests, spotting pink river dolphins, and exploring ancient archaeological sites. It’s a place where culture, nature, and the magic of the Amazon come together in one unforgettable location.
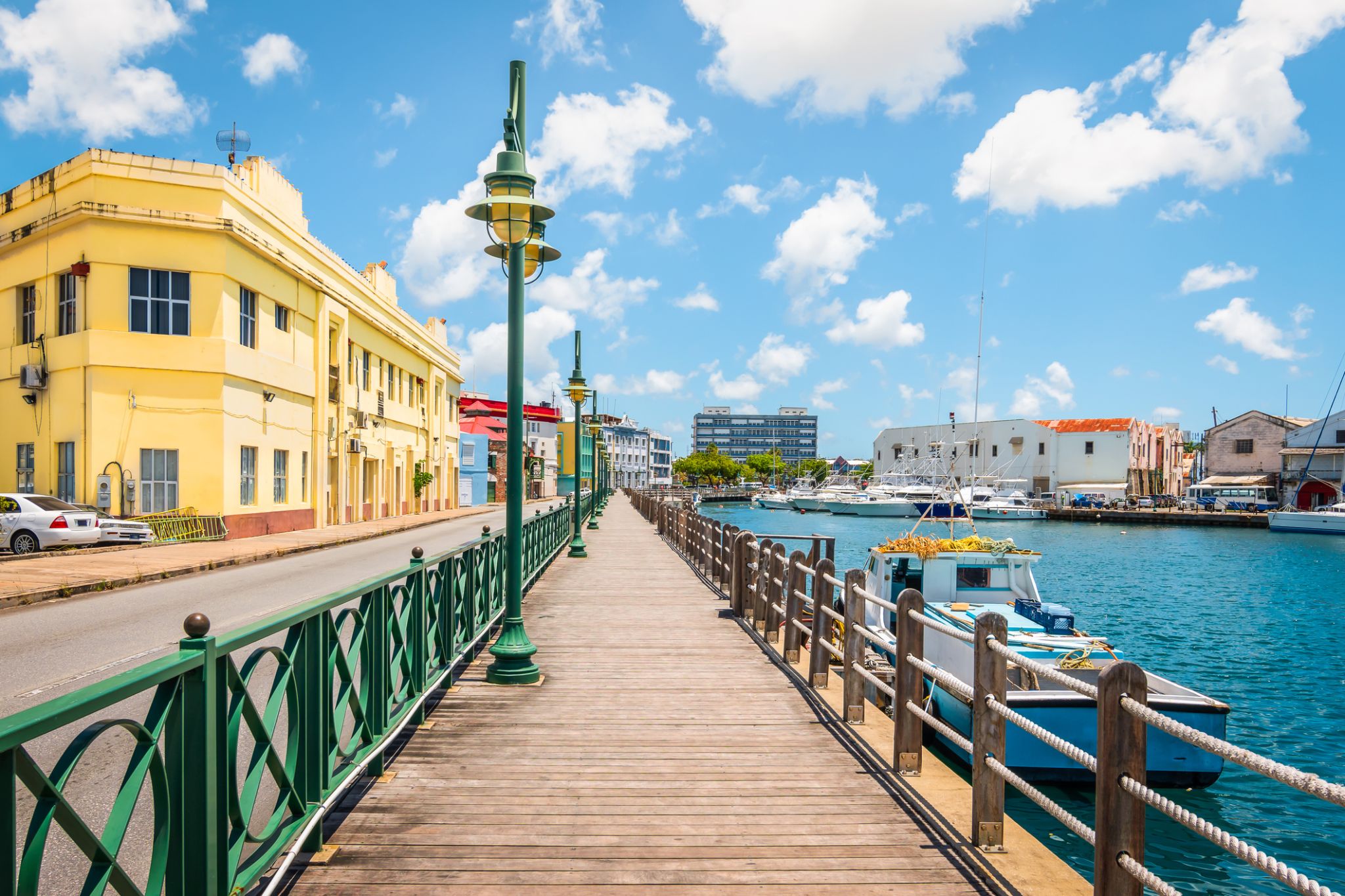




Bridgetown is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The City", but the most common reference is simply "Town". As of 2014, its metropolitan population stands at roughly 110,000.
The Bridgetown port, found along Carlisle Bay (at 13.106°N 59.632°W) lies on the southwestern coast of the island. Parts of the Greater Bridgetown area (as roughly defined by the Ring Road Bypass or more commonly known as the ABC Highway), sit close to the borders of the neighbouring parishes Christ Church and St. James. The Grantley Adams International Airport for Barbados, is located 16 kilometres (10 mi) southeast of Bridgetown city centre, and has daily flights to major cities in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada and the Caribbean. There is no longer a local municipal government, but it is a constituency of the national Parliament. During the short-lived 1950s-1960s Federation of the British West Indian Territories, Bridgetown was one of three capital cities within the region being considered to be the Federal capital of region.
The present-day location of the city was established by English settlers in 1628; a previous settlement under the authority of Sir William Courten was at St. James Town. Bridgetown is a major West Indies tourist destination, and the city acts as an important financial, informatics, convention centre, and cruise ship port of call in the Caribbean region. On 25 June 2011, "Historic Bridgetown and its Garrison" was added as a World Heritage Site of UNESCO.
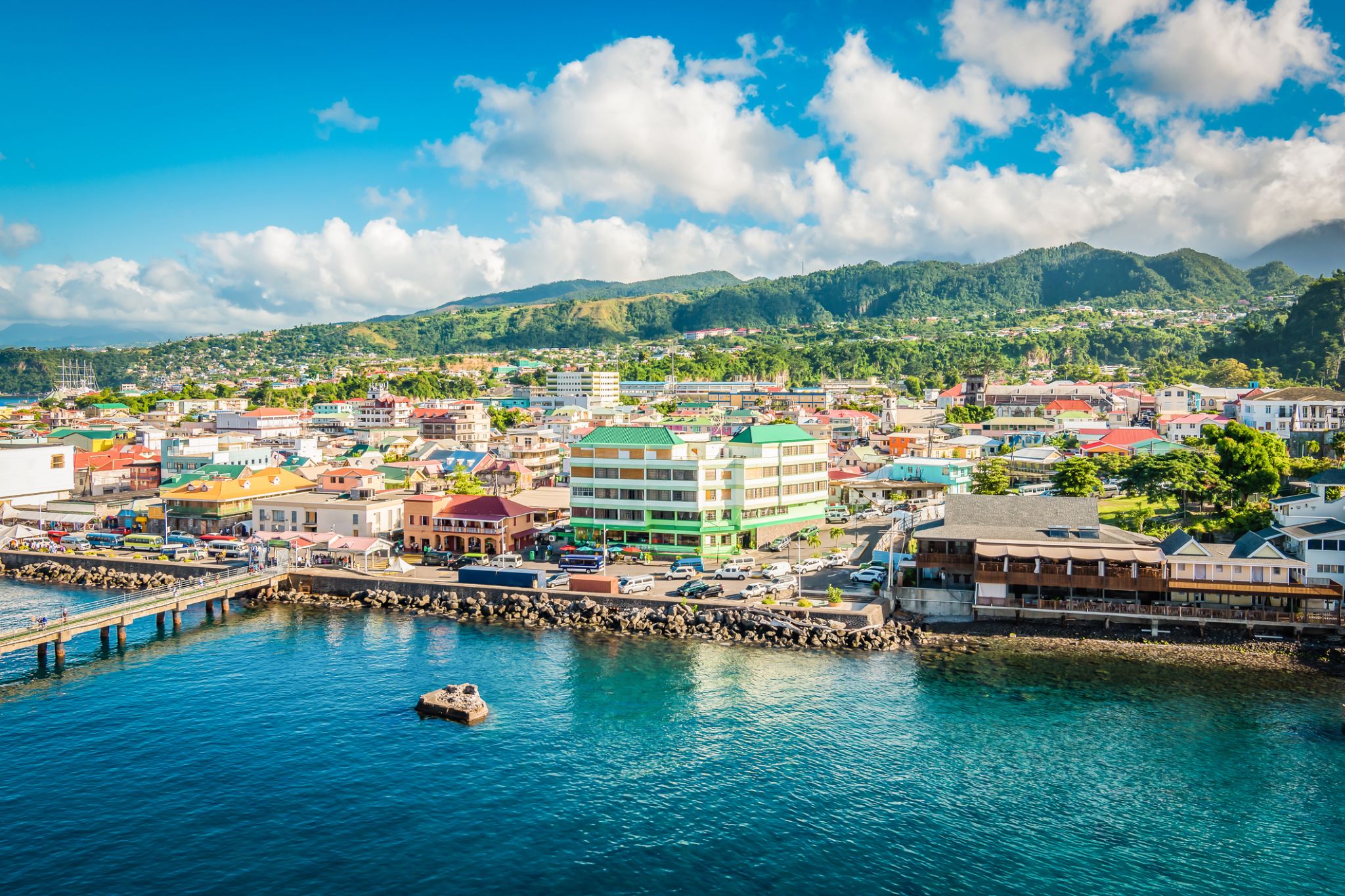

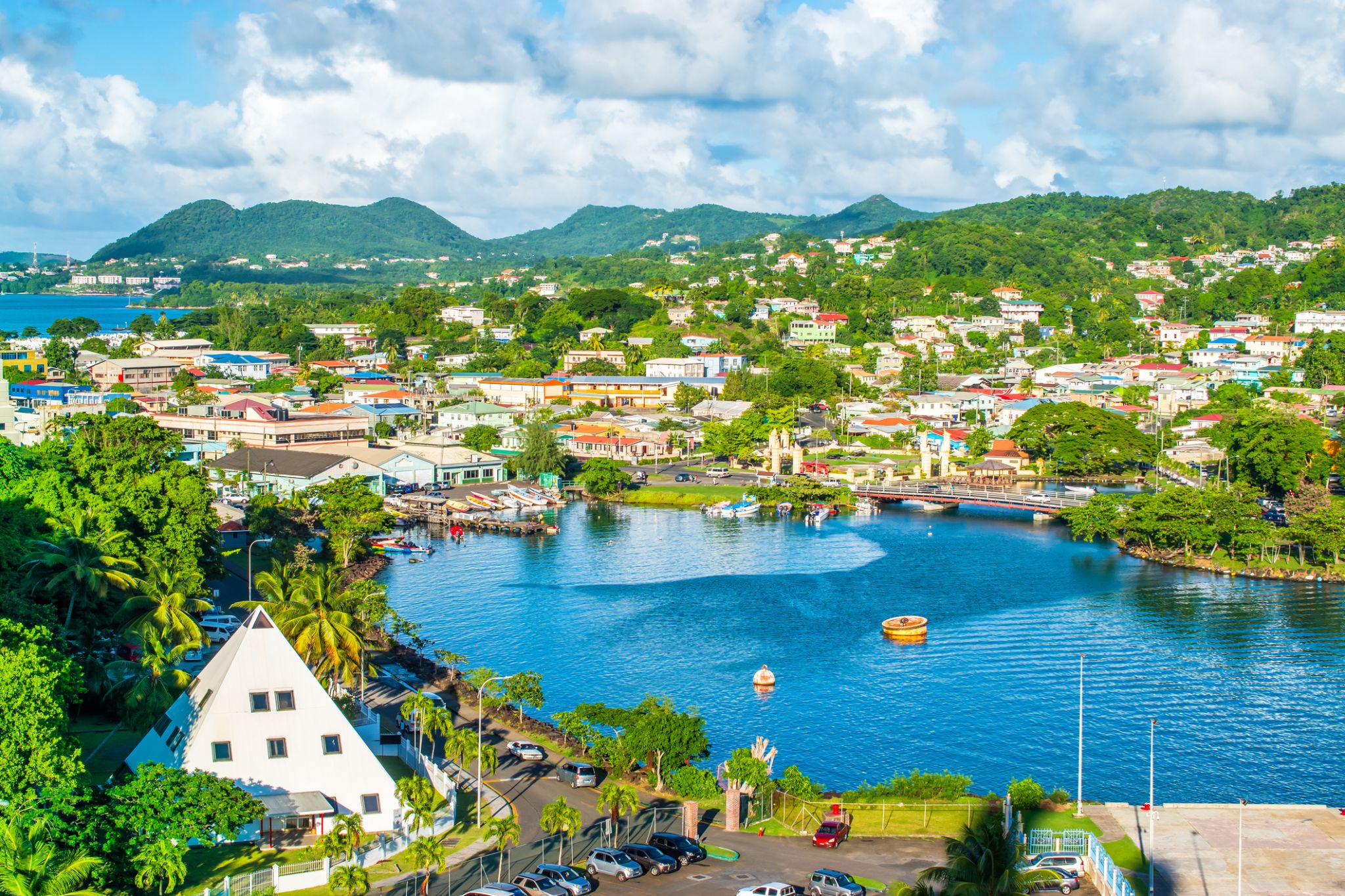
Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the West Indies. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is part of the Windward Islands in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The island is located near Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Its area is 750 km2 (290 sq mi), and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at 1,447 m (4,747 ft) in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census. The Commonwealth of Dominica is one of the Caribbean's few republics.
The island was originally inhabited by the Kalinago and later colonised by Europeans, predominantly by the French from the 1690s to 1763. Columbus is said to have passed the island on Sunday 3 November 1493, and the island's name is derived from the Latin for "Sunday". Great Britain took possession in 1763 after the Seven Years' War, and it gradually established English as its official language. The island republic gained independence in 1978.
Its name is pronounced with emphasis on the third syllable, related to its French name of Dominique. Dominica has been nicknamed the "Nature Isle of the Caribbean" for its natural environment. It is the youngest island in the Lesser Antilles, and in fact it is still being formed by geothermal-volcanic activity, as evidenced by the world's second-largest hot spring, called Boiling Lake. The island has lush mountainous rainforests, and it is the home of many rare plants, animals, and bird species. There are xeric areas in some of the western coastal regions, but heavy rainfall occurs inland. The Sisserou parrot, also known as the imperial amazon and found only on Dominica, is the island's national bird and featured on the national flag, which is one of only two national flags containing the color purple.


San Juan


a port on the island of New Providence, capital of the Bahamas; population 240,000 (est. 2007).

Miami, officially the City of Miami, is the cultural, economic and financial center of South Florida. Miami is the seat of Miami-Dade County, the most populous county in Florida. The city covers an area of about 56.6 square miles (147 km2), between the Everglades to the west and Biscayne Bay on the east; with a 2017 estimated population of 463,347, Miami is the sixth most densely populated major city in the United States. The Miami metropolitan area is home to 6.1 million people and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in the nation. Miami's metro area is the second-most populous metropolis in the southeastern United States and fourth-largest urban area in the U.S.
Miami is a major center, and a leader in finance, commerce, culture, media, entertainment, the arts, and international trade. The Miami Metropolitan Area is by far the largest urban economy in Florida and the 12th largest in the United States with a GDP of $344.9 billion as of 2017. In 2012, Miami was classified as an "Alpha−" level world city in the World Cities Study Group's inventory. In 2010, Miami ranked seventh in the United States and 33rd among global cities in terms of business activity, human capital, information exchange, cultural experience, and political engagement. In 2008, Forbes magazine ranked Miami "America's Cleanest City", for its year-round good air quality, vast green spaces, clean drinking water, clean streets, and citywide recycling programs. According to a 2009 UBS study of 73 world cities, Miami was ranked as the richest city in the United States, and the world's seventh-richest city in terms of purchasing power. Miami is nicknamed the "Capital of Latin America" and is the largest city with a Cuban-American plurality.
Greater Downtown Miami has one of the largest concentrations of international banks in the United States, and is home to many large national and international companies. The Civic Center is a major center for hospitals, research institutes, medical centers, and biotechnology industries. For more than two decades, the Port of Miami, known as the "Cruise Capital of the World", has been the number one cruise passenger port in the world. It accommodates some of the world's largest cruise ships and operations, and is the busiest port in both passenger traffic and cruise lines. Metropolitan Miami is also a major tourism hub in the southeastern U.S. for international visitors, ranking number two in the country after New York City.