
| Cruise Region : Oceania |
| Company : Oceania Cruises |
| Ship : Riviera |
| Journey Start : Tue 06 Jan 2026 |
| Journey End : Sun 08 Feb 2026 |
| Count Nights : 33 nights |
| Day | Date | Port | Arrival | Departure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.01 Tue | Papeete / French Polynesia | ||
| 2 | 7.01 Wed | Papeete / French Polynesia | 04:00 | |
| 2 | 7.01 Wed | Moorea Islands Society / French Polynesia | 08:00 | 16:00 |
| 3 | 8.01 Thu | Huahine | 07:00 | 17:00 |
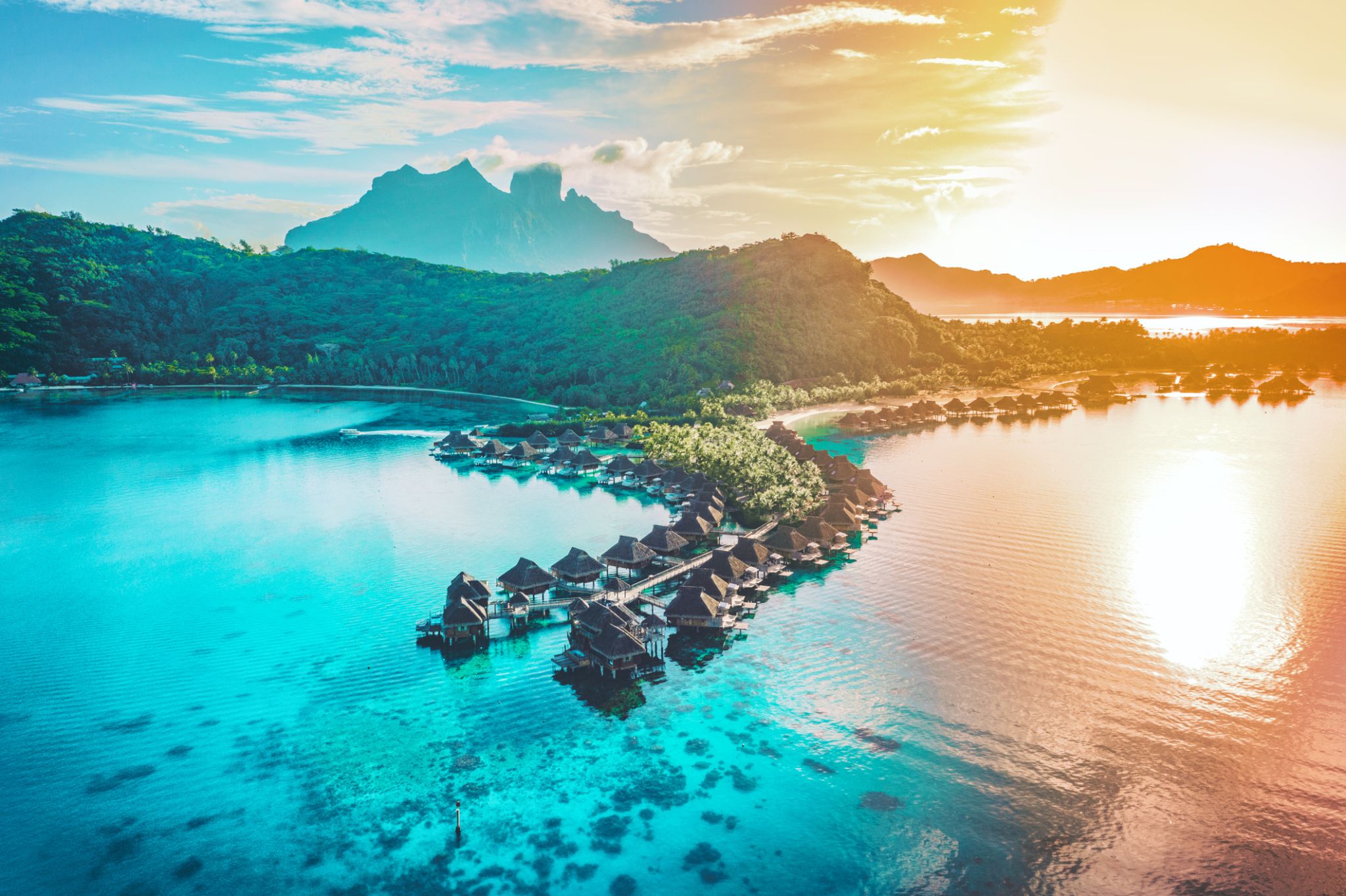
| 4 | 9.01 Fri | Bora Bora, Society Islands / French Polynesia | 07:00 | 18:00 |
| 5 | 10.01 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 6 | 11.01 Sun | Rarotonga / Cook Islands | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 7 | 12.01 Mon | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 8 | 13.01 Tue | Alofi Niue Island / Niue | 07:00 | 16:00 |
| 9 | 14.01 Wed | Pago-Pago / Samoa | 11:00 | 21:00 |
| 10 | 15.01 Thu | |||
| 11 | 16.01 Fri | Apia / Samoa | 07:00 | 16:00 |
| 12 | 17.01 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 13 | 18.01 Sun | Suva / Fiji | 08:00 | 20:00 |
| 14 | 19.01 Mon | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 15 | 20.01 Tue | Nukualofa / Tonga | 07:00 | 16:00 |
| 16 | 21.01 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 17 | 22.01 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 18 | 23.01 Fri | Cocksen Hole / Honduras | 08:00 | 19:00 |
| 19 | 24.01 Sat | Oakland / New Zealand | 08:00 | |
| 20 | 25.01 Sun | Oakland / New Zealand | 20:00 | |
| 21 | 26.01 Mon | Rotorua | 07:30 | 15:15 |
| 22 | 27.01 Tue | Napier / New Zealand | 10:30 | 18:30 |
| 23 | 28.01 Wed | Wellington / New Zealand | 10:00 | 20:00 |
| 24 | 29.01 Thu | Christchurch / New Zealand | 08:00 | 19:30 |
| 25 | 30.01 Fri | Dunedin / New Zealand | 09:00 | 17:00 |
| 26 | 31.01 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 27 | 1.02 Sun | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 28 | 2.02 Mon | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 29 | 3.02 Tue | Tasmania (Hobart) / Australia | 07:00 | 20:00 |
| 30 | 4.02 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 31 | 5.02 Thu | Melbourne / Australia | 07:00 | |
| 32 | 6.02 Fri | Melbourne / Australia | 16:00 | |
| 33 | 7.02 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 34 | 8.02 Sun | Sydney / Australia | 07:00 | 20:00 |
Your World Included
With Your World Included, you’ll enjoy a wide array of included amenities for the ultimate comfort and value in ultra-premium cruising.
Unforgettable dining experiences at a variety of exquisite restaurants — all at no extra charge.
Complimentary specialty coffees, sodas, freshly pressed juices, and still and sparkling Vero Water® served throughout the ship.
Unlimited free Wi-Fi available in your suite, stateroom, and all public areas.
In-room dining with a superb variety of hot and cold selections.
Smoothies, milkshakes, gelato, and signature Humphry Slocombe ice cream — always included.
Group fitness classes at Aquamar® Spa + Vitality Center are complimentary.
Gratuities are included for your convenience.
Laundry is free for all guests.
With complimentary self-service launderettes on board, plus laundry and pressing services for Concierge and Suite categories, you’ll always look your finest.
Along with our hallmark personalized service, you’ll enjoy an enriching cruise experience with no hidden costs or nickel-and-diming.
Elevate Your Experience
Concierge Level Veranda Staterooms offer an unrivaled combination of luxury, privilege, and value. A wealth of amenities and exclusive benefits elevate your experience to the sublime — from in-room dining selections from The Grand Dining Room and complimentary laundry services to unlimited access to the Aquamar Spa Terrace.
On board Oceania Marina and Oceania Riviera, you’ll also enjoy the services of a dedicated Concierge and exclusive access to the private Concierge Lounge.
Located in the most desired areas of the ship, Concierge Level Veranda Staterooms are far more than just staterooms — they are an experience in themselves.
Concierge Level Veranda — Exclusive Privileges
Expanded in-room dining menu for lunch and dinner from The Grand Dining Room
Laundry service — up to 3 bags per stateroom
Exclusive key-card access to the private Concierge Lounge aboard Oceania Marina, Oceania Riviera, Oceania Vista, and Oceania Allura, featuring complimentary beverages, coffees, snacks, and the services of a dedicated Concierge
Welcome bottle of fine Italian Prosecco
Priority online reservations for specialty restaurants
Unlimited access to the Aquamar Spa Terrace
Oceania Cruises logo tote bag
Cashmere lap blankets — perfect for relaxing or snuggling
Pressing of garments upon embarkation
Complimentary shoeshine service
Deposit and Payments – Oceania Cruises
General Deposit:
For Owner’s, Vista, and Oceania Suites, a deposit of 20% of the cruise fare per person is required.
For all other suite/stateroom categories, the deposit is $500 per person.
For Grand Voyages, the deposit is $1,500 per person.
Deposit and Final Payment Deadlines:
Bookings more than 150 days from sailing:
Deposit 20% for Owner’s, Vista, and Oceania Suites and $500 for all other categories is required within 5 days of booking.
Bookings 90–120 days from sailing:
Full payment required within 3 days of booking.
Bookings 0–90 days from sailing:
Full payment due on the day of booking.
Important:
Bookings that are not deposited or paid in full according to this schedule will be automatically cancelled.
Unless otherwise noted, final payment must be received by Oceania Cruises 150 days prior to departure for cruises less than 15 days, and 150 days for cruises 15 days or longer.
Oceania Cruises reserves the right to cancel any booking not fully paid at the time of final payment.
Additional Information:
Passport details and special onboard service requests are due at final payment.
Payment may be made by personal check, American Express, Discover, MasterCard, or Visa.
For convenience, final payment may be automatically charged to the credit card used for the initial deposit.
Oceania Cruises is not responsible for foreign currency or transaction fees independently charged by issuing banks. These fees do not benefit Oceania Cruises.
Third-party credit card payments are accepted only with valid authorization from the cardholder.
Deposit and Payment – 180-Day Voyages
For 180-day voyages, a deposit of 20% of the cruise fare per person for all suites and staterooms is required within 7 days of booking.
Final payment must be received no later than 181 days prior to departure, along with passport details and any special onboard service requests.
Otherwise, the booking may be immediately cancelled, and applicable penalties will apply.
Oceania Cruises accepts payment for reservations by credit/debit card or bank transfer.
Unfortunately, personal checks are not accepted.
Credit/Debit Cards:
American Express, Visa, and Mastercard are accepted.
Please note: Oceania Cruises assumes no responsibility for foreign currency/transaction processing fees assessed by your issuing bank.
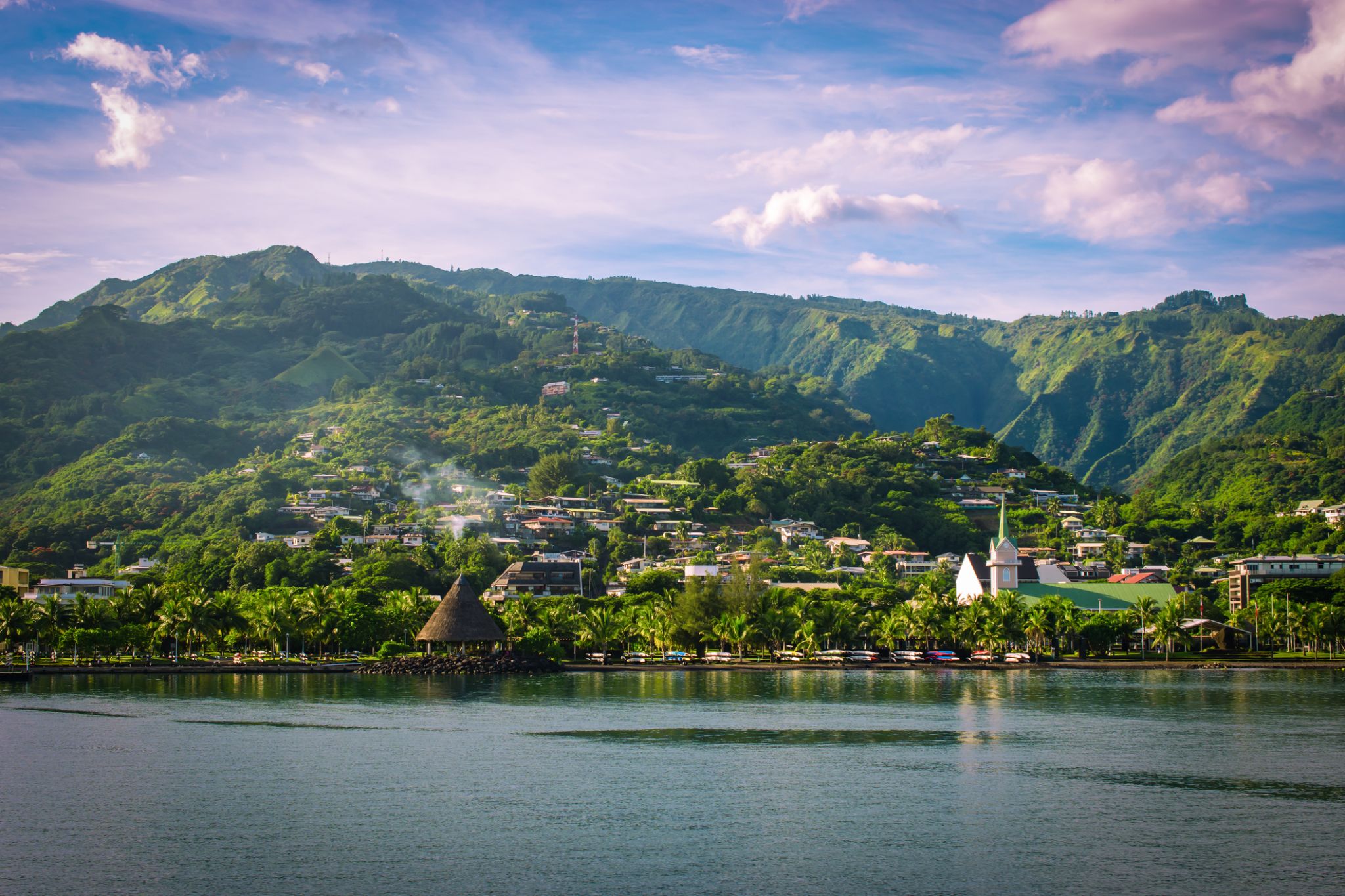

Papeete is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the Pacific Ocean. The commune of Papeete is located on the island of Tahiti, in the administrative subdivision of the Windward Islands, of which Papeete is the administrative capital. The French High Commissioner also resides in Papeete. It is the primary center of Tahitian and French Polynesian public and private governmental, commercial, industrial and financial services, the hub of French Polynesian tourism and a commonly used port of call. The Windward Islands are themselves part of the Society Islands. The name Papeete means "water from a basket".
The urban area of Papeete had a total population of 136,771 inhabitants at the August 2017 census, 26,926 of whom lived in the commune of Papeete proper.

Papeete is the capital city of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the Pacific Ocean. The commune of Papeete is located on the island of Tahiti, in the administrative subdivision of the Windward Islands, of which Papeete is the administrative capital. The French High Commissioner also resides in Papeete. It is the primary center of Tahitian and French Polynesian public and private governmental, commercial, industrial and financial services, the hub of French Polynesian tourism and a commonly used port of call. The Windward Islands are themselves part of the Society Islands. The name Papeete means "water from a basket".
The urban area of Papeete had a total population of 136,771 inhabitants at the August 2017 census, 26,926 of whom lived in the commune of Papeete proper.
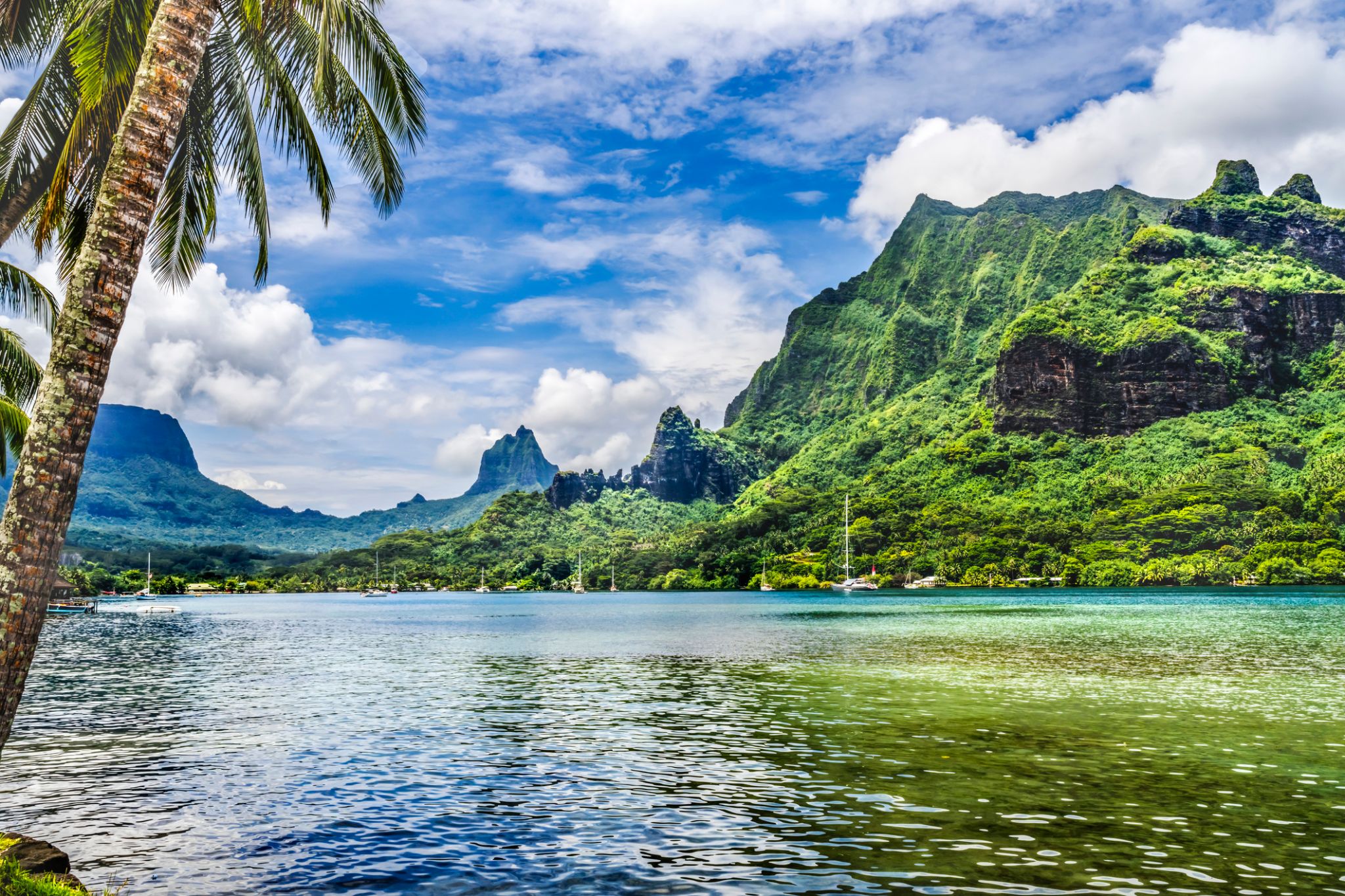

The island was formed as a volcano 1.5 to 2.5 million years ago, the result of a Society hotspot in the mantle under the oceanic plate that formed the whole of the Society Archipelago. It is theorized that the current bays were formerly river basins that filled during the Holocene searise.
Mo'orea is about 10 miles in width from the west to the east. There are two small, nearly symmetrical bays on the north shore. The one to the west is called 'Ōpūnohu Bay, which is not very populated but many travelers have come into the bay. The main surrounding communes of the bay are Piha'ena in the east and Papetō'ai to the west. The one to the east is Cook's Bay, also called Pao Pao Bay since the largest commune of Mo'orea is at the bottom of the bay. The other communes are Piha'ena to the west and busy Maharepa to the east. The highest point is Mount Tohi'e'a, near the center of Mo'orea. It dominates the vista from the two bays and can be seen from Tahiti. There are also hiking trails in the mountains. The Vai'are Bay is another small inlet, smaller than the two main bays, on the east shore. This bay has been settled a lot and has a lot of business. The main village is located just south of the bay.
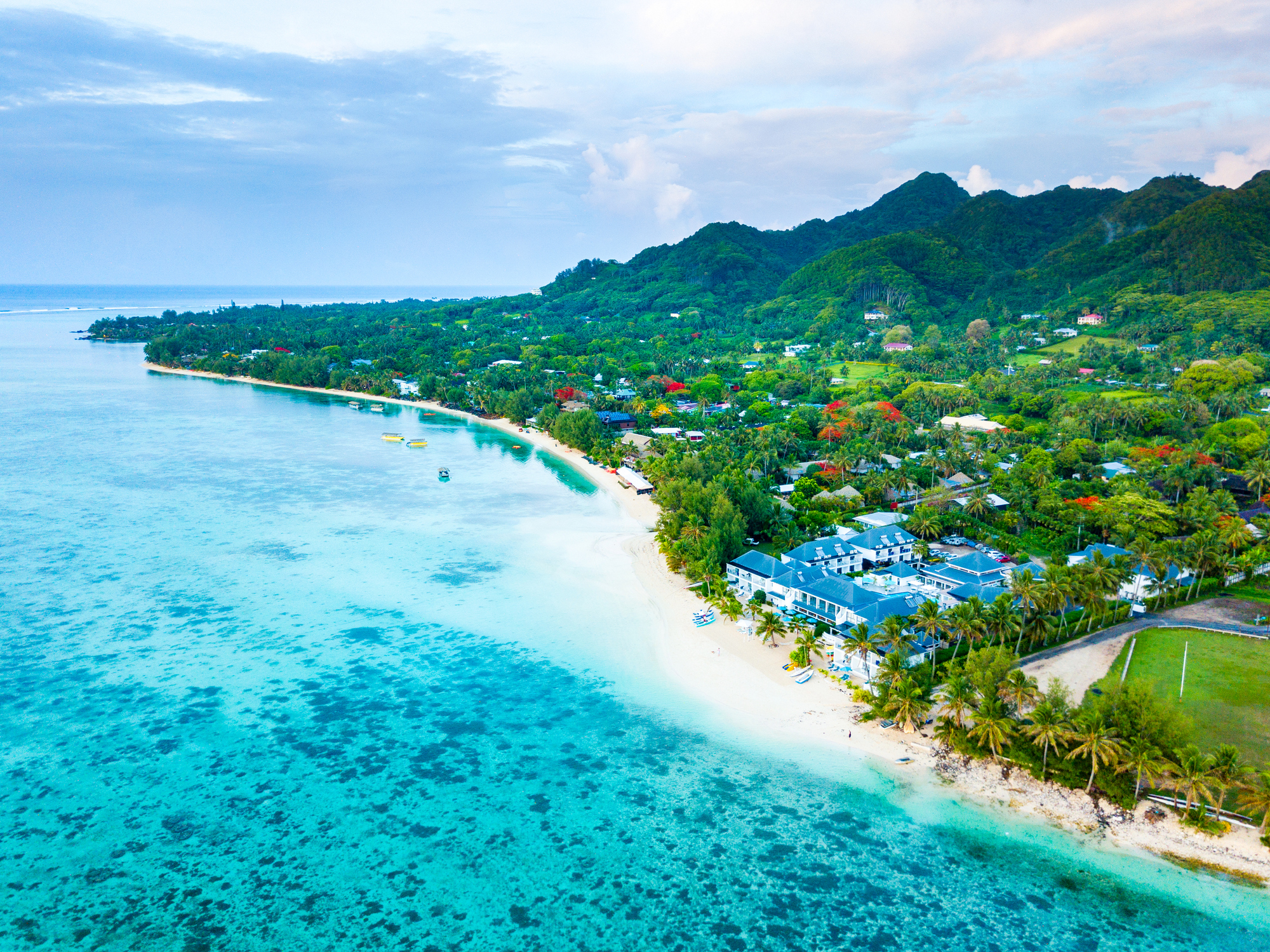




Rarotonga is the most populous island of the Cook Islands, with a population of 10,572 (census 2011), out of the country's total resident population of 14,974. Captain John Dibbs, master of the colonial brig Endeavour, is credited as the European discoverer on 25 July 1823, while transporting the missionary Rev. John Williams.
The Cook Islands' Parliament buildings and international airport are on Rarotonga. Rarotonga is a very popular tourist destination with many resorts, hotels and motels. The chief town, Avarua, on the north coast, is the capital of the Cook Islands.
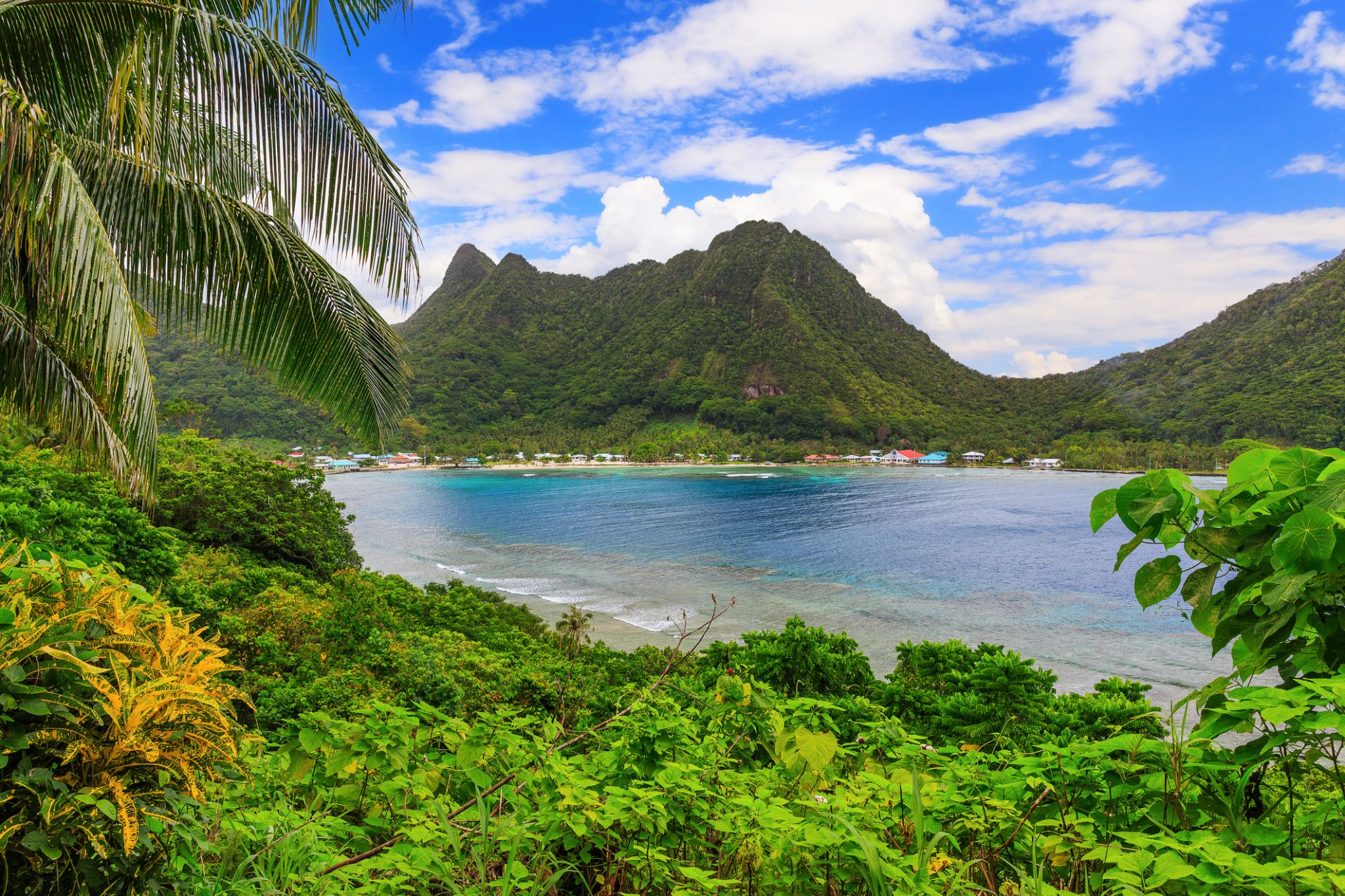



Pago Pago is the territorial capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County on the main island of American Samoa, Tutuila. It is home to one of the best and deepest natural deepwater harbors in the South Pacific Ocean, sheltered from wind and rough seas, and strategically located. The harbor is also one of the best protected in the South Pacific, which gives American Samoa a natural advantage with respect to landing fish for processing. Tourism, entertainment, food, and tunacanning are its main industries. Pago Pago was the world's 4th largest tuna processor as of 1993. It was home to two of the largest tuna companies in the world: Chicken of the Sea and StarKist, which exported an estimated $445 million in canned tuna to the U.S. mainland.
Pago Pago is the only modern urban center in American Samoa. The Greater Pago Pago Metropolitan Area encompasses several villages strung together along Pago Pago Harbor. One of the villages is itself named Pago Pago, and in 2010 had a population of 3,656. The constituent villages are, in order, Utulei, Fagatogo, Malaloa, Pago Pago, Satala and Atu'u. Fagatogo is the downtown area referred to as Town and is home to the legislature, while the executive is located in Utulei. In Fagatogo is the Fono, Police Department, Port of Pago Pago, many shops and hotels. The Greater Pago Pago Area was home to 8,000 residents in 2000.
Rainmaker Mountain (Mount Pioa) is located in Pago Pago, and gives the city the highest annual rainfall of any harbor in the world.
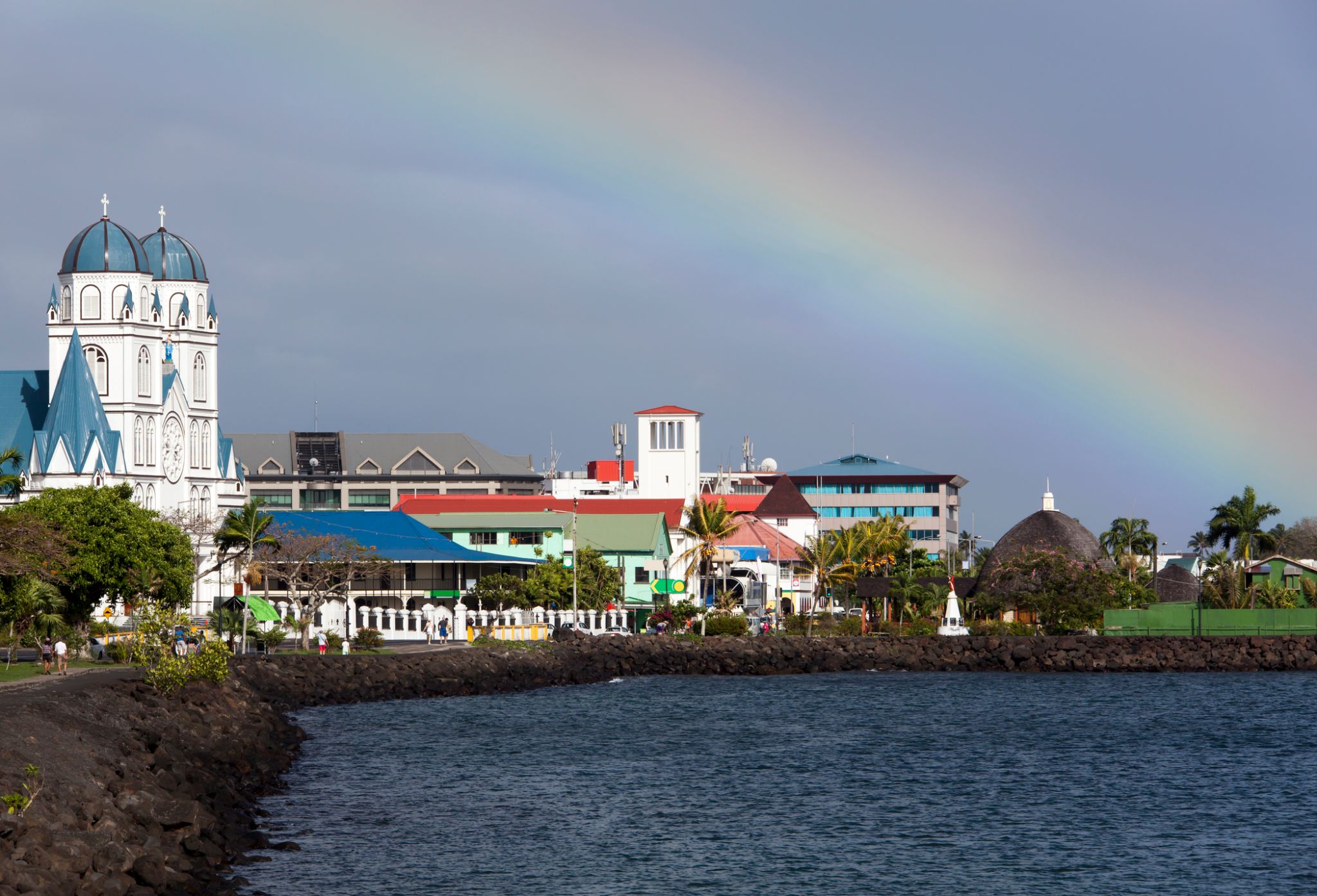


Apia is the capital and the largest city of Samoa. From 1900 to 1919, it was the capital of German Samoa. The city is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second largest island. Apia is the only city in Samoa and falls within the political district (itūmālō) of Tuamasaga.
The Apia Urban Area has a population of 36,735 (2011 census) and is generally referred to as the City of Apia. The geographic boundaries of Apia Urban Area is mainly from Letogo village to the new industrialized region of Apia known as Vaitele.
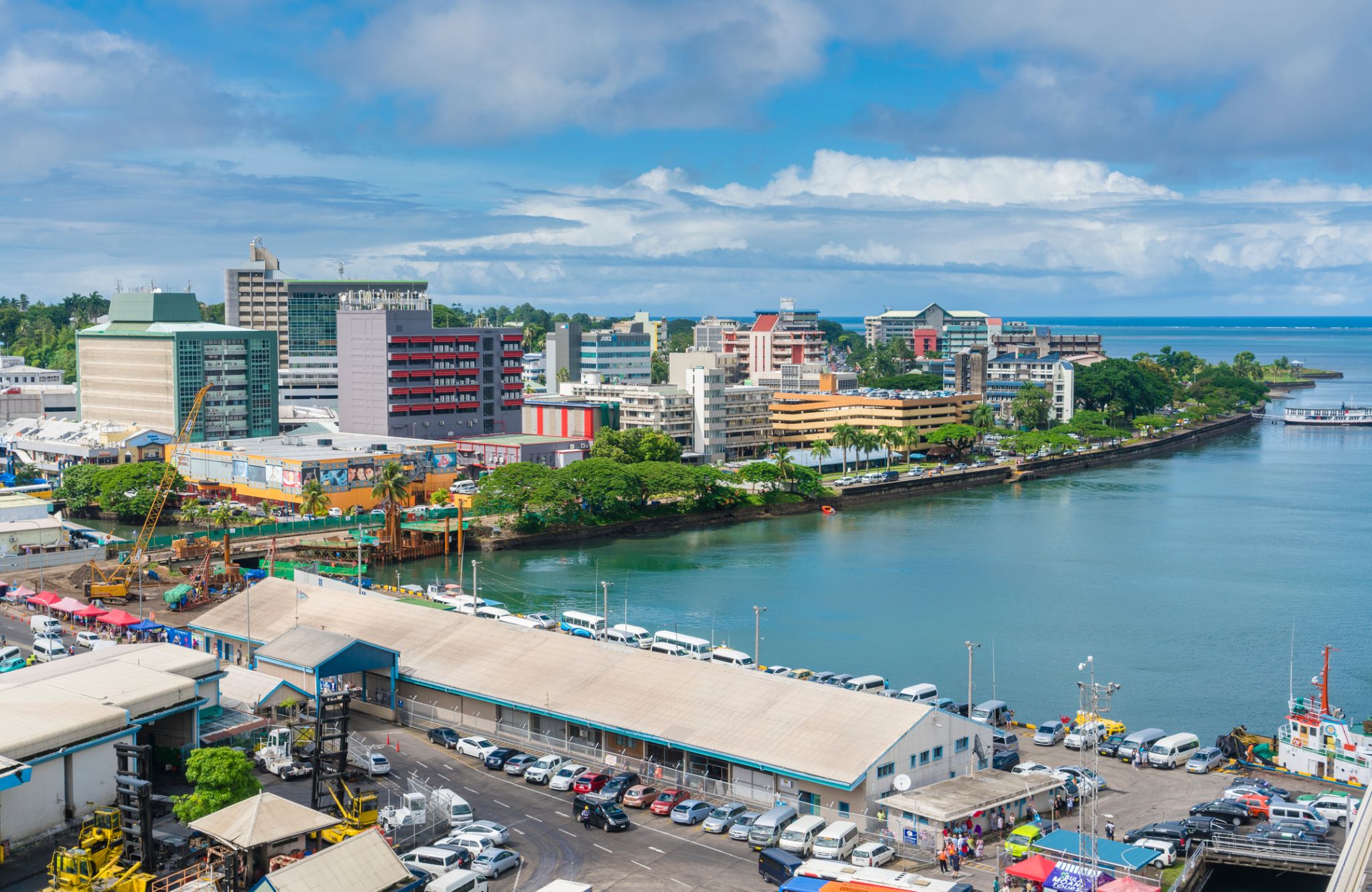


Suva is the capital and largest metropolitan city in Fiji. It is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in the Rewa Province, Central Division.
In 1877, it was decided to make Suva the capital of Fiji, as the geography of former main European settlement at Levuka on the island of Ovalau, Lomaiviti province proved too restrictive. The administration of the colony was moved from Levuka to Suva in 1882.
At the 2007 census, the city of Suva had a population of 85,691. Including independent suburbs, the population of the Greater Suva urban area was 172,399 at the 2007 census. Suva, along with the bordering towns of Lami, Nasinu, and Nausori have a total urban population of around 330,000, over a third of the nation's population. This urban complex (not including Lami) is known also as the Suva-Nausori corridor.
Suva is the political, economic, and cultural centre of Fiji. It is also the economic and cultural capital of the Pacific, hosting the majority of regional headquarters of major corporations, as well as international agencies and diplomatic missions in the region. The city also has a thriving arts and performance scene, with a growing reputation as the region’s fashion capital.
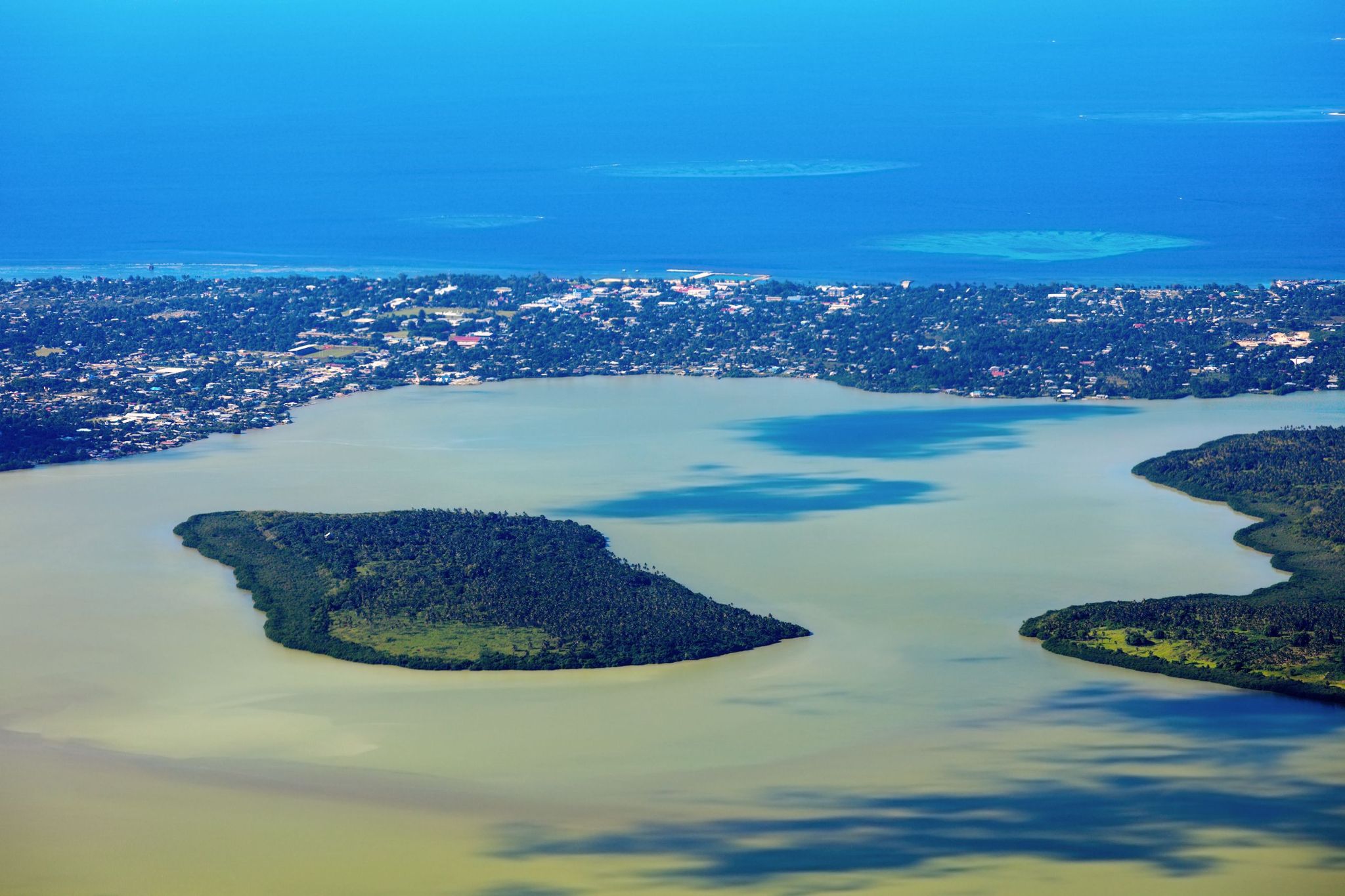


Nukuʻalofa is the cozy capital of Tonga, located on the northern coast of Tongatapu Island. The city serves as the political, cultural, and economic center of the country, while preserving the charm of tropical tranquility. One of its iconic landmarks is the Royal Palace, built in 1867, where the monarch of Tonga still resides today. Strolling through Nukuʻalofa, tourists can enjoy colorful markets where locals sell fresh tropical fruits, handmade crafts, and jewelry made from seashells.
In addition to its historical heritage, Nukuʻalofa attracts visitors with its proximity to natural wonders. Just a few kilometers from the center, one can find the dramatic Haʻatafu coastal cliffs, popular among surfing enthusiasts, as well as ancient megalithic structures such as the three-meter-high Haʻamonga ʻa Maui arch, often called the "Polynesian Stonehenge." Nukuʻalofa is the perfect destination for those seeking a blend of authentic culture, relaxed atmosphere, and stunning natural landscapes.
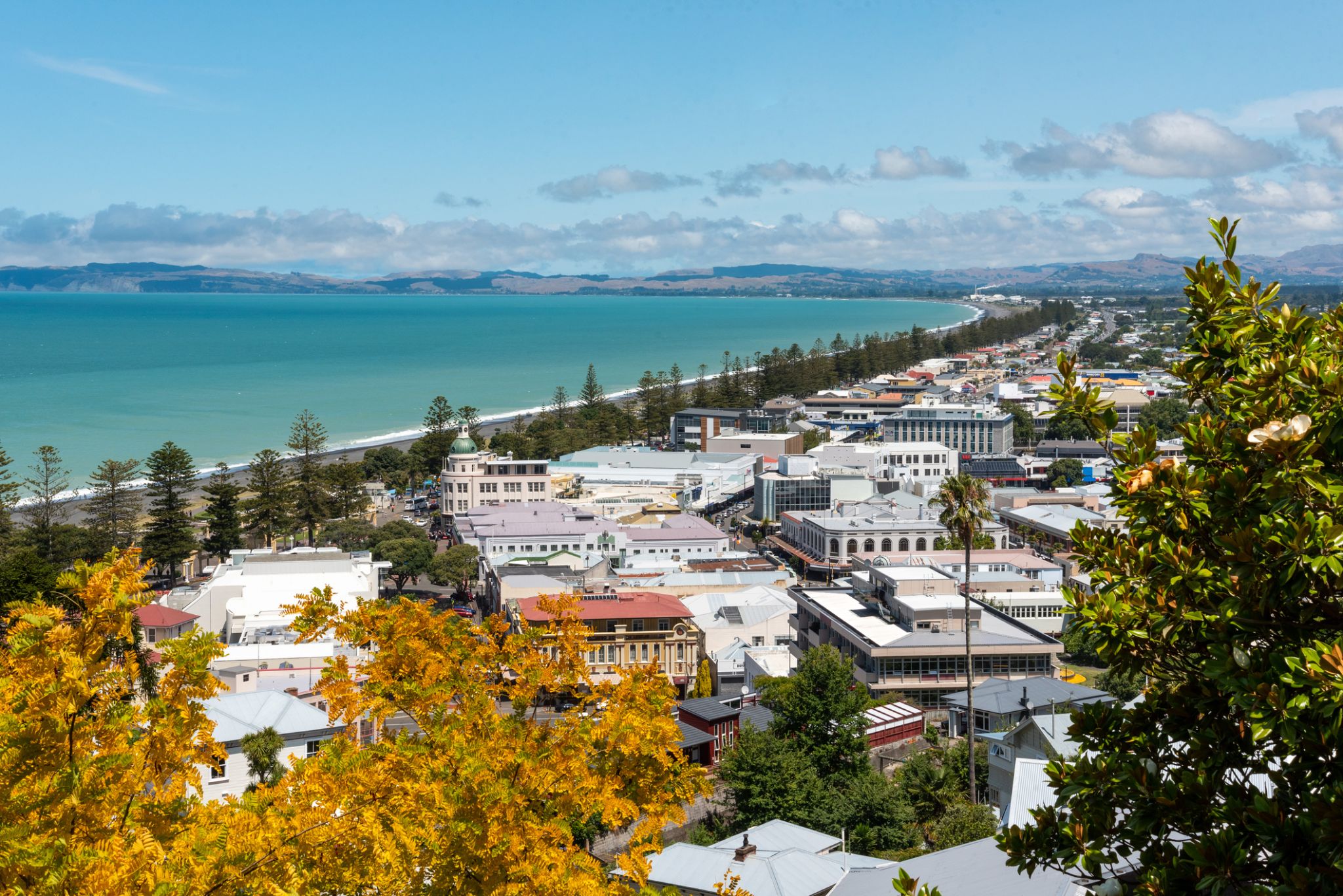







Napier is a New Zealand city with a seaport, located in Hawke's Bay on the eastern coast of the North Island. The population of Napier is about 63,900 as of the June 2018. About 18 kilometres (11 mi) south of Napier is the inland city of Hastings. These two neighbouring cities are often called "The Bay Cities" or "The Twin Cities" of New Zealand. The total population of the Napier-Hastings Urban Area is 134,500 people, which makes it the sixth-largest urban area in New Zealand, closely followed by Dunedin (122,000), and trailing Tauranga(141,600).
Napier is about 320 kilometres (200 mi) northeast of the capital city of Wellington. Napier (63,900) has a smaller population than its neighbouring city of Hastings (70,600) but is seen as the main centre due to it being closer in distance to both the seaport and the main airport that service Hawke's Bay, and Hastings' population figure includes 13,000 people living in Havelock North, which is often considered a town in its own right. The City of Napier has a land area of 106 square kilometres (41 sq mi) and a population density of 540.0 per square kilometre.
Napier is the nexus of the largest wool centre in the Southern Hemisphere, and it has the primary export seaport for northeastern New Zealand – which is the largest producer of apples, pears, and stone fruit in New Zealand. Napier has also become an important grape and wine production area, with the grapes grown around Hastings and Napier being sent through the Port of Napier for export. Large amounts of sheep's wool, frozen meat, wood pulp, and timber also pass through Napier annually for export. Smaller amounts of these materials are shipped via road and railway to the large metropolitan areas of New Zealand itself, such as Auckland, Wellington and Hamilton.
Napier is a popular tourist city, with a unique concentration of 1930s Art Deco architecture, built after much of the city was razed in the 1931 Hawke's Bay earthquake. It also has one of the most photographed tourist attractions in the country, a statue on Marine Parade called Pania of the Reef. Thousands of people flock to Napier every February for the Tremains Art Deco Weekend event, a celebration of its Art Deco heritage and history. Other notable tourist events attracting many outsiders to the region annually include F.A.W.C! Food and Wine Classic events, and the Mission Estate Concert at Mission Estate and Winery in the suburb of Taradale.
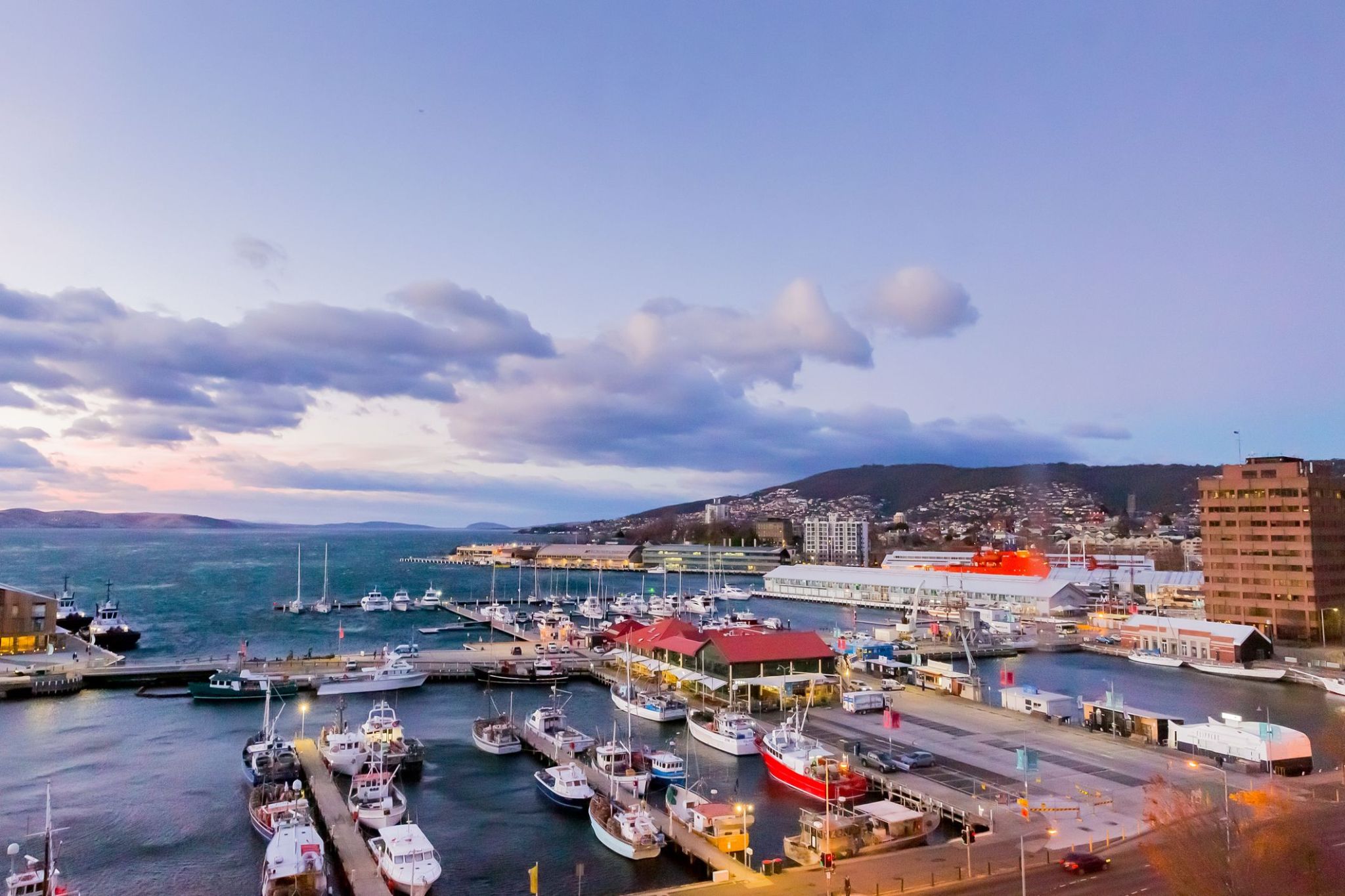







Where mountains and wild forests meet the Pacific Ocean, Hobart on the island of Tasmania invites you to explore a city where colonial architecture blends with contemporary art and cuisine. At the foot of Mount Wellington, you will find views over the bay where yachts sway on the waves and the fresh breeze carries the scent of the ocean. At Hobart markets, you can try the freshest seafood and the famous Tasmanian oysters, while the city streets are filled with cozy cafes and galleries showcasing local artists.
Those who love active recreation can hike the trails of Mount Wellington with views over the Derwent Bay and take marine tours to seal and seabird colonies. In Hobart, you can feel the rhythm of Tasmania: local festivals, nearby wineries, and proximity to untouched nature make it an ideal starting point to discover this unique island, where each day brings new impressions.
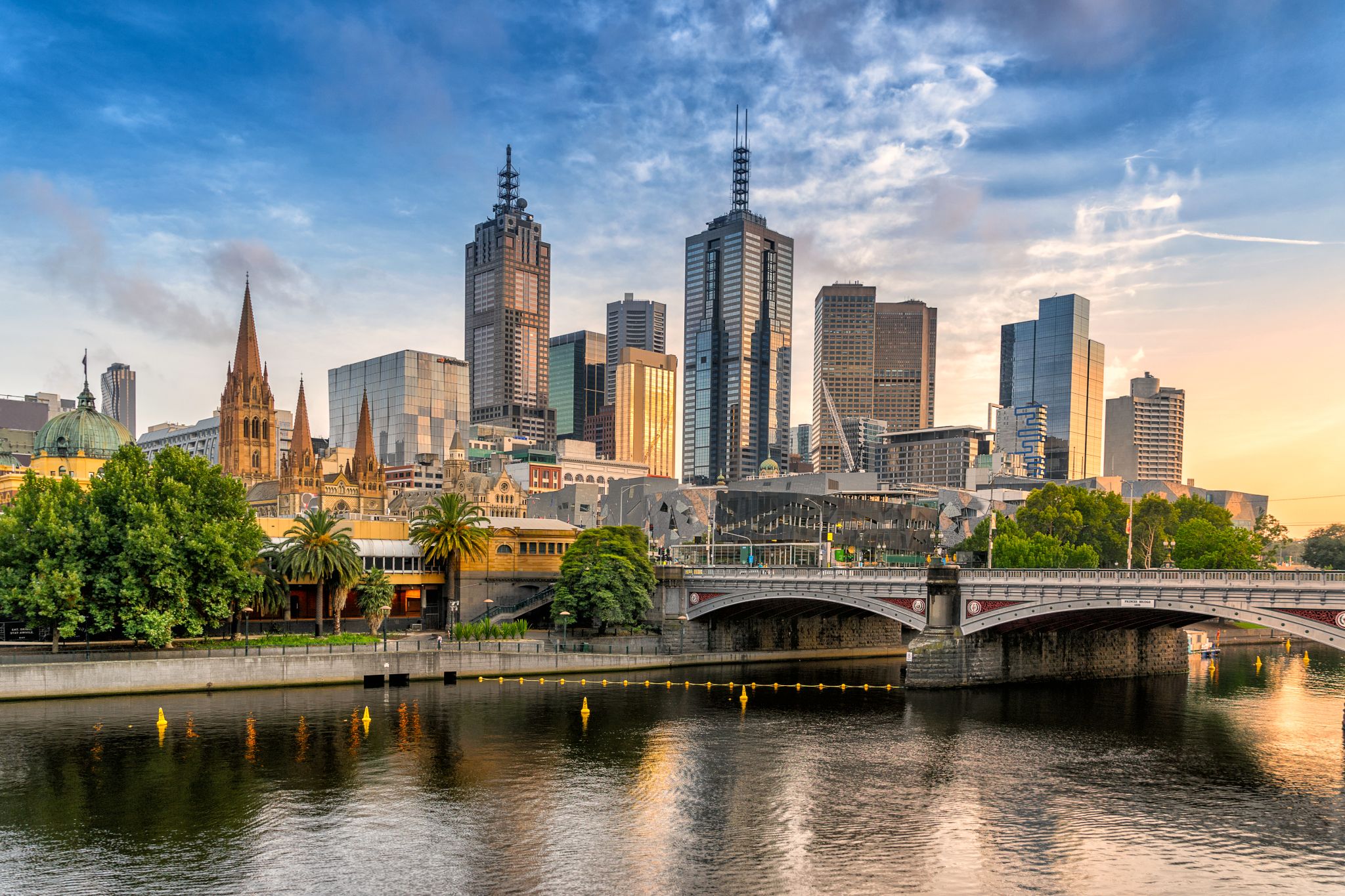


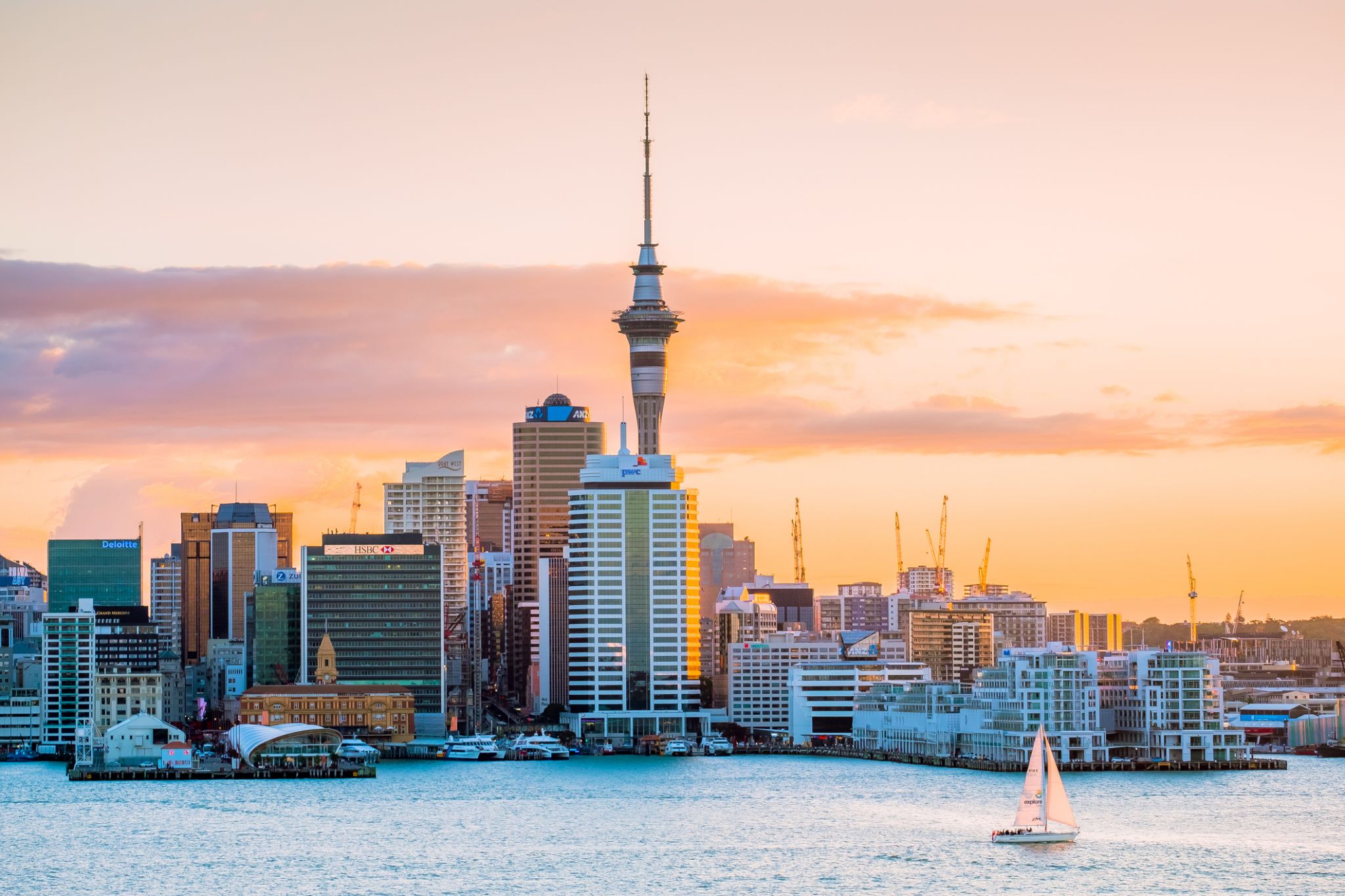
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia and Oceania. Its name refers to an urban agglomeration of 9,992.5 km2 (3,858.1 sq mi), comprising a metropolitan area with 31 municipalities, and is also the common name for its city centre. The city occupies much of the coastline of Port Phillip bay and spreads into the hinterlands towards the Dandenong and Macedon ranges, Mornington Peninsula and Yarra Valley. It has a population of approximately 4.9 million (19% of the population of Australia), and its inhabitants are referred to as "Melburnians".
The city was founded on 30 August 1835, in what was the British colony of New South Wales, by free settlers from the colony of Van Diemen’s Land. It was incorporated as a Crown settlement in 1837 and named in honour of the British Prime Minister, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne. It was declared a city by Queen Victoria in 1847, after which it became the capital of the new colony of Victoria in 1851. In the wake of the 1850s Victorian gold rush, the city entered the "Marvellous Melbourne" boom period, transforming into one of the most important cities in the British Empire and one of the largest and wealthiest in the world. After the federation of Australia in 1901, it served as interim seat of government of the new nation until Canberra became the permanent capital in 1927. Today, it is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region and ranks 20th in the Global Financial Centres Index.

Melbourne is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia and Oceania. Its name refers to an urban agglomeration of 9,992.5 km2 (3,858.1 sq mi), comprising a metropolitan area with 31 municipalities, and is also the common name for its city centre. The city occupies much of the coastline of Port Phillip bay and spreads into the hinterlands towards the Dandenong and Macedon ranges, Mornington Peninsula and Yarra Valley. It has a population of approximately 4.9 million (19% of the population of Australia), and its inhabitants are referred to as "Melburnians".
The city was founded on 30 August 1835, in what was the British colony of New South Wales, by free settlers from the colony of Van Diemen’s Land. It was incorporated as a Crown settlement in 1837 and named in honour of the British Prime Minister, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne. It was declared a city by Queen Victoria in 1847, after which it became the capital of the new colony of Victoria in 1851. In the wake of the 1850s Victorian gold rush, the city entered the "Marvellous Melbourne" boom period, transforming into one of the most important cities in the British Empire and one of the largest and wealthiest in the world. After the federation of Australia in 1901, it served as interim seat of government of the new nation until Canberra became the permanent capital in 1927. Today, it is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region and ranks 20th in the Global Financial Centres Index.
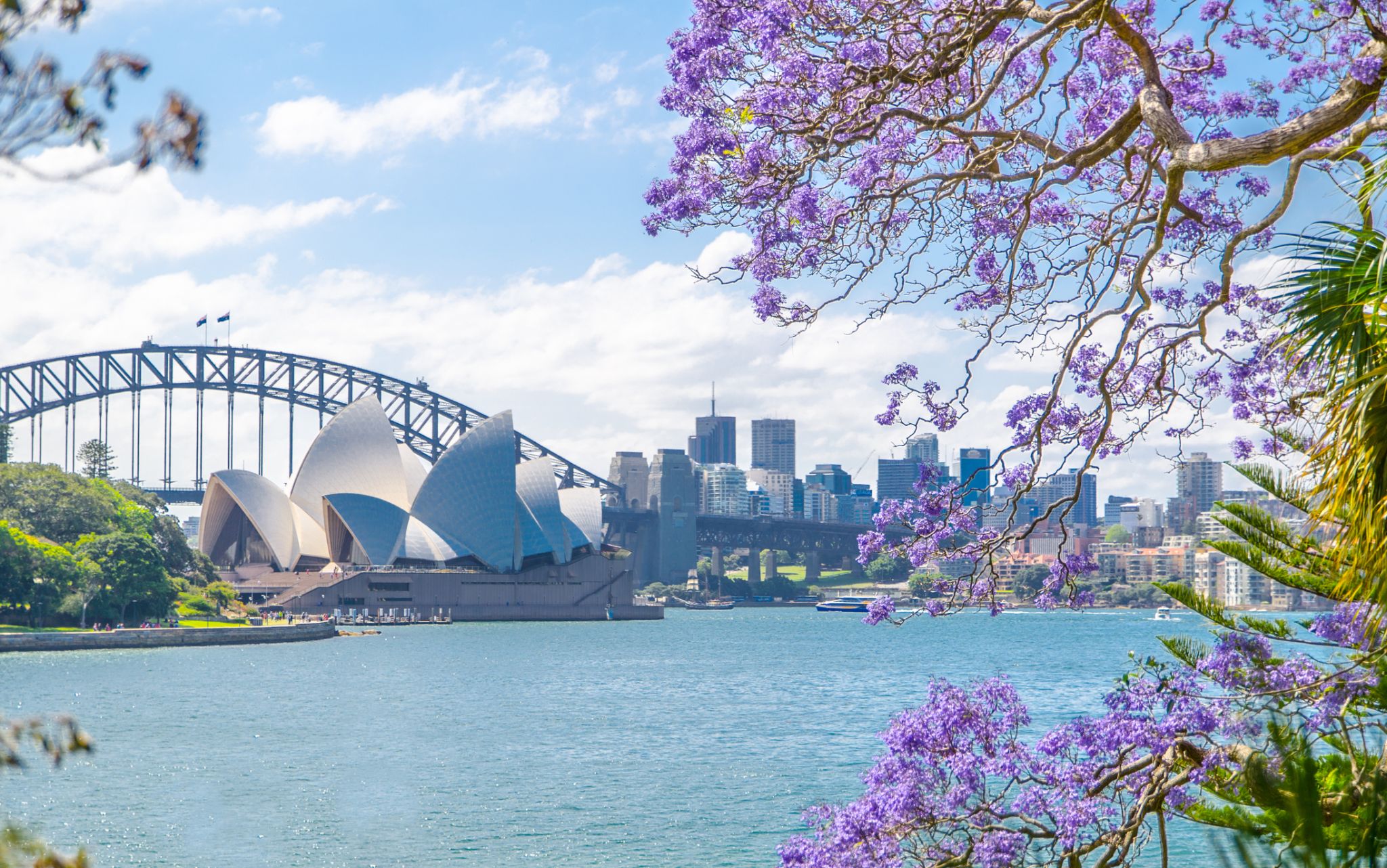


Sydney is the state capital of New South Wales and the most populous city in Australiaand Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Port Jackson and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) on its periphery towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, and Macarthur to the south. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, 40 local government areas and 15 contiguous regions. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". As of June 2017, Sydney's estimated metropolitan population was 5,131,326, and is home to approximately 65% of the state's population.