
| Cruise Region : Northern Europe, Europe |
| Company : Azamara Cruises |
| Ship : Azamara Quest |
| Journey Start : Thu 29 Jul 2027 |
| Journey End : Fri 10 Sep 2027 |
| Count Nights : 43 nights |
| Day | Date | Port | Arrival | Departure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29.07 Thu | Copenhagen / Denmark | 17:00 | |
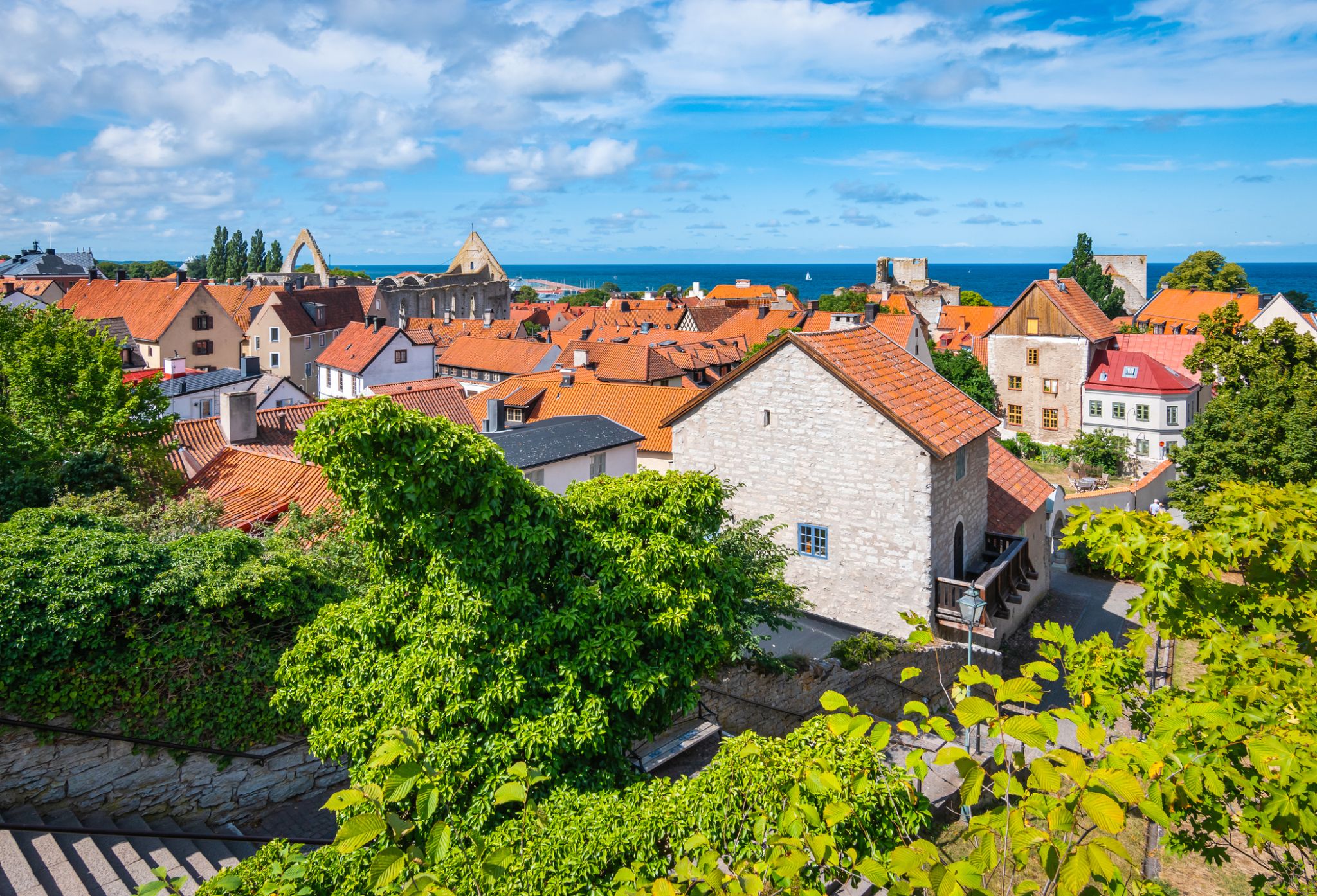
| 2 | 30.07 Fri | Visby / Sweden | 13:30 | 19:00 |
| 3 | 31.07 Sat | Stockholm / Sweden | 08:00 | |
| 4 | 1.08 Sun | Stockholm / Sweden | 16:00 | |
| 5 | 2.08 Mon | Turku / Finland | 08:00 | 20:00 |
| 6 | 3.08 Tue | Helsinki / Finland | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 7 | 4.08 Wed | Tallinn / Estonia | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 8 | 5.08 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 9 | 6.08 Fri | Riga / Latvia | 07:00 | 18:00 |
| 10 | 7.08 Sat | Klaipeda (Memel) / Lithuania | 13:00 | 22:00 |
| 11 | 8.08 Sun | Gdańsk / Poland | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 12 | 9.08 Mon | Ronne / Denmark | 13:00 | 20:00 |
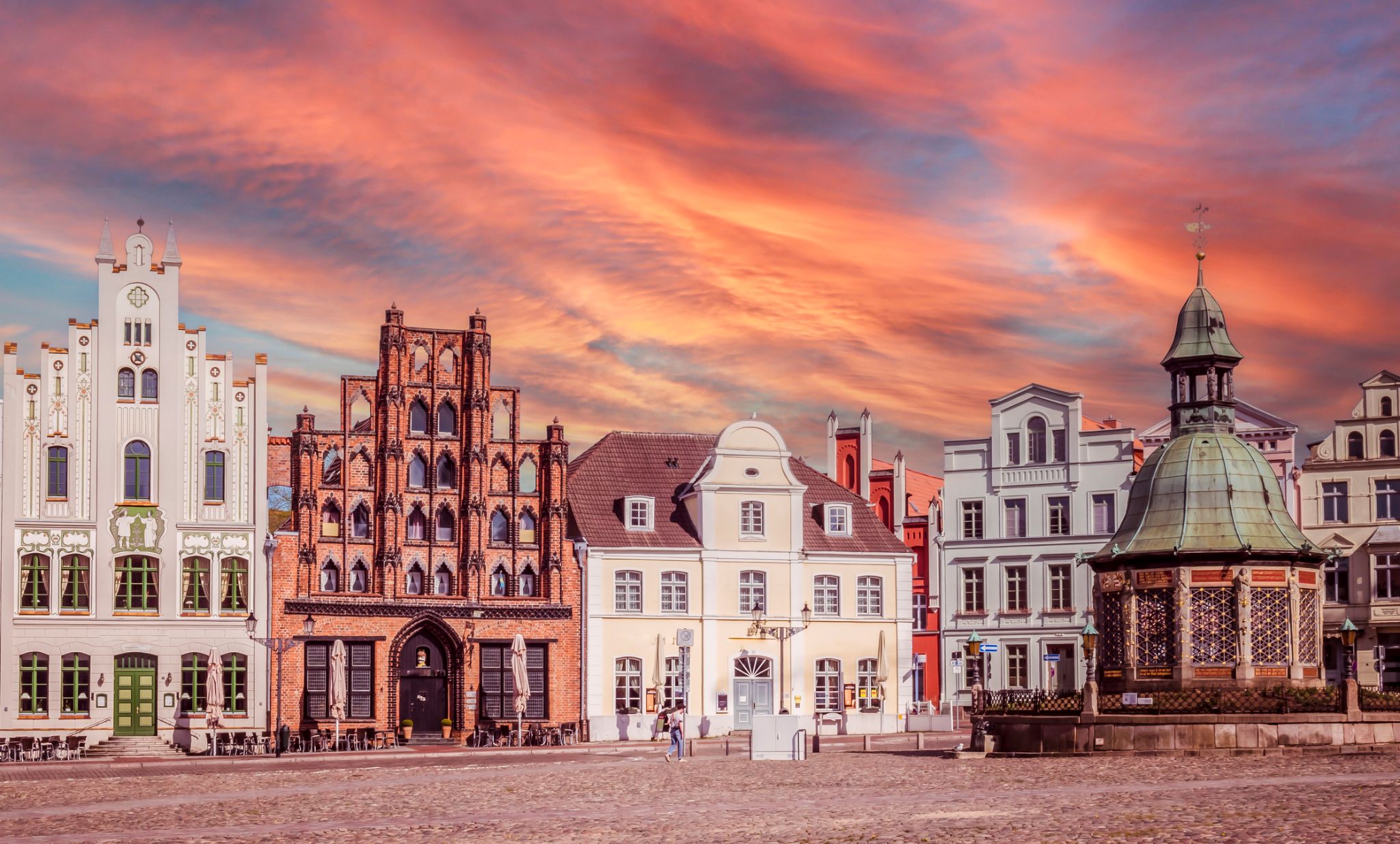
| 13 | 10.08 Tue | Wismar / Germany | 08:00 | 22:00 |
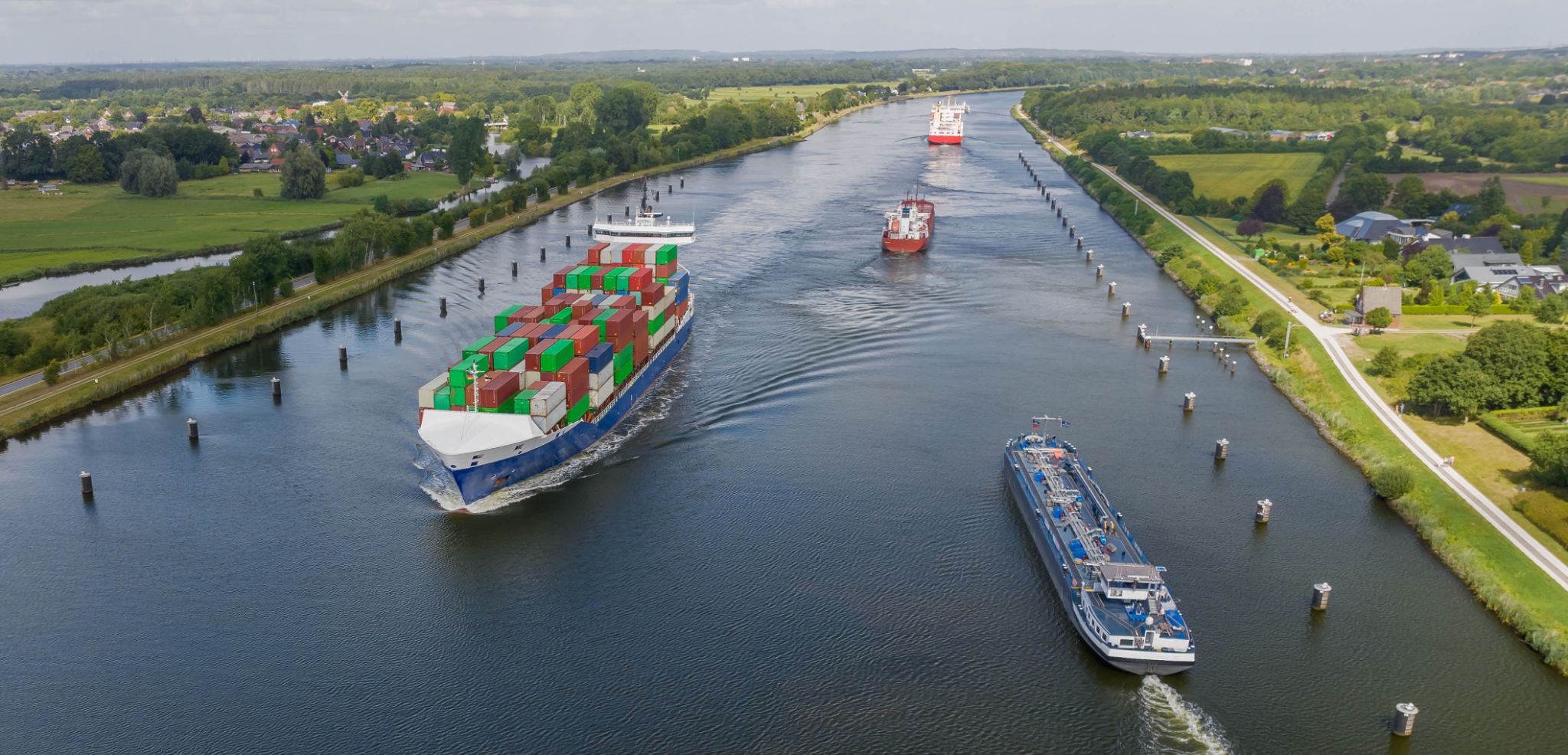
| 14 | 11.08 Wed | Kiel Canal / Germany | 06:00 | 17:00 |
| 15 | 12.08 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 16 | 13.08 Fri | Portsmouth / Dominica | 06:00 | 17:00 |
| 17 | 14.08 Sat | Falmouth / Jamaica | 07:00 | 15:00 |
| 18 | 15.08 Sun | Dublin / Ireland | 09:30 | 22:00 |
| 19 | 16.08 Mon | Belfast / Great Britain | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 20 | 17.08 Tue | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 21 | 18.08 Wed | Torshavn / Faroe Islands | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 22 | 19.08 Thu | Runavík Runavík / Faroe Islands | 07:30 | 13:30 |
| 23 | 20.08 Fri | Eskifjordur / Iceland | 09:00 | 20:00 |
| 24 | 21.08 Sat | Husavik / Iceland | 13:00 | 20:00 |
| 25 | 22.08 Sun | Akureyri / Iceland | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 26 | 23.08 Mon | Isafjordur / Iceland | 11:00 | 18:00 |
| 27 | 24.08 Tue | Reykjanesbaer | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 28 | 25.08 Wed | Reykjavik / Iceland | 06:00 | 17:00 |
| 29 | 26.08 Thu | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 30 | 27.08 Fri | Prince Christian Sound / Greenland | 13:00 | 18:00 |
| 31 | 28.08 Sat | Nanortalik / Greenland | 08:00 | 20:00 |
| 32 | 29.08 Sun | Kakortok / Greenland | 07:30 | 13:00 |
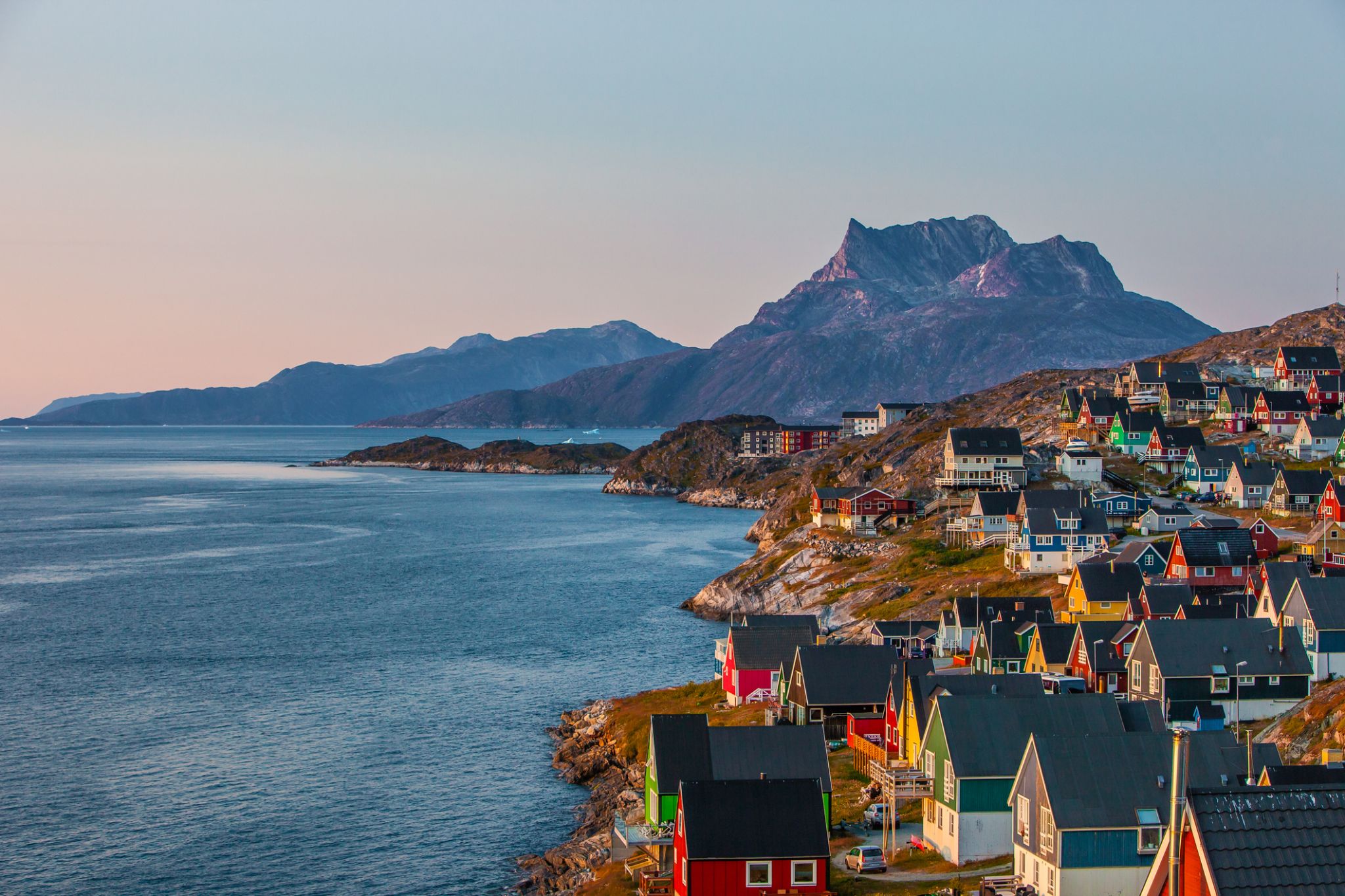
| 33 | 30.08 Mon | Nuuk / Greenland | 10:00 | 18:00 |
| 34 | 31.08 Tue | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 35 | 1.09 Wed | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 36 | 2.09 Thu | St. John`s | 13:00 | |
| 37 | 3.09 Fri | St. John`s | 17:00 | |
| 38 | 4.09 Sat | Day at sea / Sea | ||
| 39 | 5.09 Sun | Halifax / Canada | 08:00 | 22:00 |
| 40 | 6.09 Mon | Lunenburg Nova Scotia / Canada | 07:30 | 13:30 |
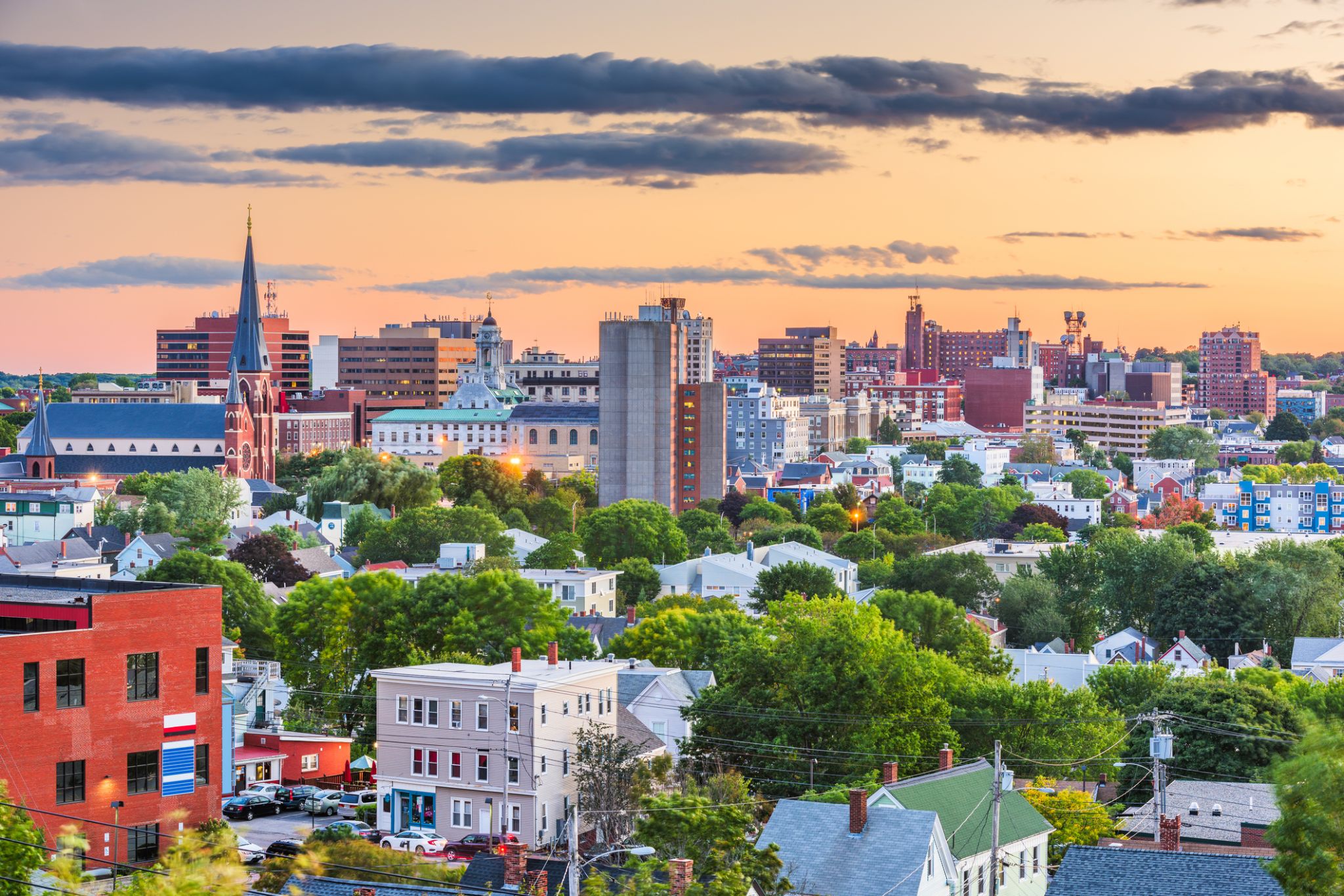
| 41 | 7.09 Tue | Portland / USA | 09:30 | 22:00 |
| 42 | 8.09 Wed | Boston / USA | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 43 | 9.09 Thu | CAPE COD CANAL | 22:30 | |
| 44 | 10.09 Fri | Newport / USA | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 45 | 11.09 Sat | New York / USA | 06:00 |
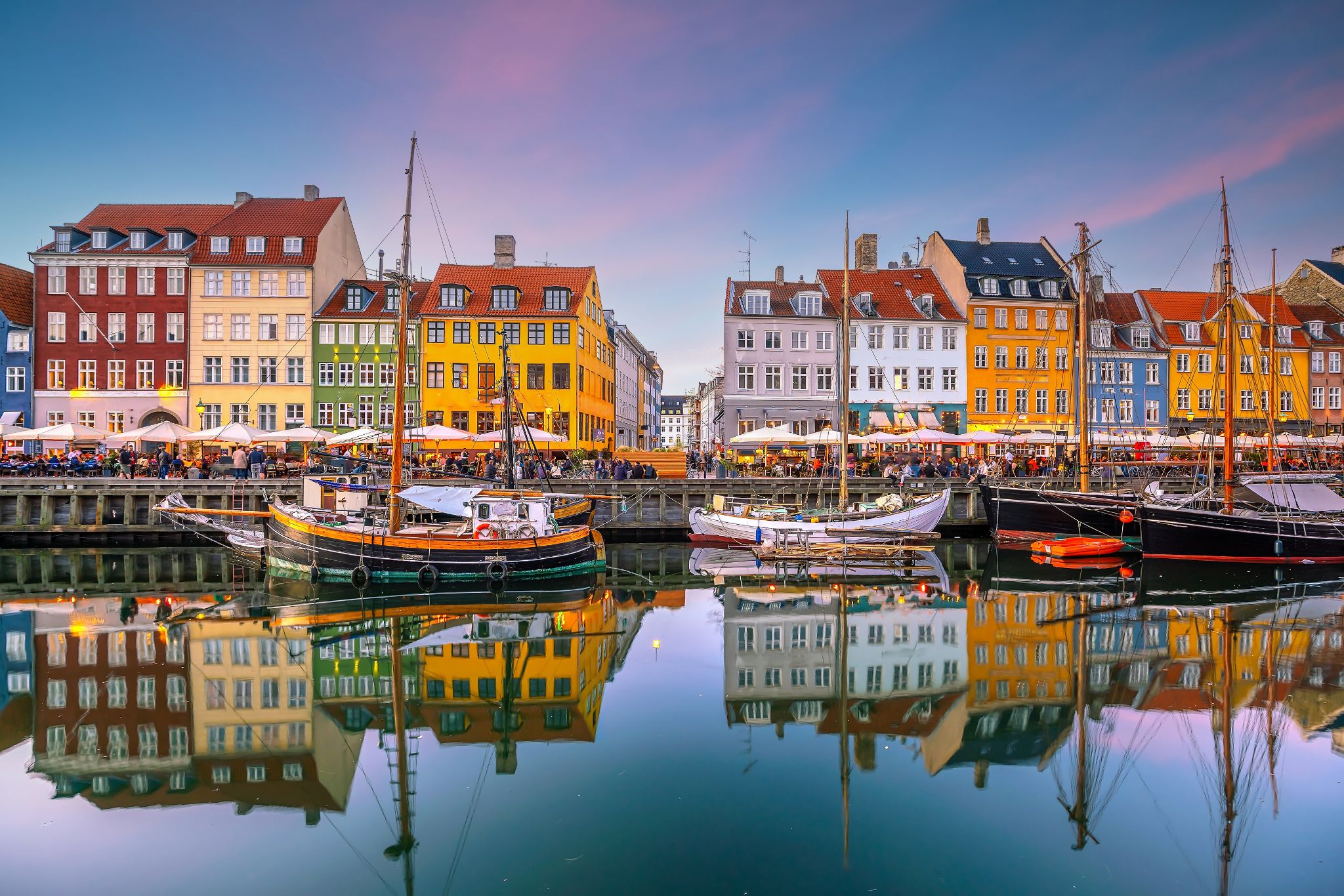

the capital and chief port of Denmark, a city that occupies the eastern part of Zealand and northern part of the island of Amager; population 518,574 (2009).
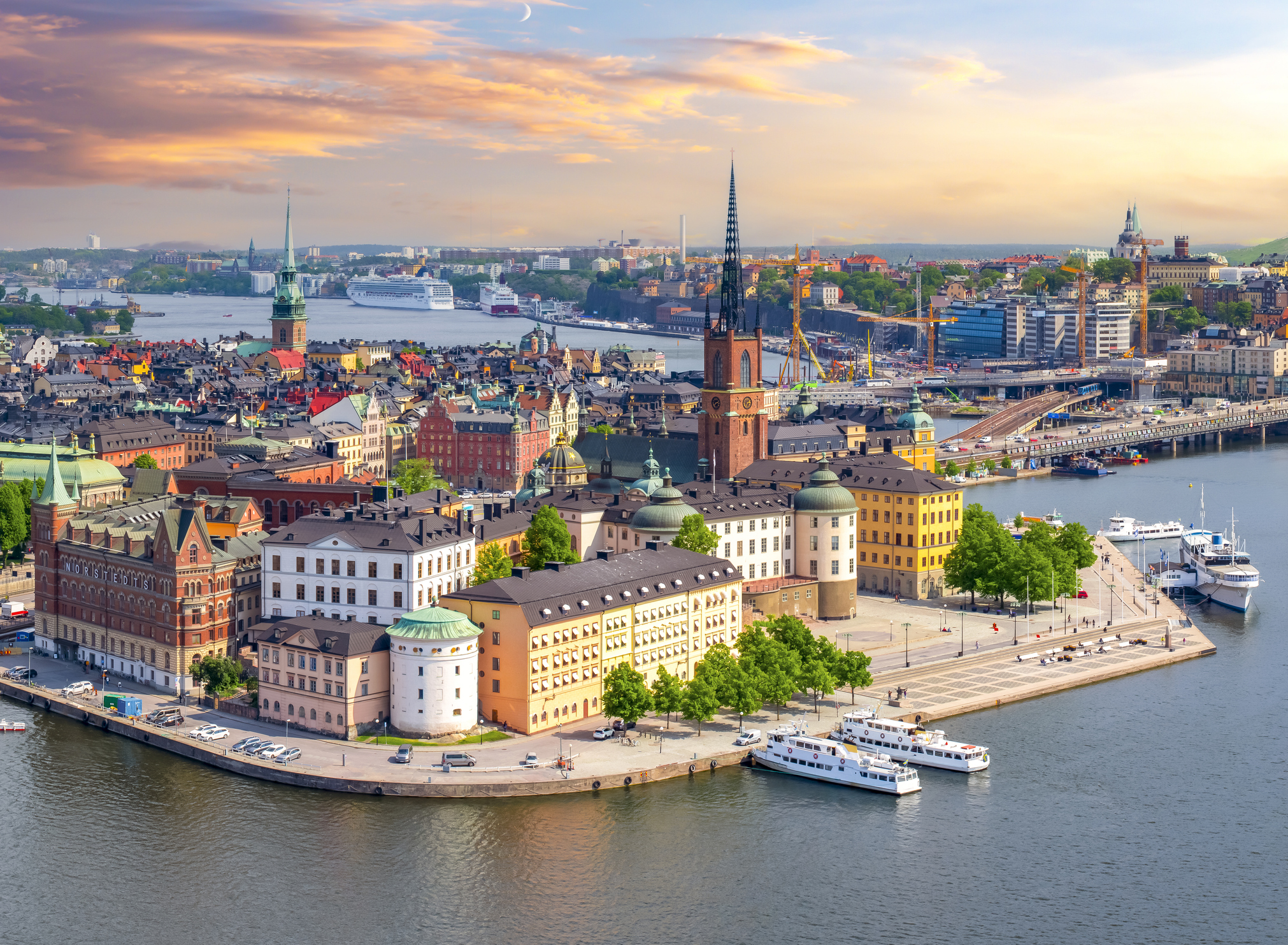


Stockholm is the capital of Sweden and the most populous urban area in the Nordic countries; 960,031 people live in the municipality, approximately 1.5 million in the urban area, and 2.3 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Just outside the city and along the coast is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the capital of Stockholm County.
Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP, and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. It is an important global city, and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region. The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia. The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for the decor of its stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world. Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solna. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics, and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympicsotherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Stockholm is the seat of the Swedish government and most of its agencies, including the highest courts in the judiciary, and the official residencies of the Swedish monarch and the Prime Minister. The government has its seat in the Rosenbad building, the Riksdag (Swedish parliament) is seated in the Parliament House, and the Prime Minister's residence is adjacent at Sager House. Stockholm Palace is the official residence and principal workplace of the Swedish monarch, while Drottningholm Palace, a World Heritage Site on the outskirts of Stockholm, serves as the Royal Family's private residence.

Stockholm is the capital of Sweden and the most populous urban area in the Nordic countries; 960,031 people live in the municipality, approximately 1.5 million in the urban area, and 2.3 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Just outside the city and along the coast is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the capital of Stockholm County.
Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP, and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. It is an important global city, and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region. The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia. The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for the decor of its stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world. Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solna. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics, and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympicsotherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Stockholm is the seat of the Swedish government and most of its agencies, including the highest courts in the judiciary, and the official residencies of the Swedish monarch and the Prime Minister. The government has its seat in the Rosenbad building, the Riksdag (Swedish parliament) is seated in the Parliament House, and the Prime Minister's residence is adjacent at Sager House. Stockholm Palace is the official residence and principal workplace of the Swedish monarch, while Drottningholm Palace, a World Heritage Site on the outskirts of Stockholm, serves as the Royal Family's private residence.
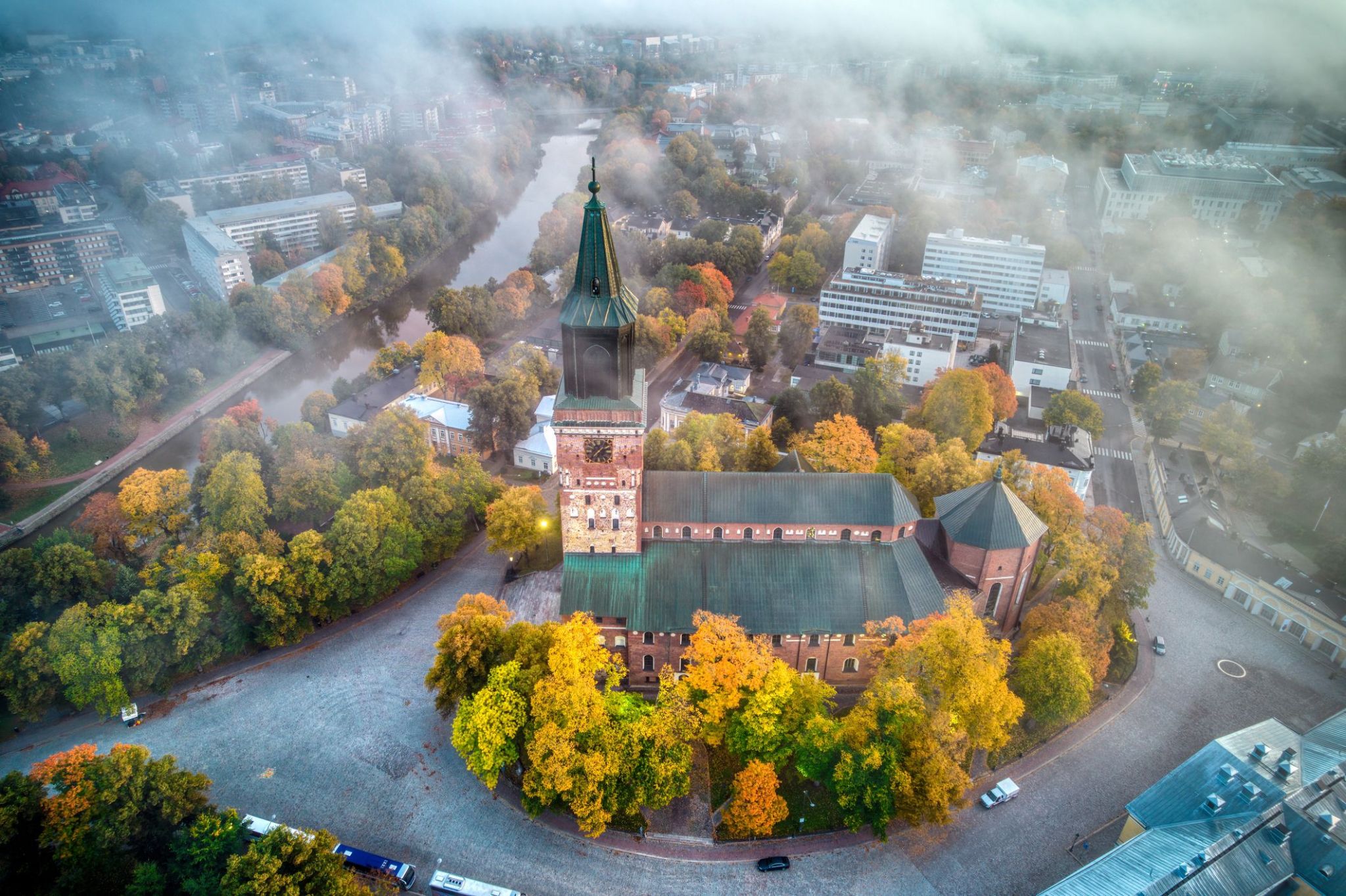

A cozy northern rhythm can be felt in every corner of Turku, the oldest city in Finland, founded in the 13th century. Here, the past meets the present: cobbled streets, the Turku Cathedral, the medieval castle, and inviting cafes along the riverside create an atmosphere where you want to linger and slowly explore each turn of the Aura River.
In summer, Turku comes alive with festivals, music evenings, and boat trips, letting you feel the charm of Finnish coastal life. In winter, the city glows with soft lights, Christmas markets, and warmth, where travelers can enjoy traditional saunas and Finnish cuisine, discovering Finland from its warmest side.
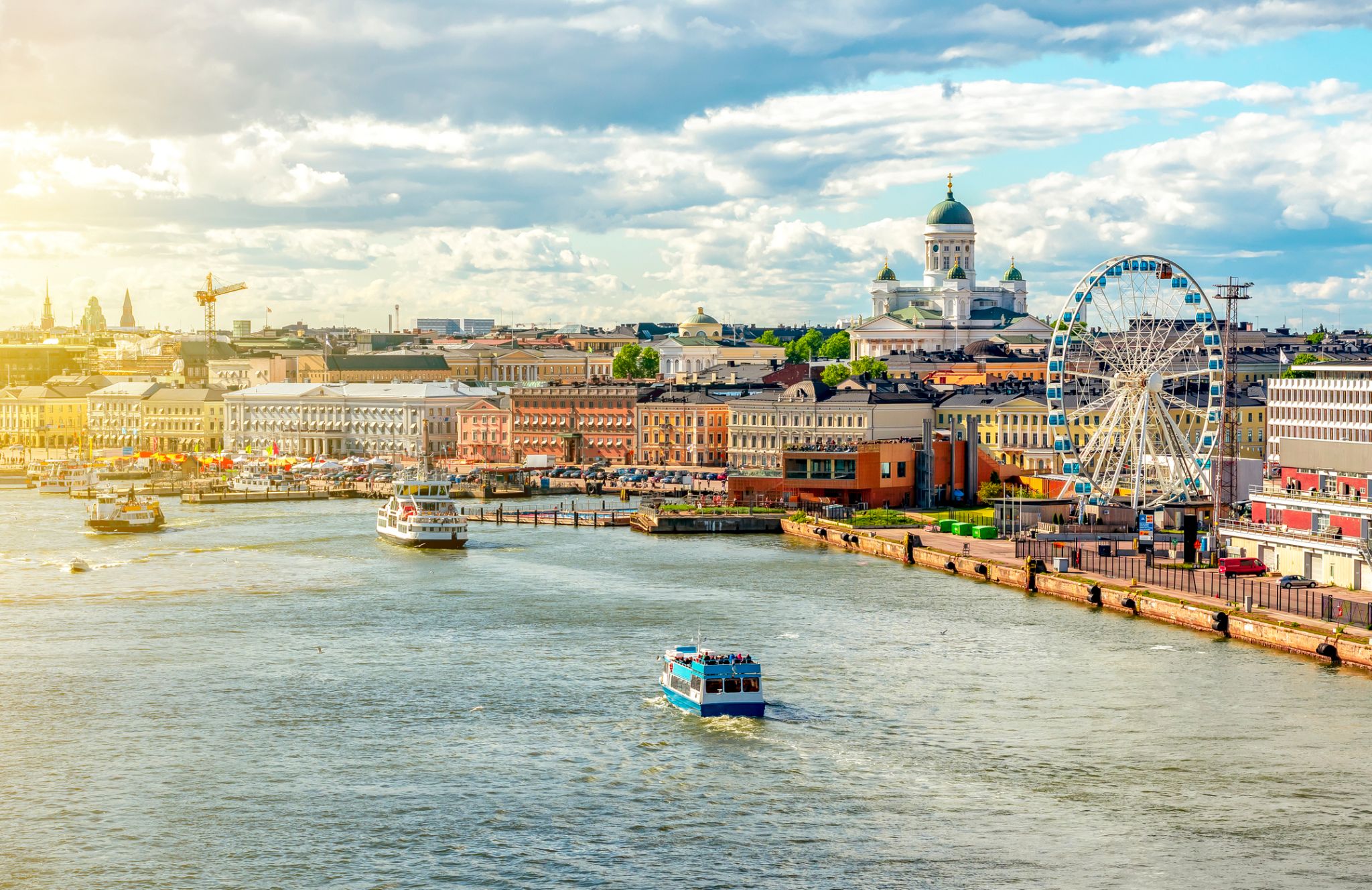

Helsinki located in the southern Finland, and has a population of 648,650. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, it’s the most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research. Helsinki is located 80 kilometers (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 390 km (240 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close ties with these three cities.
Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen, and the surrounding commuter towns, Helsinki forms the Greater Helsinki metropolitan area, which has a population of nearly 1.5 million. Often being considered a metropolis of the EU member state. After Stockholm and Oslo, Helsinki is the third largest city in the Nordic countries. It is located in the city of Vantaa and is located in the city of Vantaa.
Helsinki was the World Design Capital for 2012, the 1952 Summer Olympics and the 52nd Eurovision Song Contest.
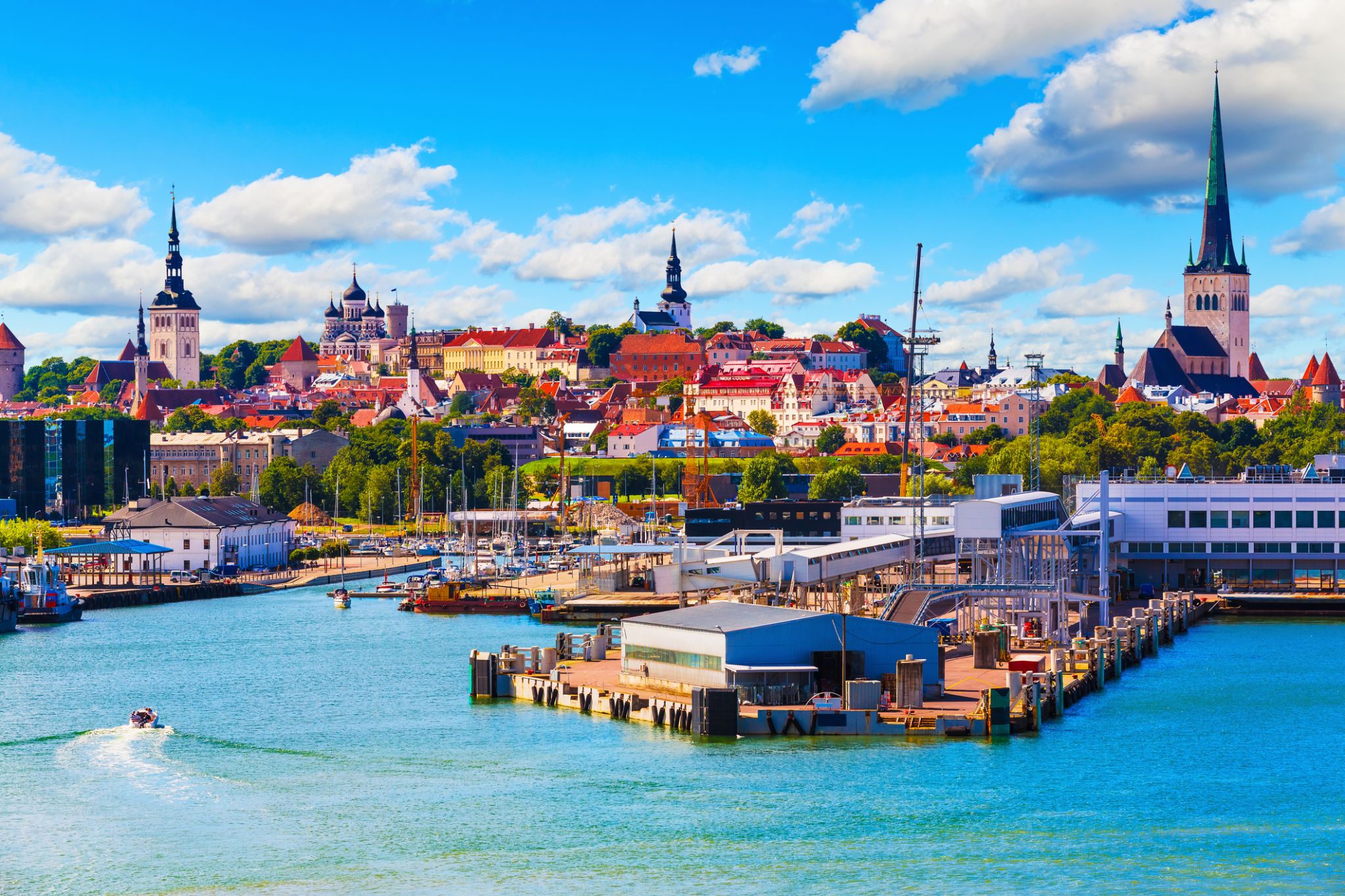

Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It is on the northern coast of the country, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland in Harju County. From the 13th century until 1918 (and briefly during the Nazi occupation of Estonia from 1941 to 1944), the city was known as Reval. Tallinn occupies an area of 159.2 km2 (61.5 sq mi) and has a population of 453,033.
Tallinn, first mentioned in 1219, received city rights in 1248, but the earliest human settlements date back 5,000 years. The initial claim over the land was laid by the Danes in 1219, after a successful raid of Lindanise led by Valdemar II of Denmark, followed by a period of alternating Scandinavian and German rule. Due to its strategic location, the city became a major trade hub, especially from the 14th to the 16th century, when it grew in importance as part of the Hanseatic League.


Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 637,827 inhabitants (2018), it is also the largest city in the three Baltic states, home to one third of Latvia's population and one tenth of the three Baltic states' combined population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga, at the mouth of the Daugava. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3 ft 3 in–32 ft 10 in) above sea level, on a flat and sandy plain.
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture during 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships and the 2013 World Women's Curling Championship. It is home to the European Union's office of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC).
In 2016, Riga received over 1.4 million visitors. It is served by Riga International Airport, the largest and busiest airport in the Baltic states. Riga is a member of Eurocities, the Union of the Baltic Cities (UBC) and Union of Capitals of the European Union (UCEU).
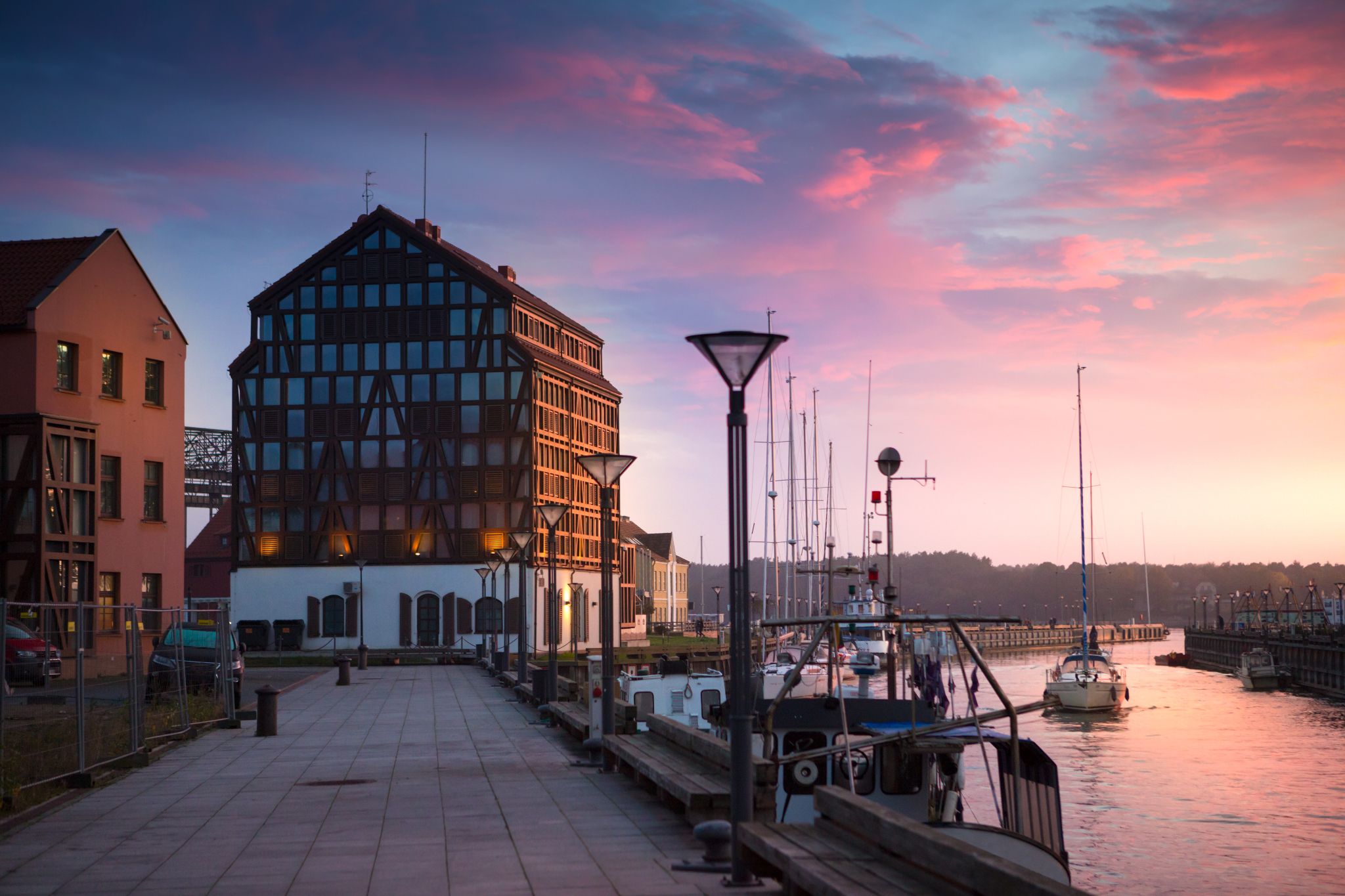

Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County.
The city has a complex recorded history, partially due to the combined regional importance of the usually ice-free Port of Klaipėda at the mouth of the Akmena-Danė River. It was controlled by successive German states until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. As a result of the 1923 Klaipėda Revolt it was added to Lithuania and has remained with Lithuania to this day, except for the period between 1939 and 1945 when it returned to Germany following the 1939 German ultimatum to Lithuania and the German–Soviet Union Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.
The population has shrunk from the city to suburbs and the hinterland. The city had a population of 207,100 in 1992 to 157,350 in 2014 but the city is growing again. Popular seaside resorts found close to Klaipėda are Nida to the south on the Curonian Spit and Palanga to the north.


Quiet streets lined with half-timbered houses make Ronne (Rønne) a cozy corner on the Danish island of Bornholm, where every step is filled with the scent of the sea and fresh pastries from local bakeries. The town is known for its ceramics and glass workshops, as well as the cozy atmosphere of its fishing port, where you can taste freshly smoked herring while watching ships slowly enter the harbor. Here, time seems to slow down, allowing you to enjoy strolls through the old town with its cobblestone streets and picturesque houses that have preserved their 18th-century charm.
In Ronne, travelers will find a peaceful retreat with a touch of Danish coziness and the creative spirit of the island. The Bornholm Museum offers insights into the island's history and maritime traditions, while walks along the coast reveal rocky shores and clean beaches inviting relaxation year-round. This town is the perfect place for those who wish to experience authentic Denmark, breathe in the sea air, and discover the warm hospitality of Bornholm.





Falmouth (Jamaica) – a Caribbean gem with colonial charm
Falmouth is a vibrant town on Jamaica’s northern coast, where the warm waves of the Caribbean Sea meet the atmosphere of a colonial past. As one of the most authentic historic towns in the region, Falmouth is renowned for its well-preserved 18th-century Georgian architecture, old plantation estates, and cultural sites. Its streets breathe history and tropical color.
For travelers seeking the true spirit of Jamaica, this town is a perfect starting point: from here, it's easy to reach the white-sand beaches of Montego Bay or the picturesque waterfalls of Ocho Rios. Visitors can enjoy leisurely walks, colorful local cuisine, plantation tours, and relaxation in the glowing lagoon. Falmouth is a place where Caribbean beauty blends harmoniously with colonial elegance.
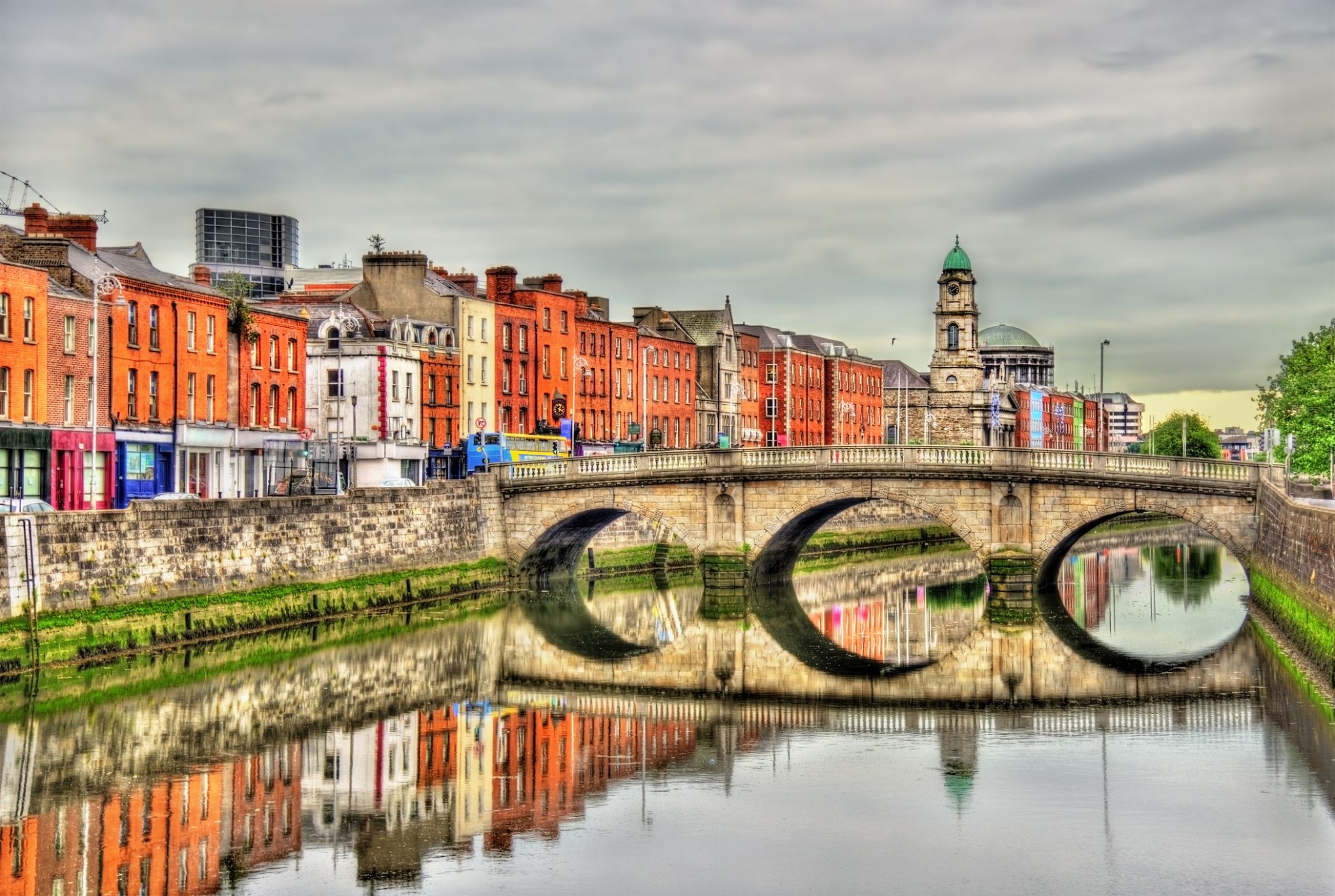

Dublin is the capital of, and largest city in, Ireland. It is on the east coast of Ireland, in the province of Leinster, at the mouth of the River Liffey, and is bordered on the south by the Wicklow mountains. It has an urban area population of 1,173,179, while the population of the Dublin Region (formerly County Dublin), as of 2016, was 1,347,359, and the population of the Greater Dublin area was 1,904,806.
There is archaeological debate regarding precisely where Dublin was established by Celtic-speaking people in the 7th century AD. Later expanded as a Viking settlement, the Kingdom of Dublin, the city became Ireland's principal settlement following the Norman invasion. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest city in the British Empire before the Acts of Union in 1800. Following the partition of Ireland in 1922, Dublin became the capital of the Irish Free State, later renamed Ireland.
Dublin is a historical and contemporary centre for education, the arts, administration and industry. As of 2018 the city was listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a global city, with a ranking of "Alpha -", which places it amongst the top thirty cities in the world.
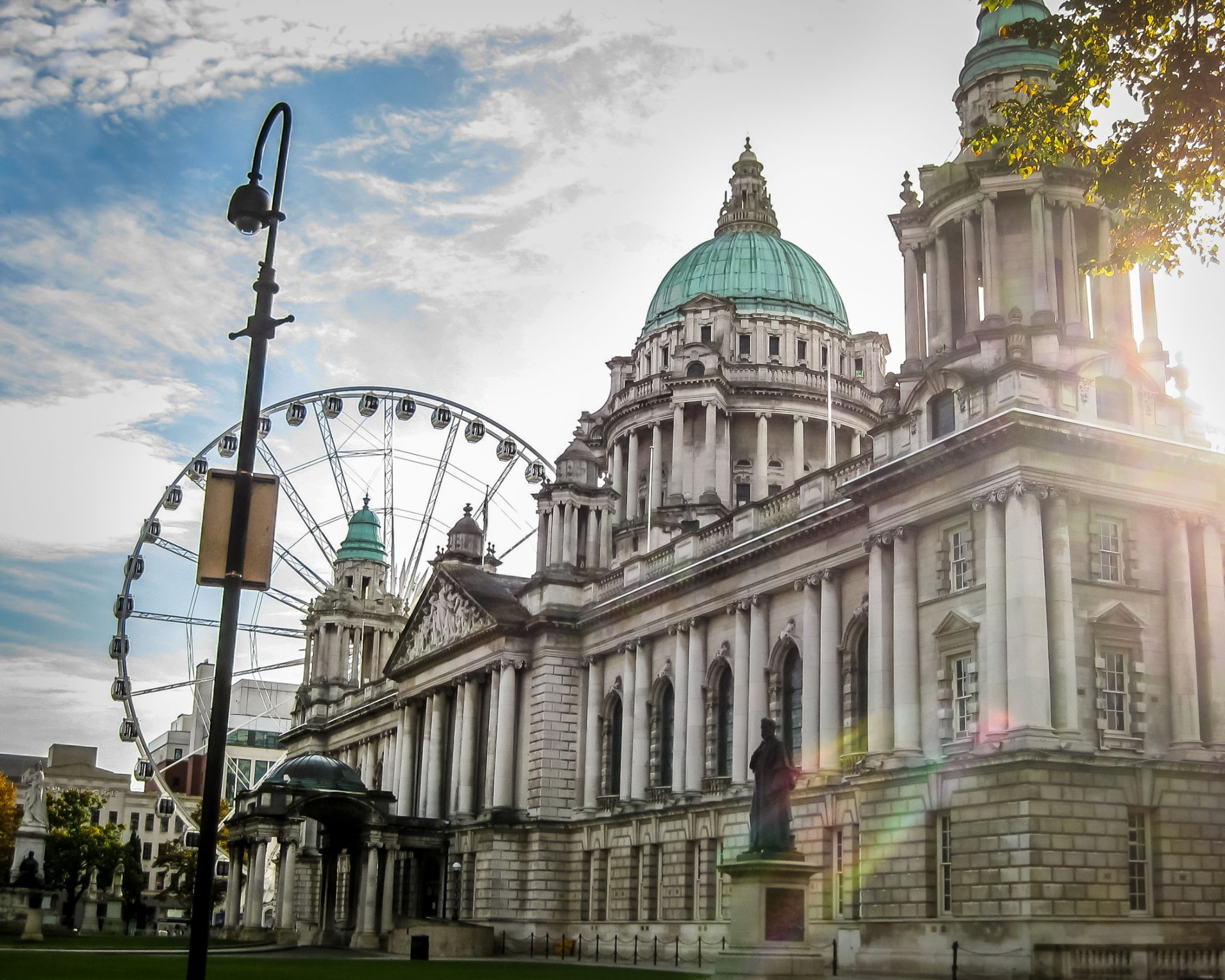

Belfast is a port city in the United Kingdom and the capital city of Northern Ireland, on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast of Ireland. It is the largest city in Northern Ireland and second largest on the island of Ireland. It had a population of 333,871 in 2015.
By the early 1800s Belfast was a major port. It played a key role in the Industrial Revolution, becoming the biggest linen producer in the world, earning it the nickname "Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, where the RMS Titanic was built, was the world's biggest shipyard. It also has a major aerospace and missiles industry. Industrialisation and the inward migration it brought made Belfast Ireland's biggest city and it became the capital of Northern Ireland following the Partition of Ireland in 1922. Its status as a global industrial centre ended in the decades after the Second World War.
Belfast suffered greatly in the Troubles, and in the 1970s and 1980s was one of the world's most dangerous cities. However, the city is now considered to be one of the safest within the United Kingdom. Throughout the 21st century, the city has seen a sustained period of calm, free from the intense political violence of former years and has benefitted from substantial economic and commercial growth. Belfast remains a centre for industry, as well as the arts, higher education, business, and law, and is the economic engine of Northern Ireland. Belfast is still a major port, with commercial and industrial docks dominating the Belfast Lough shoreline, including the Harland and Wolff shipyard. It is served by two airports: George Best Belfast City Airport, and Belfast International Airport 15 miles (24 km) west of the city. It is listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a Gamma global city.
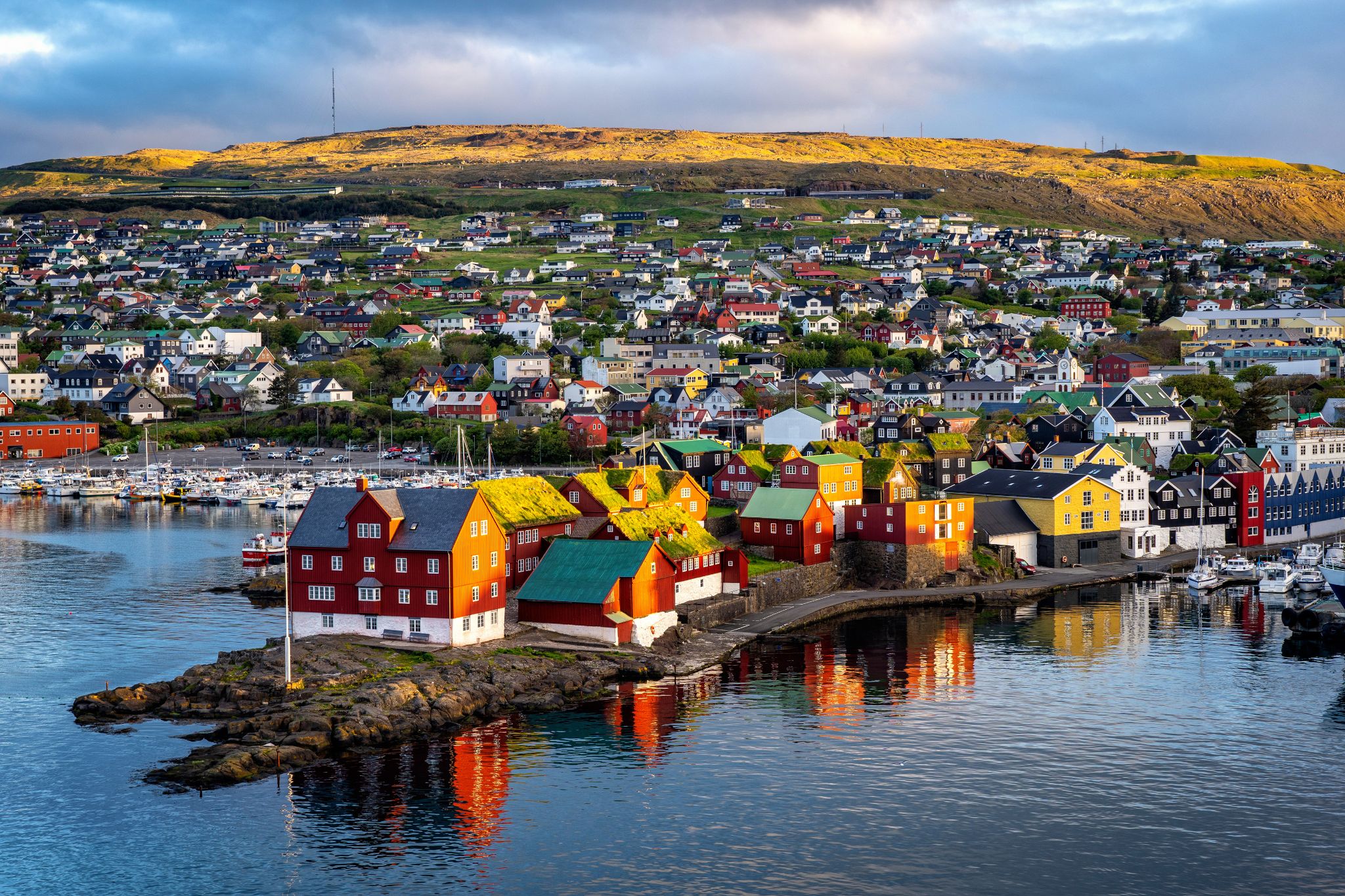


Tórshavn is the capital and largest town of the Faroe Islands. Tórshavn is in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the 347-meter-high (1,138 ft) mountain Húsareyn, and to the southwest, the 350-meter-high (1,150 ft) Kirkjubøreyn. They are separated by the Sandá River. The town proper has a population of 13,089 (2017), and the greater urban area a population of 21,000.
The Norse established their parliament on the Tinganes peninsula in AD 850.[3] Tórshavn thus became the capital of the Faroe Islands and has remained so ever since. All through the Middle Ages the narrow peninsula jutting out into the sea made up the main part of Tórshavn. Early on, Tórshavn became the centre of the islands' trade monopoly, thereby being the only legal place for the islanders to sell and buy goods. In 1856, the trade monopoly was abolished and the islands were left open to free trade.


Eskifjordur is a small yet picturesque fjord located in Eastern Iceland, attracting tourists with its natural beauty and peaceful atmosphere. Surrounded by high mountain ranges, Eskifjordur is an ideal destination for those seeking tranquility away from crowded tourist spots. Visitors can enjoy the fresh air and breathtaking views of the fjord, which connects to the Atlantic Ocean. Traditional Icelandic houses with turf roofs add to the charm of this peaceful town.
The town is also known for its cultural heritage and history. Nearby villages offer a glimpse into the traditional lifestyle of the locals, and several interesting museums, including a fishing museum, tell the story of the region's fishing industry. Eskifjordur is also an excellent base for exploring Eastern Iceland, with opportunities for hiking, fishing, and wildlife watching, including local birds and marine mammals.
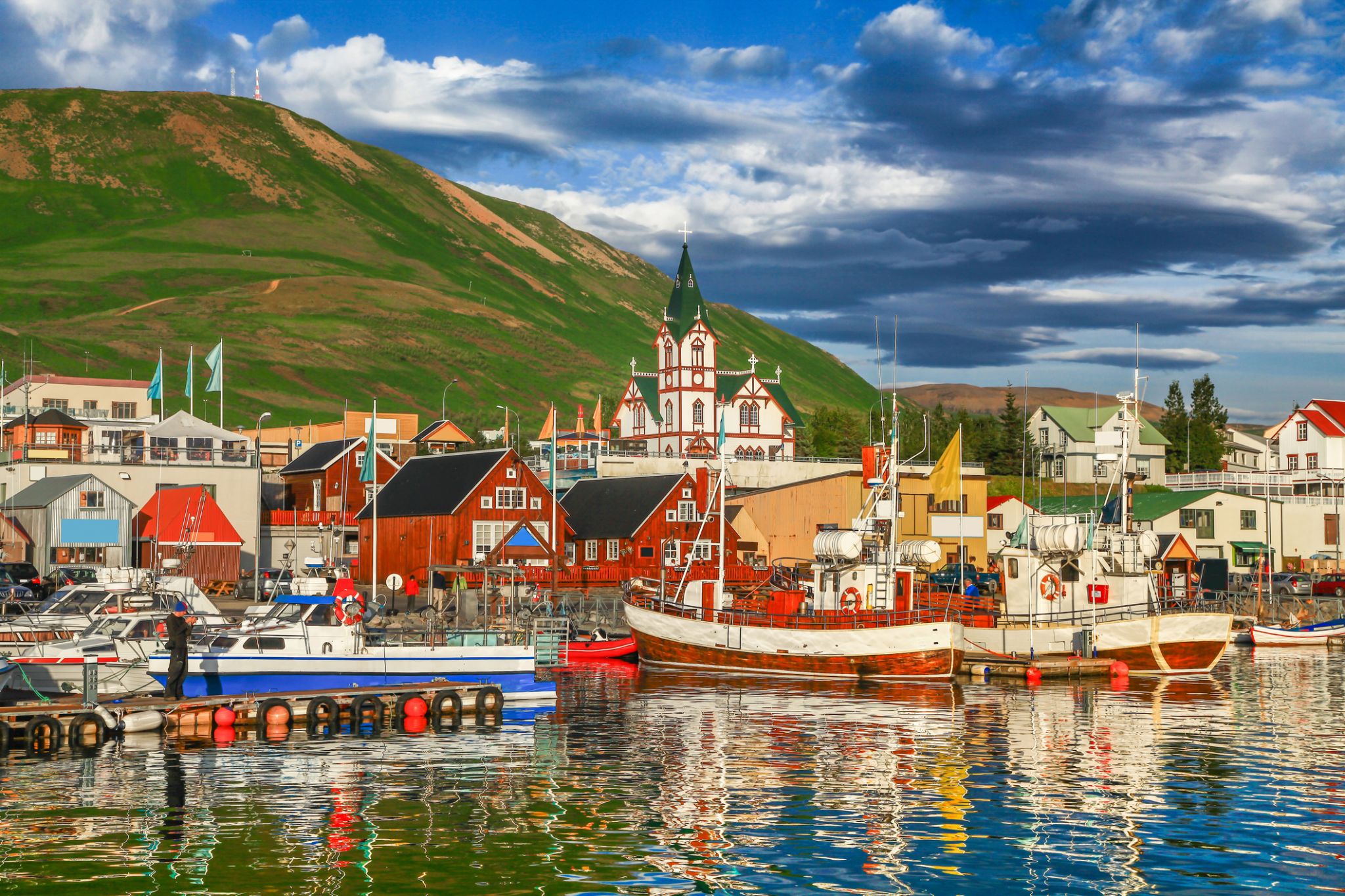
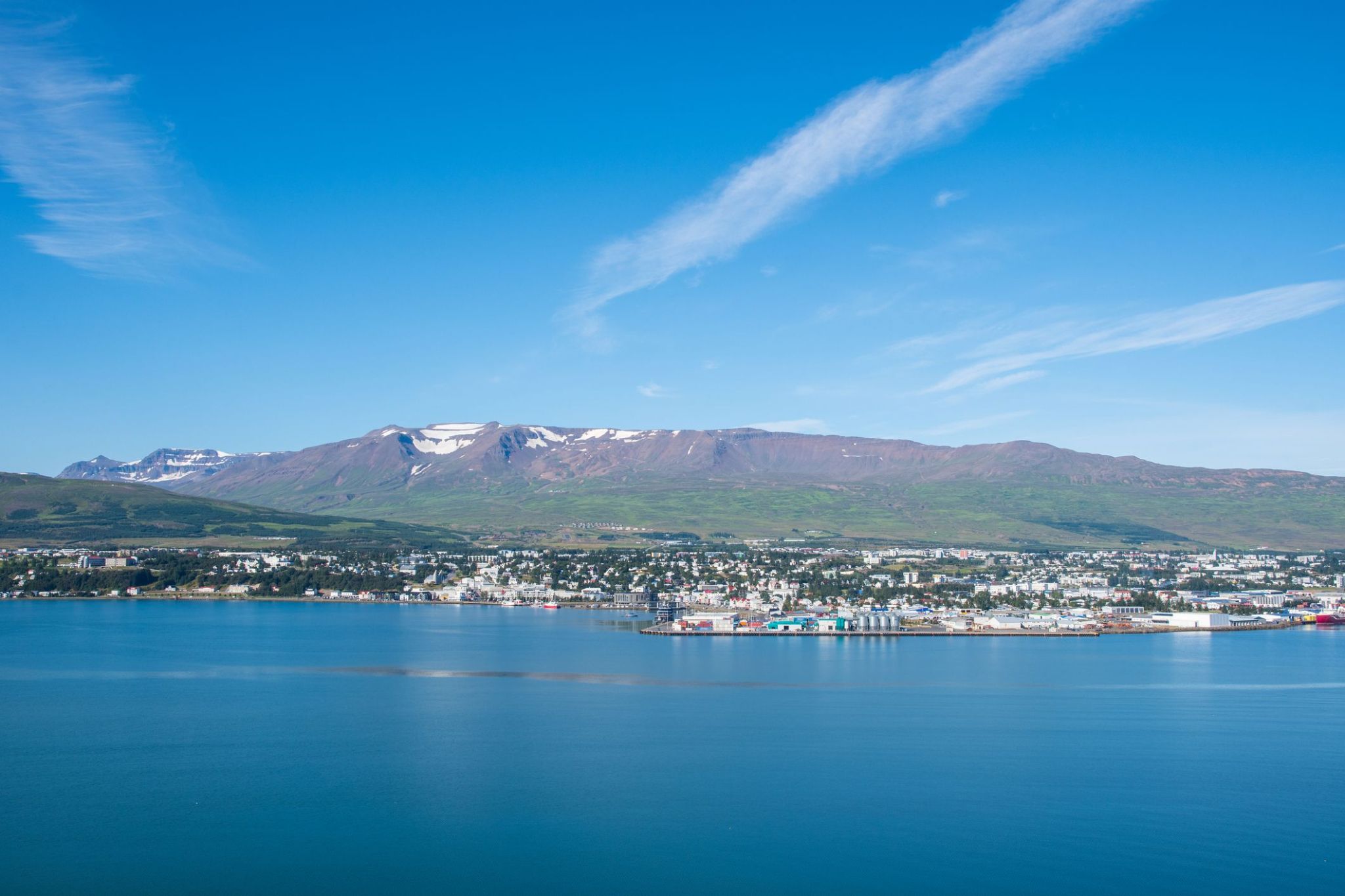


Akureyri is a town in northern Iceland. It is Iceland's Fifth largest municipality.
Nicknamed the Capital of North Iceland, Akureyri is an important port and fishing centre. The area where Akureyri is located was settled in the 9th century but did not receive a municipal charter until 1786. The town was the site of Alliedunits during World War II. Further growth occurred after the war as the Icelandic population increasingly moved to urban areas.
The area has a relatively mild climate because of geographical factors, and the town's ice-free harbour has played a significant role in its history.
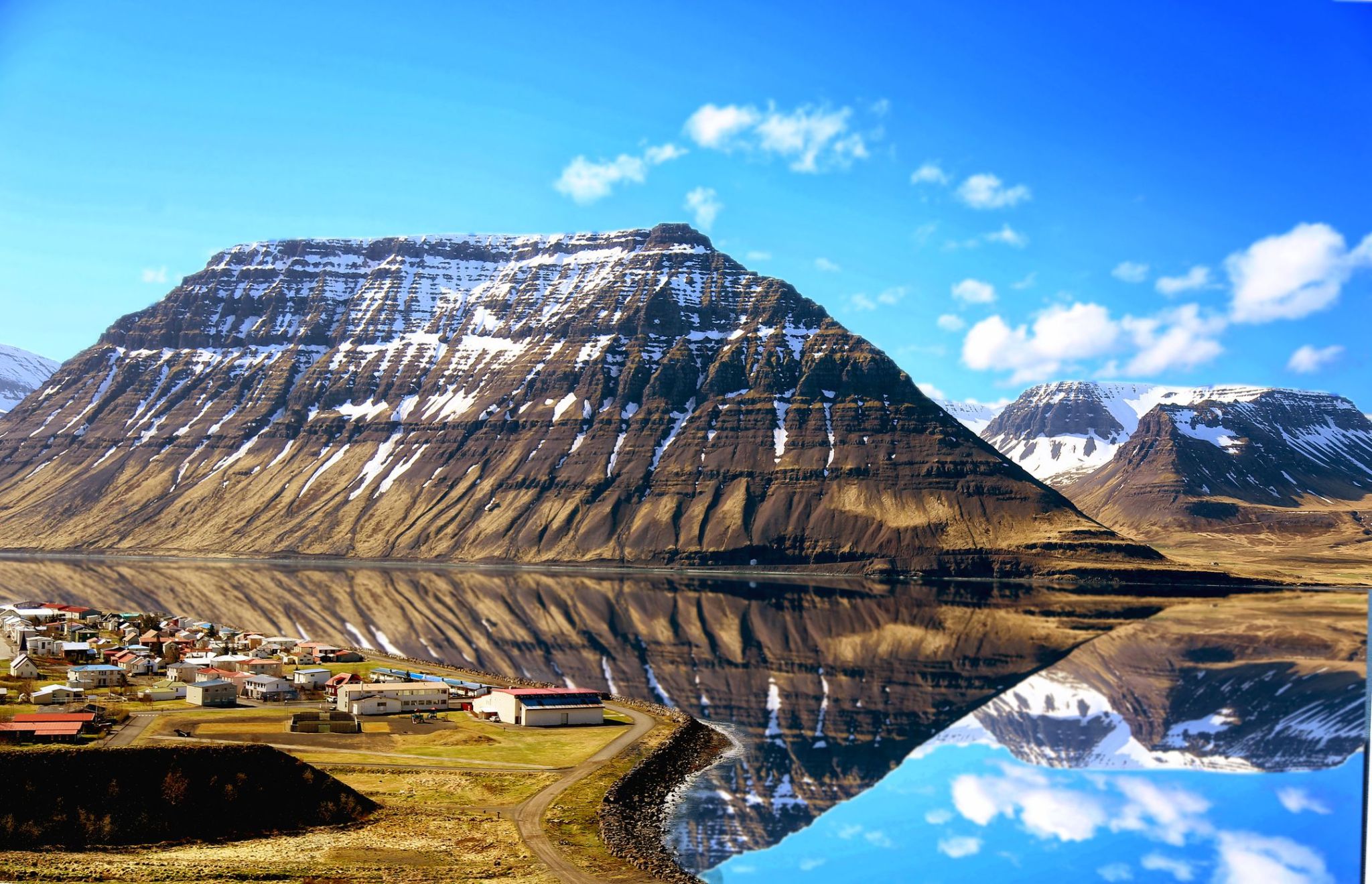

Isafjörður, meaning ice fjord or fjord of ice, ice in plural genitive) is a town in the northwest of Iceland.
The oldest part of Ísafjörður with the town centre is located on a spit of sand, or eyri, in Skutulsfjörður, a fjord which meets the waters of the larger fjord Ísafjarðardjúp. With a population of about 2,600, Ísafjörður is the largest settlement in the peninsula of Vestfirðir (Westfjords) and the administration centre of the Ísafjarðarbær municipality, which includes – besides Ísafjörður – the nearby villages of Hnífsdalur, Flateyri, Suðureyri, and Þingeyri.
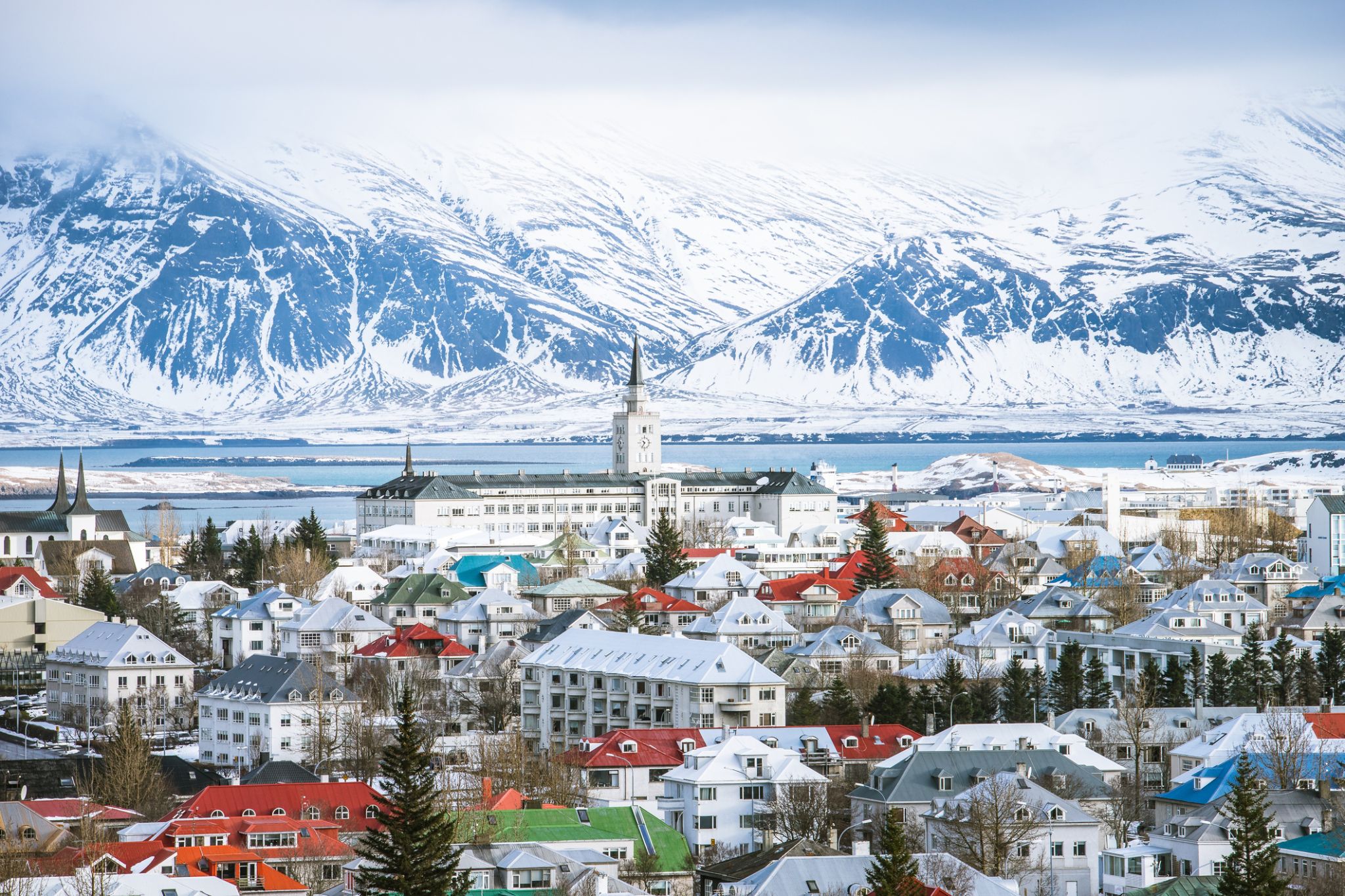


Reykjavík is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxa Bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a population of around 123,300 (and over 216,940 in the Capital Region), it is the heart of Iceland's cultural, economic and governmental activity, and is a popular tourist destination.
Reykjavík is believed to be the location of the first permanent settlement in Iceland, which, according to Ingólfr Arnarson, was established in AD 874. Until the 19th century, there was no urban development in the city location. The city was founded in 1786 as an official trading town and grew steadily over the following decades, as it transformed into a regional and later national centre of commerce, population, and governmental activities. It is among the cleanest, greenest, and safest cities in the world.
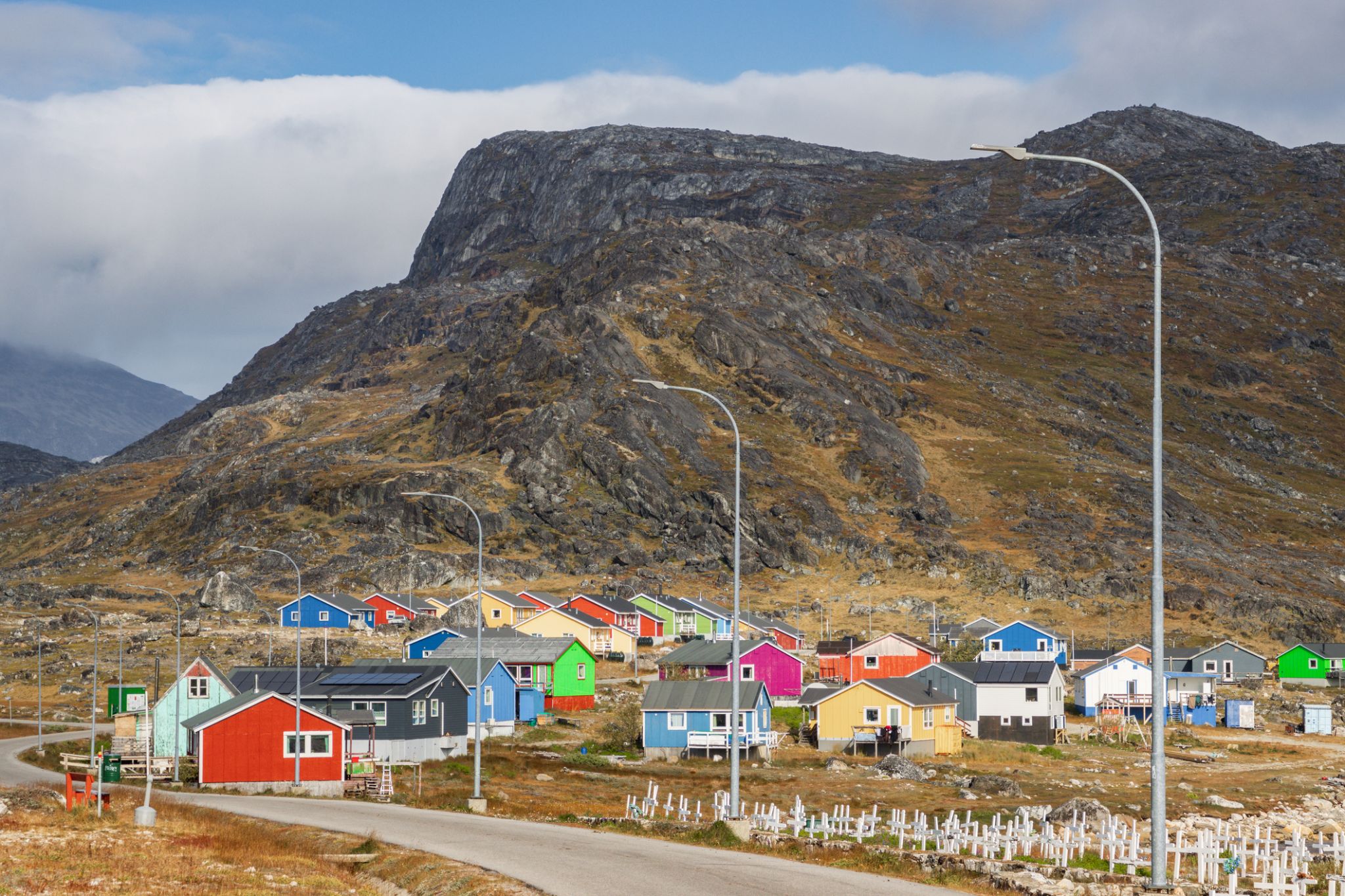



Nanortalik is a town in Nanortalik Island, Kujalleqmunicipality, southern Greenland. With 1,337 inhabitants as of 2013, it is the tenth-largest town in the country. The name Nanortalik means "Place of Polar Bears" or "Place Where the Polar Bears Go" (from Greenlandic: nanoq). It is the southernmost town in Greenland, with a population of over 1,000.
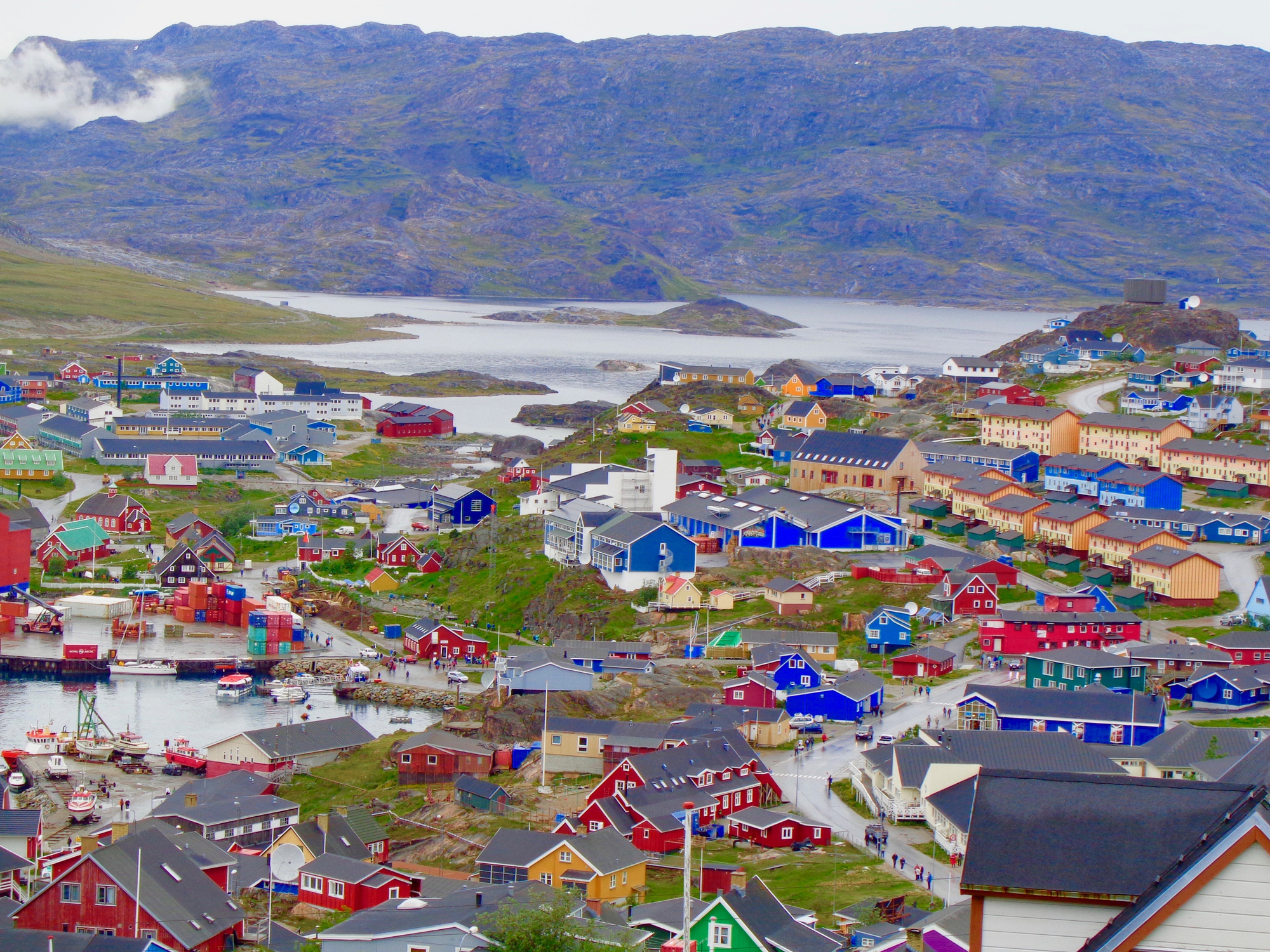

Qaqortoq, formerly Julianehåb, is a town in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland, located near Cape Thorvaldsen. With a population of 3,089 in 2016, it is the most populous town in southern Greenland and the fourth-largest town on the island.
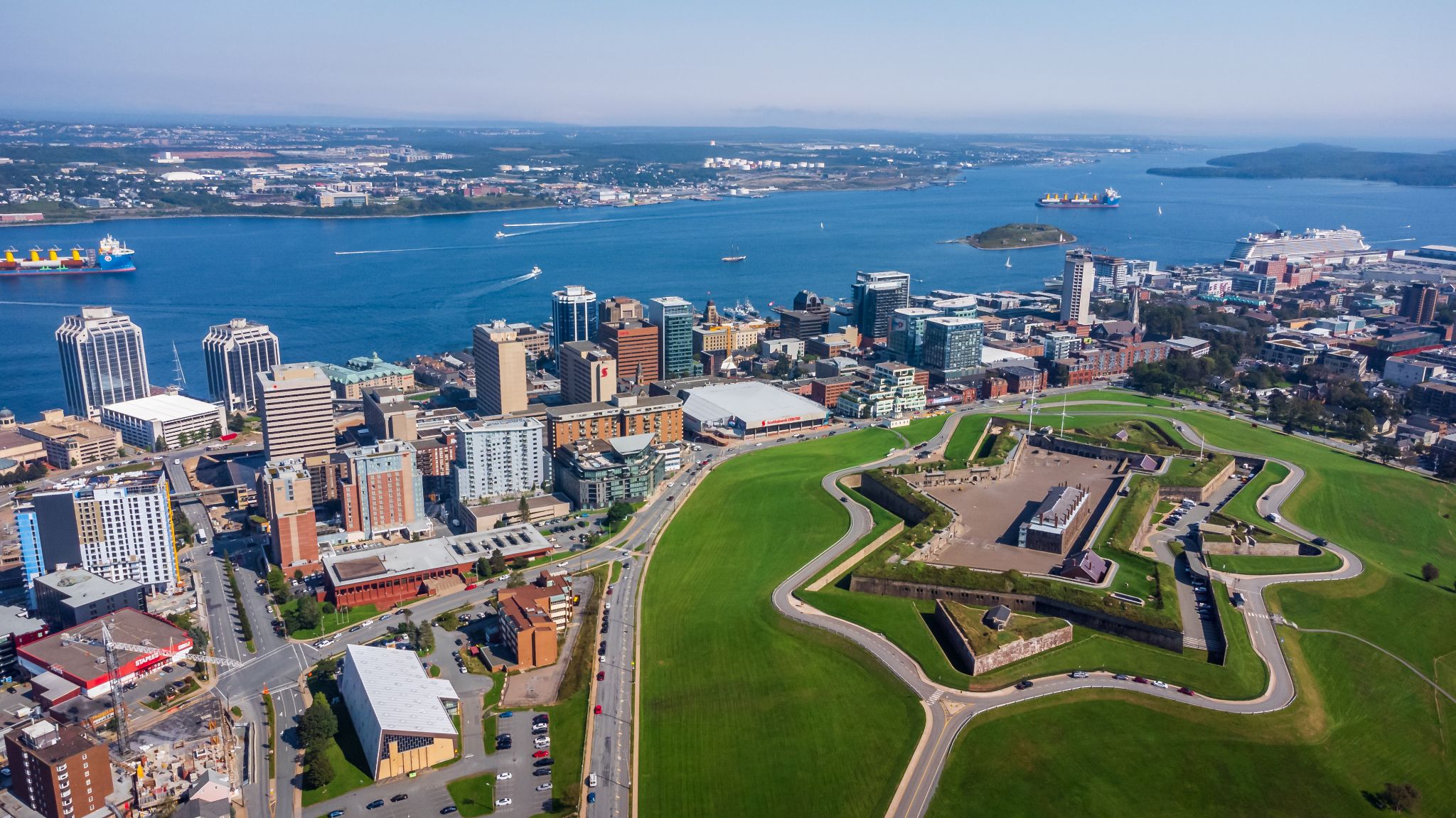







Halifax, also known as the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM), is the capital of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. The municipality had a population of 403,131 in 2016, with 316,701 in the urban area centred on Halifax Harbour. The regional municipality consists of four former municipalities that were amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County.
Halifax is a major economic centre in Atlantic Canada with a large concentration of government services and private sector companies. Major employers and economic generators include the Department of National Defence, Dalhousie University, Saint Mary's University, the Halifax Shipyard, various levels of government, and the Port of Halifax. Agriculture, fishing, mining, forestry and natural gas extraction are major resource industries found in the rural areas of the municipality.
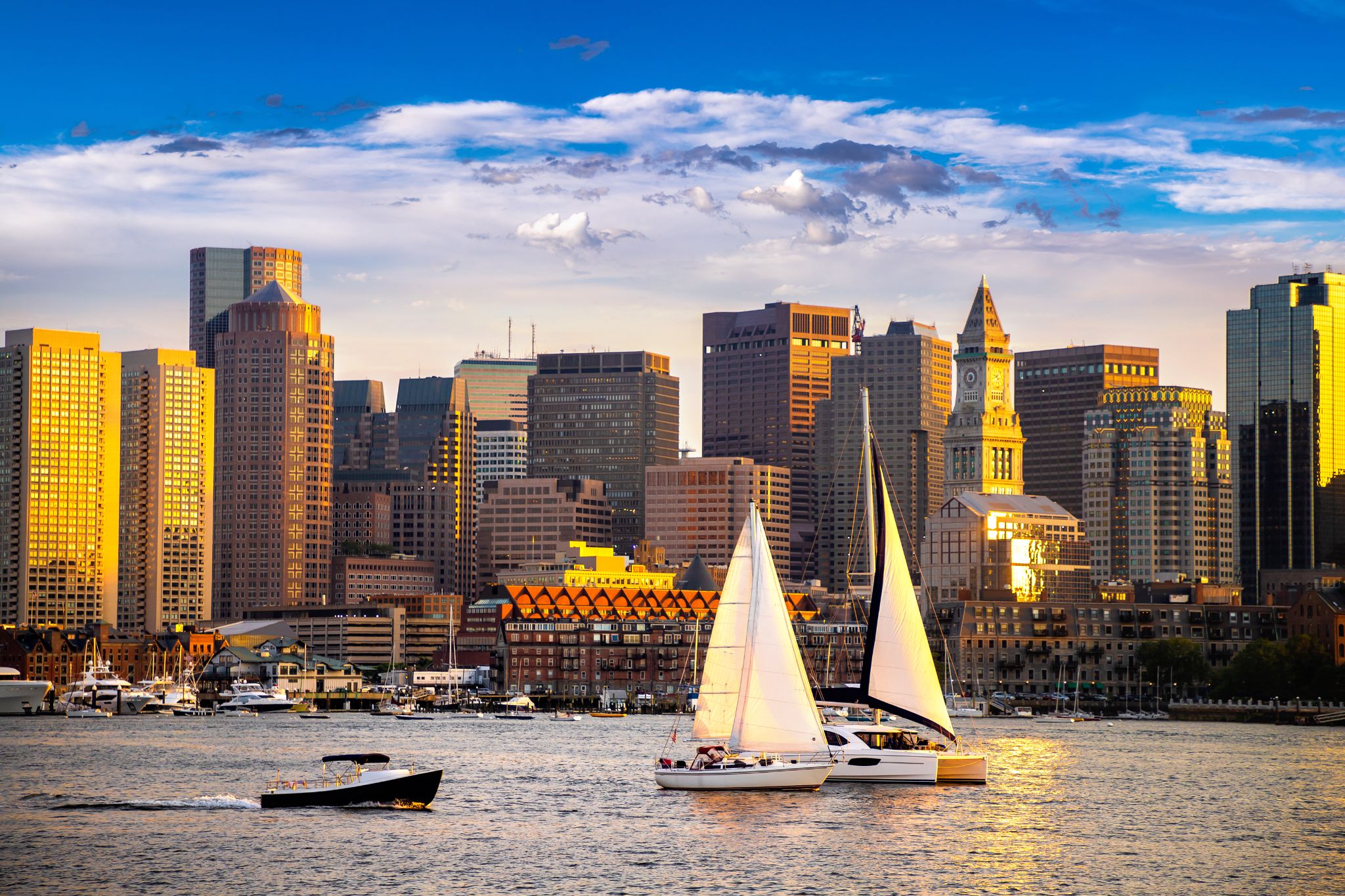



Boston is the capital and most populous municipality of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city proper covers 48 square miles (124 km2) with an estimated population of 685,094 in 2017, making it also the most populous city in New England. Boston is the seat of Suffolk County as well, although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999. The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest such area in the country. As a combined statistical area (CSA), this wider commuting region is home to some 8.2 million people, making it the sixth-largest in the United States.
Boston is one of the oldest cities in the United States, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritansettlers from England. It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution, such as the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill, and the Siege of Boston. Upon gaining U.S. independence from Great Britain, it continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture. The city has expanded beyond the original peninsula through land reclamation and municipal annexation. Its rich history attracts many tourists, with Faneuil Hall alone drawing more than 20 million visitors per year. Boston's many firsts include the United States' first public park (Boston Common, 1634), first public or state school (Boston Latin School, 1635) and first subway system (Tremont Street Subway, 1897).
The Boston area's many colleges and universities make it an international center of higher education, including law, medicine, engineering, and business, and the city is considered to be a world leader in innovationand entrepreneurship, with nearly 2,000 startups. Boston's economic base also includes finance, professional and business services, biotechnology, information technology, and government activities. Households in the city claim the highest average rate of philanthropy in the United States; businesses and institutions rank among the top in the country for environmental sustainability and investment. The city has one of the highest costs of living in the United States as it has undergone gentrification, though it remains high on world livability rankings.
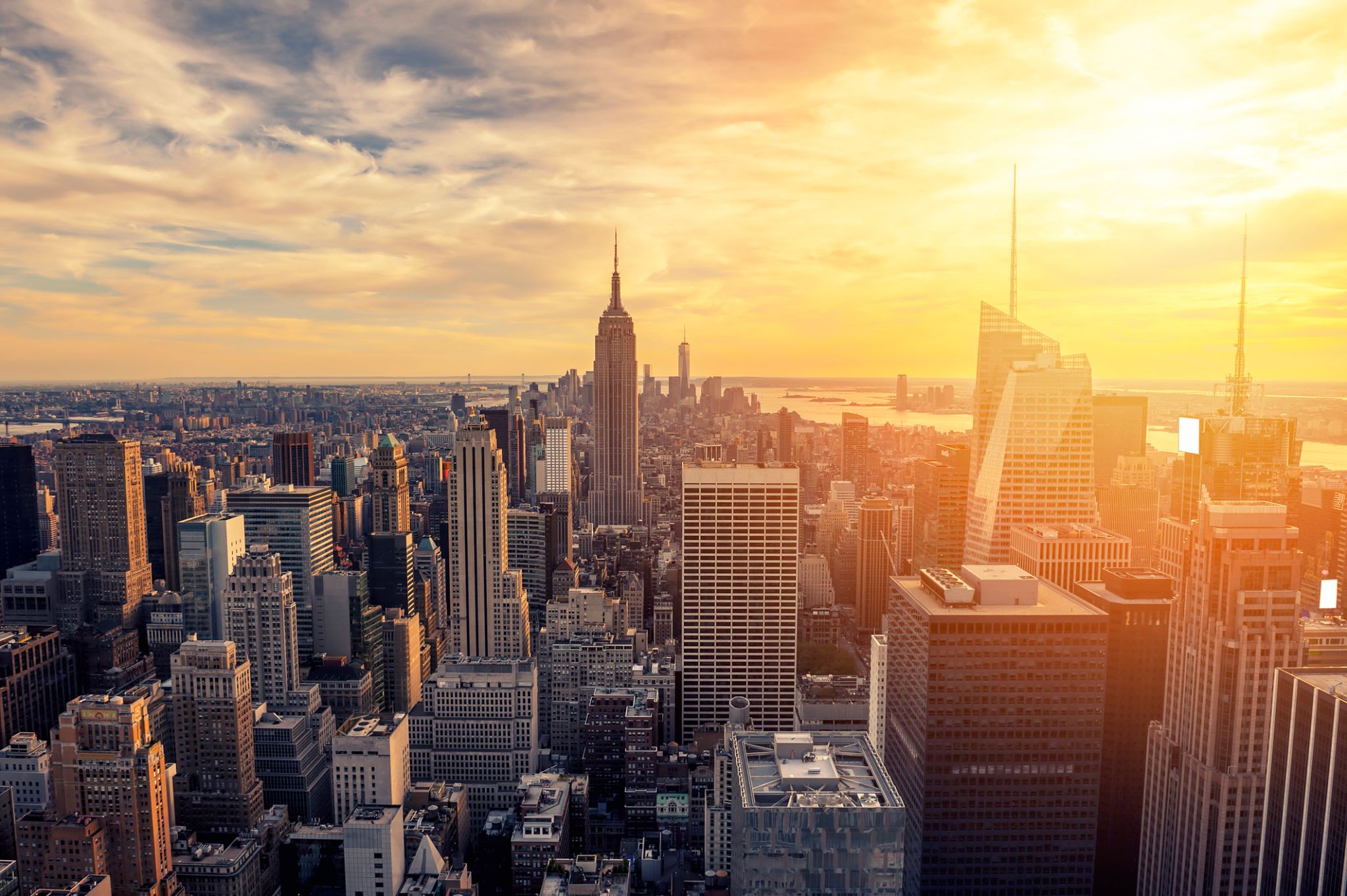



The world famous city of New York , the largest city in the United States, with a population of 8.5 million people, and with suburbs - 20.6 million. New York is the largest economic, political, scientific, and cultural center of the United States. It is rightly called the "Main Gate" in the United States, and the world's largest John F. Kennedy Airport is located here. One of the distinguishing features of the city is the variegated national composition of the population, also called the United States in Miniature.
New York gathered in itself the whole essence of this country: fashion, religion, goods, pace and rhythm of American life. The UN headquarters is located here. There are also many universities in New York, the Academy of Sciences, and many other scientific institutions. Like any other metropolis in the world, New York invites you to visit numerous museums in the city, theaters and concert halls, including the Metropolitan Opera and Carnegie Hall. A great place to relax in New York is Central Park, where you can feed hand-held squirrels, which, to everyone's surprise, are not afraid of people. You can also appreciate the beauty of the famous Empire State Building, with a height of 102 floors, it is an example of skyscrapers, although it was built in 1829-1831. "Must see" in New York, of course, the Statue of Liberty ("Lady Liberty"), located at the mouth of the Hudson River, on the small island of Liberty. And of course, don't forget to stroll along Broadway.